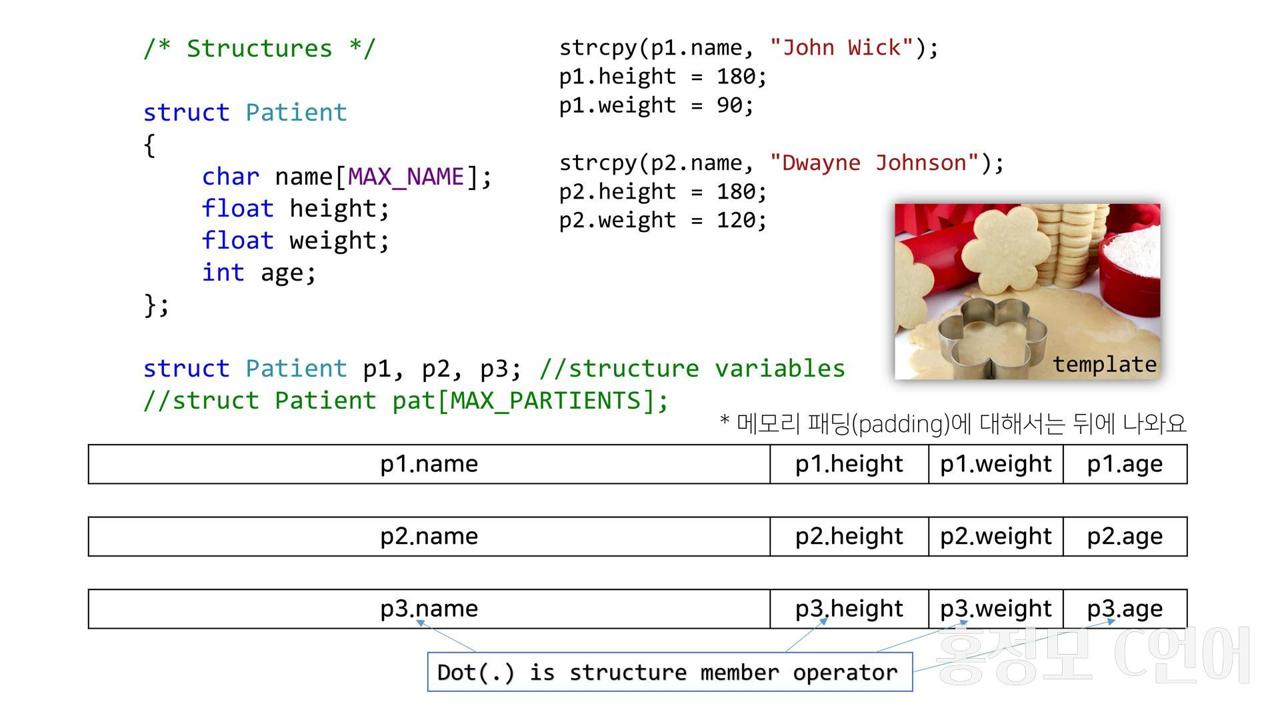
1. 구조체(Structure)
- 서로 다른 자료형의 변수를 모아놓은 것.
- 특정 구조체에 속한 변수들을 멤버라고 부름.
- 구조체를 변수로 선언하여 사용 가능.
- 점(.)을 사용하여 구조체 멤버에 접근 가능. (Structure Member Operator)
사용법
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct person // person 이라는 이름(tag)의 구조체 선언.
{
char name[30]; // 구조체 person의 멤버 name 선언.
int age; // 구조체 person의 멤버 age 선언.
float height; // 구조체 person의 멤버 height 선언.
};
// 구조체 선언에서는 Memory를 할당 받지 않음.(구조체의 형태만 나타냄)
// 구조체에 필요한 Memory 할당은, 구조체의 변수를 선언했을 때 수행 됨.
int main()
{
int height;
/* 1. 구조체 변수 선언 */
struct person taeil; // 구조체 person의 변수 taeil 선언.
// 구조체 멤버들의 크기만큼 memory가 할당 됨.
strcpy(taeil.name, "Taeil Nam");
// 구조체 변수 taeil의 멤버 name에 문자열 "Taeil Nam" 대입.
taeil.age = 27;
// 구조체 변수 taeil의 멤버 age에 27 대입.
height = scanf("%f", &taeil.height);
// 입력 받은 값을 구조체 변수 taeil의 멤버 height에 대입.
printf("%f\n", taeil.height);
// 구조체 변수 taeil의 멤버 height 값 출력.
