1. 문자열 정의 방법
- 배열을 사용하여 문자열 저장.
- [] 에 배열의 크기를 적어주면, 배열의 크기보다 낮은 문자열 저장 가능.
- 배열의 크기 = 10, 문자열 크기 = 4 일때, 남는 6개의 공간은 NULL로 채워짐. - [] 에 배열의 크기를 적어주지 않으면, 컴파일러가 문자열 길이만큼 배열 크기 할당.
- [] 에 배열의 크기를 적어주면, 배열의 크기보다 낮은 문자열 저장 가능.
- 포인터를 사용하여 문자열 저장.
- 문자열이 저장된 memory 주소 값이 저장됨.
- 포인터에 문자열을 저장하면, read-only memory에 저장됨.
- read-only memory를 수정하려고 하면 런타임에러 발생.
- 런타임에러 방지를 위해 const 를 사용하여 포인터 선언.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char words[50] = "A string in an array"; //배열에 문자열 저장.
const char* pt1 = "A pointer to a string"; //const 포인터를 사용하여 문자열 저장.
puts(words); // words에 저장된 문자열 출력. puts() = 문자열 출력 함수.
puts(pt1); // pt1에 해당하는 문자열 출력.
//pt1[8]= 'A'; //string이 저장된 memory를 수정하려고 하면 에러 발생. (read-only memory)
return 0;
}2. 문자열의 배열
코드
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
const char* mythings[5] = { //문자열을 포인터로 선언.
"Dancing in the rain",
"Couting apples",
"Watching movies with friends",
"Writing sad letters",
"Studying the C language"
};
char yourthings[5][40] = { //문자열을 배열로 선언.
"Studying the C++ language",
"Eating",
"Watching Netflix",
"Walking around till dark",
"Deleting spam emails"
};
const char* temp1 = "Dancing in the rain"; //포인터 temp1에 "Dancing in the rain"이 저장되어 있는 memory 주소 저장.
const char* temp2 = "Studying the C++ language"; //포인터 temp2에 "Studying the C++ language"이 저장되어 있는 memory 주소 저장.
printf("%s %u %u\n", mythings[0], (unsigned)mythings[0], (unsigned)temp1);
//mythings의 첫번째 원소 값, mythings의 첫번째 원소 memory 주소, temp1의 값 출력.
printf("%s %u %u\n", yourthings[0], (unsigned)yourthings[0], (unsigned)temp2);
//yourthings의 첫번째 원소 값, yourthings의 첫번째 원소 memory 주소, temp2의 값 출력.
return 0;
}결과
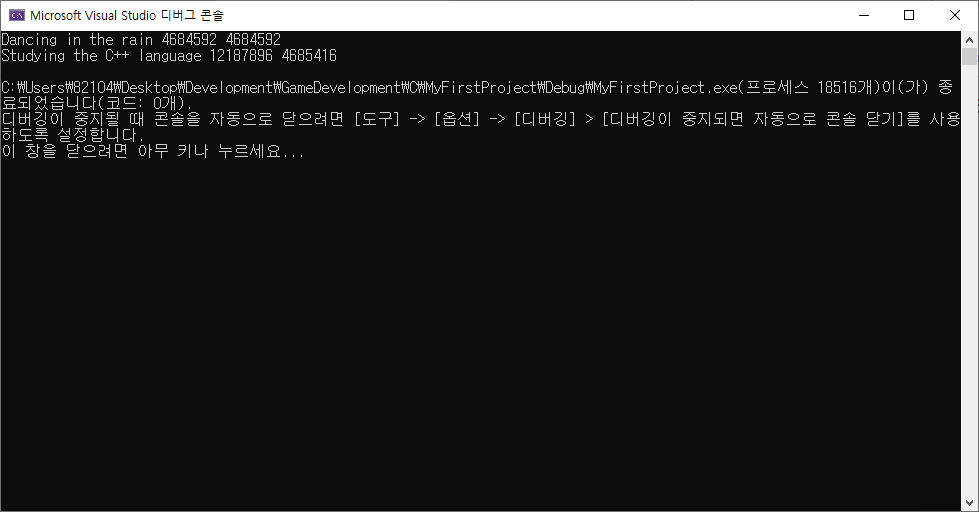
- 포인터로 문자열을 선언한 경우, 주소 값이 같음. (read-only memory에 저장되어 있는 문자열을 가리키므로)
- 배열로 문자열을 선언한 경우, 주소 값이 다름. (배열의 memory 에 저장된 문자열과 read-only memory에 저장되어 있는 문자열이기 때문)
3. 문자열을 입력받는 방법들
- 문자열을 입력 받을 때는, 입력받은 문자열을 저장할 memory 공간을 확보해둬야 함.