/* 2. 구조체 변수 초기화 */
struct person yundoo = { "Yundoo Gang", 8, 80.0f };
// 구조체 person 변수 yundoo 초기화.
/* 3. 구조체 변수 초기화2(Designated initializers - C99) */
struct person yundoo = {
.age = 8,
.name = "Yundoo Gang",
.height = 80.0f
};
/* 4. 구조체 변수의 포인터 선언 */
struct person* someone;
someone = &taeil;
someone->age = 27; // 구조체 변수의 포인터에서 멤버 선택 = 화살표(->) 사용.
printf("%s %d\n", someone->name, (*someone).age);
/* 5. typedef를 사용한 자료형 선언 */
typedef struct person my_person;
// struct person 이라는 형태를 my_person 이라는 이름의 자료형으로 선언.
my_person person1;
// my_person 자료형의 변수 person1 선언.
typedef struct {
char name[30];
char hobby[30];
} my_person2;
// 구조체 선언시 typedef를 사용하여 my_person2 이라는 이름의 자료형으로 선언.
my_person2 person2;
return 0;
}2. 구조체의 Memory 할당
- 구조체의 변수가 선언될 때 memory를 할당 받음.
- 구조체의 멤버들은 서로 다른 memory 공간을 할당 받음.
- 구조체의 대표 memory 주소 = 구조체의 첫번 째 멤버 memory 주소. (배열의 memory 할당과 동일)
- 구조체 멤버들의 memory 간격 = 멤버의 자료형 + padding.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
struct Aligned // 구조체 Aligned 선언.
{
int a; // 4 bytes.
float b; // 4 bytes.
double c; // 8 bytes.
};
struct Aligned a1, a2; // 구조체 Aligned의 변수 a1, a2 선언.
printf("struct Aligned a1\n");
printf("Size of %zd\n", sizeof(struct Aligned)); // 구조체 Aligned의 memory 크기 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&a1); // 구조체 변수 a1의 memory 주소 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&a1.a); // 구조체 변수 a1 멤버 a의 memory 주소 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&a1.b); // 구조체 변수 a1 멤버 b의 memory 주소 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&a1.c); // 구조체 변수 a1 멤버 c의 memory 주소 출력.
printf("struct Aligned a2\n");
printf("Size of %zd\n", sizeof(a2)); // 구조체 변수 a2의 memory 크기 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&a2); // 구조체 변수 a2의 memory 주소 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&a2.a); // 구조체 변수 a2 멤버 a의 memory 주소 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&a2.b); // 구조체 변수 a2 멤버 b의 memory 주소 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&a2.c); // 구조체 변수 a2 멤버 c의 memory 주소 출력.
return 0;
}padding
- 데이터 전송의 효율을 위해 padding 을 사용.
- cpu는 memory를 읽어올 때 한 번에 4byte(x86) 또는 8byte(x64) 만큼 가능.
- 자료형 1개를 두 번에 나눠서 전달 하지 않도록 하기 위해 padding 사용. (효율성 향상)
코드
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
/*
padding (struct member alignment)
- 1 word = CPU가 memory로 부터 한번에 받을 수 있는 데이터 크기.
- 1 word: 4 bytes(x86) or 8 bytes(x64)
*/
struct test1
{
char a;
float b;
double c;
};
/*
1. padding을 사용하지 않는 경우.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7|8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15|16
|a| b | c | ? ? ?
1 + 4 + 8 = 13.
CPU 입장에서 c 를 2번 불러옴 (5~7 1번, 8~12 1번).
*/
/*
2. padding을 사용하는 경우.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7|8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15|16
| a | b | c |
4 + 4 + 8 = 16.
*/
struct test1 test1;
printf("Size of %zd\n", sizeof(test1)); // 구조체 변수 test의 memory 크기 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&test1); // 구조체 변수 test의 memory 주소 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&test1.a); // 구조체 변수 test 멤버 a의 memory 주소 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&test1.b); // 구조체 변수 test 멤버 b의 memory 주소 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&test1.c); // 구조체 변수 test 멤버 c의 memory 주소 출력.
return 0;
}결과
- char 자료형의 memory가 padding이 더해져 4 bytes의 공간을 가짐.