gets()
- scanf() 함수로 문자열을 입력 받으면 한 단어만 저장. (띄어쓰기 불가능)
- gets() 함수는 문자열을 입력 받으면 한 줄을 저장하며, 맨 마지막에 있는 '\n'을 '\0' 으로 변경.
- gets() 함수는 저장될 memory 주소 값만 받기 때문에, memory의 시작 점만 알고 끝나는 부분은 알지 못함.
- gets()의 단점 보완을 위해 C11 표준에서 gets_s() 함수를 사용할 것을 권고.
- gets_s() 함수는 저장될 memory 주소 값과 memory 크기를 같이 받음.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr[20] = "";
gets(arr); // gets() 함수로 문자열 입력 받고 arr에 저장.
printf("%s\n", arr); // gets() 함수로 입력 받은 값 출력.
gets_s(arr, 20); // gets_s() 함수로 문자열 입력 받고 arr에 저장.
printf("%s\n", arr); // gets_s() 함수로 입력 받은 값 출력.
return 0;
}fgets()
- gets(), gets_s() 함수는 입력 받는 문자열의 크기가 저장될 memory 크기보다 클 경우 런타임 에러 발생.
- fgets() 함수는 gets(), gets_s() 함수에서 발생하는 런타임에러를 방지.
- fgets() 함수는 기본적으로 파일을 가져올 때 사용.
- fgets() 함수에서 사용하는 인자 = 저장될 memory 주소, memory 크기, 가져올 파일.
- 콘솔 입력을 위해서는 파일 입력을 위한 인자에 stdin을 사용.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr[20] = "";
fgets(arr, 20, stdin); // 콘솔로 입력받은(stdin) 문자열을 arr에 저장.
printf("%s\n", arr);
return 0;
}4. 문자열을 출력하는 방법들
puts()
- puts() 함수는 문자열 맨 뒤에 '\n' 을 추가하여 출력.
- puts() 함수는 문자열에 '\0'를 만나면 종료됨.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr[50] = "puts() function test. puts() has \\n";
puts(arr); // arr의 문자열 출력. (with '\n')
puts("END"); // 출력된 문자열 밑에 END 출력.
return 0;
}fputs()
- fputs() 함수는 원래 파일에 값을 출력해줄 때 사용.
- fputs() 함수에서 사용하는 인자 = 값이 저장되어 있는 memory 주소와 값을 출력시킬 파일.
- 콘솔 출력을 위해서는 값을 출력시킬 파일 인자에 stdout을 사용.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr[50] = "fputs() function test. fputs() doesn't has \\n";
fputs(arr, stdout); // arr의 문자열을 콘솔 창에 출력.
return 0;
}
5. 문자열 함수들
- #include <string.h> 필요.
strlen()
- 문자열의 길이를 반환.
- 문자열의 마지막에 포함되어 있는 '\0'는 제외한 문자열 길이를 반환.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr[50] = "Hello my name is taeil. nice to meet you.";
int strlength = strlen(arr); // arr 문자열의 길이를 변수 strlength에 저장.
printf("%d", strlength); // strlength 값 출력.
return 0;
}strcat()
- 문자열에 다른 문자열을 덧붙여 주는 함수.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr[100] = "Hello my name is taeil. nice to meet you. ";
strcat(arr, "Have a nice day!"); // arr 문자열에 Have a nice day! 문자열 덧붙임.
printf("%s", arr);
return 0;
}strcmp()
- 문자열을 비교해주는 함수.
- 문자 비교가 아닌, 문자열 비교.
- 반환 값이 특이하니 주의.
- 같으면 '0' 반환.
- 왼쪽 문자열의 ASCII 코드가 더 높으면 '1' 반환.
- 오른쪽 문자열의 ASCII 코드가 더 높으면 '-1' 반환.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//char arr[100] = "Hello my name is taeil. nice to meet you. ";
printf("%d\n", strcmp("Taeil", "Taeil")); // 0 반환.
printf("%d\n", strcmp("Taeil", "Nam")); // 1 반환. (T > N)
printf("%d\n", strcmp("Nam", "Taeil")); // -1 반환. (N < T)
return 0;
}strncmp()
- strcmp() 와 동일하나, 몇 번째 문자까지 비교할지 결정 가능. (인자 추가)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
//char arr[100] = "Hello my name is taeil. nice to meet you. ";
printf("%d\n", strncmp("Taeil", "Taeil", 1)); // 0 반환. 1 번째 까지만 비교
printf("%d\n", strncmp("Taeil", "TaNam", 2)); // 0 반환. 2 번째 까지만 비교
printf("%d\n", strncmp("Taeil", "Taeil Nam", 3)); // 0 반환. 3 번째 까지만 비교
return 0;
}strcpy()
- 문자열을 복사하여 저장해주는 함수.
- destination에 source 의 문자열을 복사 후 저장.
- 인자에 포인터 산술연산 사용 가능.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char dst1[100] = "";
char dst2[100] = "";
char src[] = "strcpy TEST !";
strcpy(dst1, src); //dst1에 src 문자열 복사.
printf("%s\n", dst1); //dst1 출력.
strcpy(dst2, src + 7); //dst2에 src 문자열의 7 번째부터 복사.
printf("%s", dst2); //dsr2 출력.
return 0;
}sprintf()
- 지정한 문자열대로 배열에 저장.
- 형식 지정자 사용 가능.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr[100] = ""; //문자열이 저장될 배열 arr.
char name[10] = "Taeil"; //배열 name 의 값 = Taeil.
sprintf(arr, "First Name = %s, Last Name = Nam.", name);
//"First Name = %s, Last Name = Nam." 문자열을 배열 arr에 저장. %s에 대입될 값 = 배열 name의 값.
printf("%s", arr); // 배열 arr 값 출력. ("First Name = Taeil, Last Name = Nam." 출력)
return 0;
}6. 선택 정렬
- 주어진 값을 오름차순으로 정렬하기.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
void swap(int* xp, int* yp);
void printArray(int arr[], int size);
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n);
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
selectionSort(arr, n);
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
void swap(int* xp, int* yp)
{
long long int temp = 0;
temp = *xp;
*xp = *yp;
*yp = temp;
}
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
}
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int min_index = 0;
int count = 0;
while (count != (n - 1))
{
for (int i = count; i < n - 1; ++i)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j)
if (arr[i] > arr[j])
{
min_index = j;
swap(arr + i, arr + min_index);
}
}
count++;
}
}
💡 강의 안보고 혼자서 직접 구현했음!! (코드가 더러움)7. 문자열의 포인터 정렬
- strcmp() 함수 사용.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h> //strcmp() 함수의 라이브러리.
void swap(char** xp, char** yp);
void printStringArray(char* arr[], int size);
void selectionSort(char* arr[], int n);
int main()
{
char* arr[] = { "Cherry", "AppleBee", "Pineapple", "Apple", "Orange" };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printStringArray(arr, n);
selectionSort(arr, n);
printStringArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
void swap(char** xp, char** yp)
{
char* temp = *xp ;
*xp = *yp;
*yp = temp;
}
void printStringArray(char* arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
printf("%s\n", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void selectionSort(char* arr[], int n)
{
int i, j, min_index;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i)
{
min_index = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; ++j)
{
if (strcmp(arr[j], arr[min_index]) < 0) //비교할 값의 문자가 기존 값의 문자보다 작을 경우.
min_index = j; // 비교할 값의 index를 min_index에 저장.
}
swap(&arr[i], &arr[min_index]); // arr[i]와 arr[min_index]의 값을 서로 바꿈.
}
}8. 문자 함수를 문자열에 사용
- 입력 받은 문자열을 전부 대문자로 변환하고, 기호가 몇 개 포함되어 있는지 출력.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h> //toupper(), ispunct() 함수 사용.
void ToUpper(char* str); //문자열을 전부 대문자로 변경해주는 함수.
int PunctCount(const char* str); //문자열에 포함된 기호가 몇 개인지 알려주는 함수.
int main()
{
char str[100];
char* new_str = NULL;
fgets(str, 100, stdin);
new_str = strchr(str, '\n'); //문자열 str에서 \n 을 찾으면 해당 포인터 값을 반환.
if (new_str) //new_str이 값을 가지고 있는 경우 = if (new_str != NULL)
*new_str = '\0'; //찾은 \n 을 \0으로 변환.