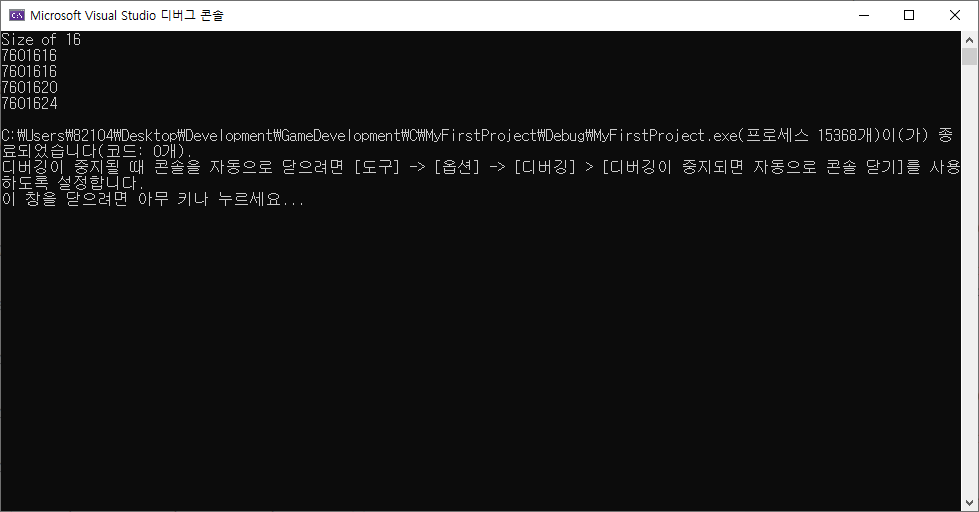
3. 구조체의 배열
- 구조체를 배열처럼 사용 가능.
- 첫번 째 구조체 = p[0], 두번 째 구조체 = p[1]...
4. 구조체와 포인터
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct names {
char given[30];
char family[30];
};
struct friend {
struct names full_name; // 구조체 names를 구조체 friend의 멤버로 설정. (중첩 구조체)
char mobile[30];
};
int main()
{
struct friend my_friends[2] = { // 구조체를 배열로 초기화.
{ {"Ariana", "Grande"}, "1234-1234"},
{ {"Taylor", "Swift"}, "5678-5678"}
};
struct friend* girl_friend; // 구조체 friend의 포인터 girl_friend 선언.
girl_friend = &my_friends[0]; // 포인터 girl_friend에 my_friends[0]의 memory 주소를 저장.
printf("%zd\n", sizeof(struct friend)); // 구조체 friend의 크기 출력.
printf("%lld %s\n", (long long)girl_friend, girl_friend->full_name.given);
// girl_friend의 memory 크기와 girl_friend가 가리키는 구조체의 full_name.given 값 출력.
girl_friend++; // 포인터의 산술 연산.
printf("%lld %s\n", (long long)girl_friend, (*girl_friend).full_name.given);
// girl_friend의 memory 크기와 girl_friend indirection 값의 full_name.given 값 출력.
return 0;
}5. 구조체를 함수로 전달하는 방법
- 구조체를 함수로 전달 가능.
- 구조체의 포인터를 함수로 전달 가능. (매개변수에 const 사용)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define FUNDLEN 50
struct fortune { // 구조체 fortune 선언.
char bank_name[FUNDLEN];
double bank_saving;
char fund_name[FUNDLEN];
double fund_invest;
};
double sum(struct fortune *mf); // 함수 sum의 프로토타입.
int main()
{
struct fortune my_fortune = { // 구조체 fortune의 변수 my_fortune 초기화.
"Wells-Fargo",
4032.27,
"JPMorgan Chase",
8543.94
};
printf("Total : $%.2f.\n", sum(&my_fortune)); // 함수 sum의 반환 값을 소수점 두 자리까지 출력.
return 0;
}
double sum(const struct fortune *mf) // 함수 sum 정의. 매개 변수 = 구조체의 포인터
{
return mf->bank_saving + mf->fund_invest; // 구조체 멤버의 합을 반환.