ToUpper(str);
puts(str);
printf("%d\n", PunctCount(str));
return 0;
}
void ToUpper(char* str)
{
while (*str) //*str이 값을 가지고 있는 경우 = while (str != NULL)
{
*str = toupper(*str); //해당 값을 대문자로 변경.
str++; //다음 문자로 전환. (포인터 산술연산)
}
}
int PunctCount(const char* str)
{
int ct = 0;
while (*str) //*str이 값을 가지고 있는 경우 = while (str != NULL)
{
if (ispunct(*str)) // *str이 기호에 해당하는 경우.
ct++; // ct 1 증가.
str++;
}
return ct;
}9. Command line 인자
- main() 함수에서 프롬프트에 입력된 명령어 저장 및 개수 확인을 위한 인자 사용.
- main() 함수에서 인자를 사용하는 경우, main() 함수가 호출될 때 운영체제가 인자에 값을 넣어 줌.
- main() 함수에서 인자를 사용하지 않는 경우, 운영체제가 인자에 값을 넣지 않음.
코드
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) //argc = 명령어의 문자열 개수, argv[] = 명령어의 문자열들이 저장되는 배열.
{
int count;
printf("The command line has %d arguments:\n", argc); //명령어의 문자열 개수 출력.
for (count = 0; count < argc; ++count)
printf("Arg %d : %s\n", count, argv[count]); // 명령어의 문자열들 출력.
printf("\n");
return 0;
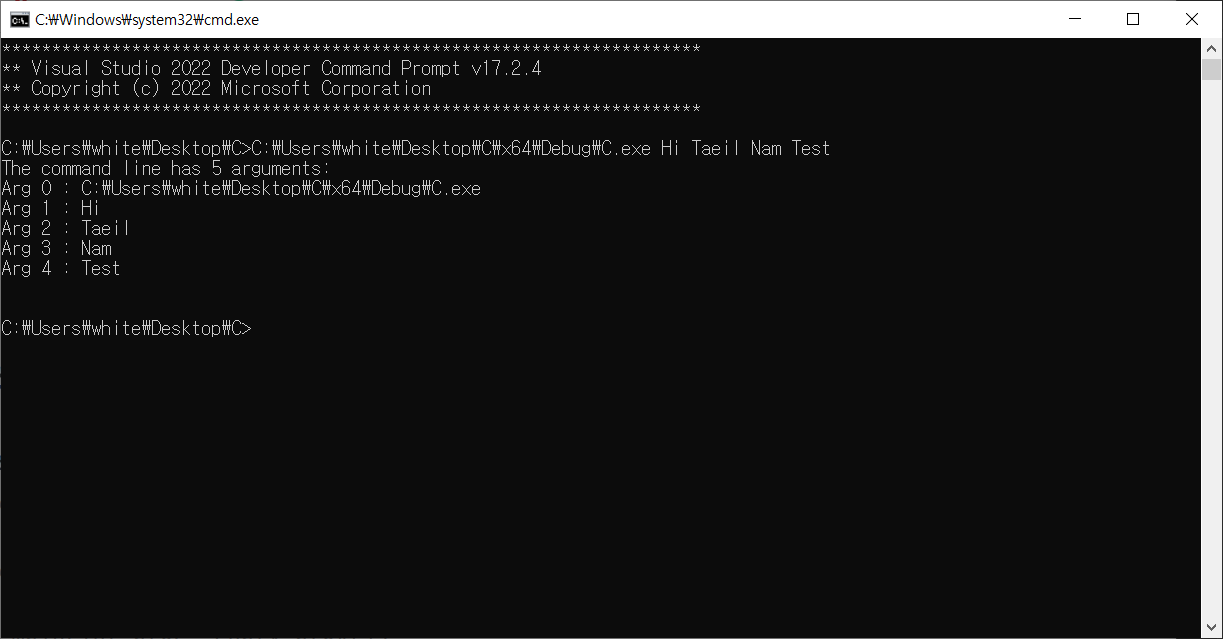
}결과
- 프롬프트로 exe 파일 직접 실행.
🚩 출처 및 참고자료 : 홍정모의 따라하며 배우는 C 언어 (따배씨)