}6. 구조체와 함수 연습문제
- scanf로 문자열 입력 받기 = scanf("%[^\n]%*c", [저장될 곳]);
코드
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define NLEN 30
struct name_count { // 구조체 name_count 선언.
char first[NLEN];
char last[NLEN];
int num;
};
void receive_input(struct name_count*); // 함수 receive_input 프로토타입.
void count_characters(struct name_count*); // 함수 count_characters 프로토타입.
void show_result(const struct name_count*); // 함수 show_result 프로토타입.
int main()
{
struct name_count user_name; // 구조체 name_count 변수 username 선언.
receive_input(&user_name); // 함수 receive_input 호출.
count_characters(&user_name); // 함수 count_characters 호출.
show_result(&user_name); // 함수 show_result 호출.
return 0;
}
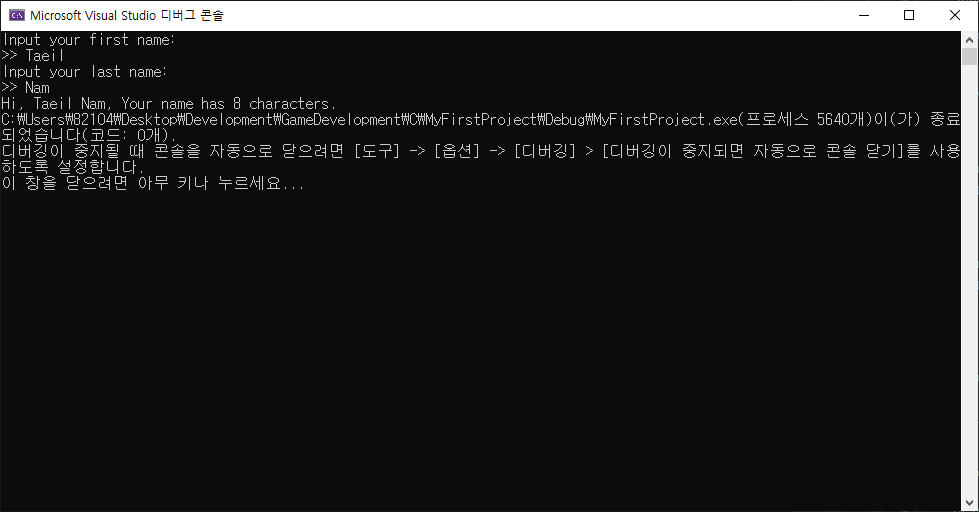
void receive_input(struct name_count* ptr_nc) // 함수 receive_input 정의.
{
int flag;
printf("Input your first name:\n>> ");
flag = scanf("%[^\n]%*c", ptr_nc->first); // 입력받은 줄바꿈(\n) 전까지의 문자열을 저장.
if (flag != 1)
printf("Wrong name.");
printf("Input your last name:\n>> ");
flag = scanf("%[^\n]%*c", ptr_nc->last); // 입력받은 줄바꿈(\n) 전까지의 문자열을 저장.
if (flag != 1)
printf("Wrong name.");
}
void count_characters(struct name_count* ptr_nc) // 함수 count_characters 정의.
{
ptr_nc->num = strlen(ptr_nc->first) + strlen(ptr_nc->last);
// 구조체 name_count의 멤버 first, last의 문자열 개수를 더해서 멤버 num에 저장.
}
void show_result(const struct name_count* ptr_nc) // 함수 show_result 정의.
{
printf("Hi, %s %s, Your name has %d characters.",
ptr_nc->first, ptr_nc->last, ptr_nc->num);
}결과
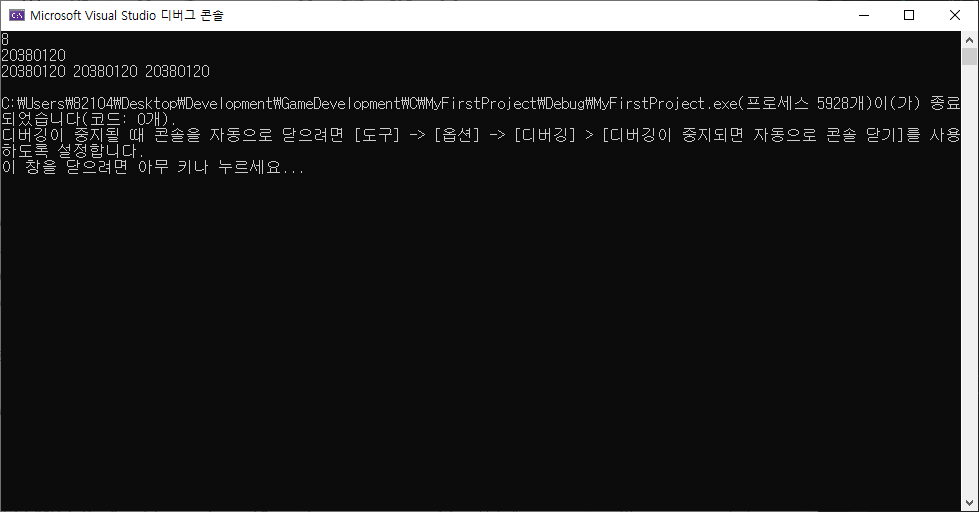
7. 공용체(Union)
- 서로 다른 자료형을 같은 memory 공간에 저장.
- 구조체는 멤버들이 서로 다른 memory 공간을 가지지만, 공용체는 동일한 memory 공간을 가짐.
- 공용체의 memory 크기는 멤버 자료형 중 가장 큰 자료형의 크기와 같음.
코드
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
union my_union { // 공용체 my_union 선언.
int i;
double d;
char c;
};
// 멤버 자료형 중 가장 큰 자료형 = double = 구조체의 memory 크기 = 8 Bytes.
union my_union uni; // 공용체 my_union의 변수 uni 선언.
printf("%zd\n", sizeof(union my_union)); // 공용체 my_union의 memory 크기 출력.
printf("%lld\n", (long long)&uni); // 공용체 my_union의 memory 주소 출력.
printf("%lld %lld %lld\n", // 공용체 my_union의 각 멤버 memory 주소 출력.
(long long)&uni.i, (long long)&uni.d, (long long)&uni.c);
return 0;
}결과
- 공용체의 모든 멤버의 memory 주소는 같음.
8. 구조체와 공용체를 같이 사용하기
코드
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
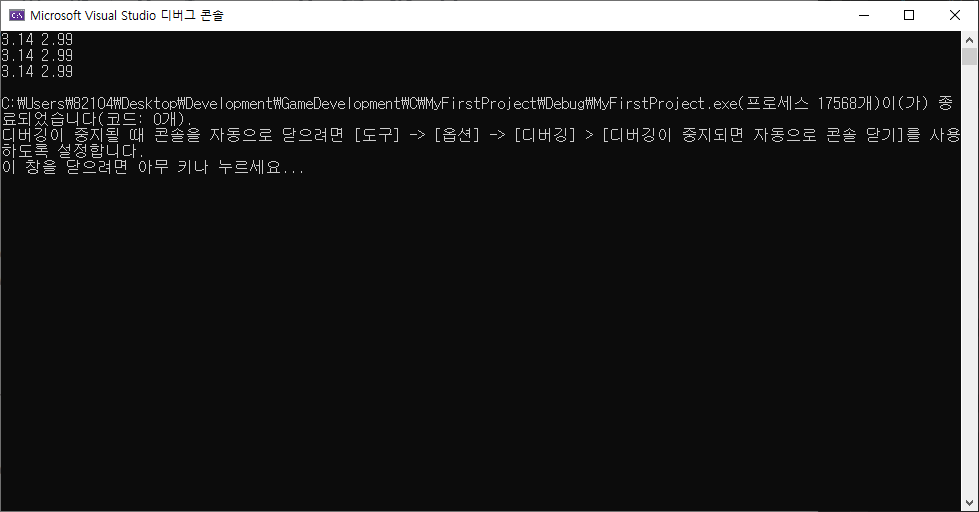
struct Vector2D { // 구조체 Vector2D 선언.
union { // 구조체 Vector2D 내부에 익명 공용체(no tag) 선언.
struct { double x, y; }; // 익명 공용체 내부에 익명 구조체 선언.
struct { double i, j; }; // 익명 공용체 내부에 익명 구조체 선언.
struct { double arr[2]; }; // 익명 공용체 내부에 익명 구조체 선언.
};
};
typedef struct Vector2D vec2; // struct Vector2D 형태를 vec2 라는 이름의 자료형으로 선언.
vec2 v = { 3.14, 2.99 }; // 구조체 Vector2D의 변수 v 초기화.
printf("%.2f %.2f\n", v.x, v.y); // 구조체 Vector2D의 멤버 x, y 값 출력.
printf("%.2f %.2f\n", v.i, v.j); // 구조체 Vector2D의 멤버 i, j 값 출력.
printf("%.2f %.2f\n", v.arr[0], v.arr[1]); // 구조체 Vector2D의 멤버 arr[0], arr[1] 값 출력.
return 0;
}결과
9. 열거형(Enumerated Type)
- 정수형 상수가 이름이 있는 것처럼 만들어 줌.
- 열거형의 원소에 0부터 차례대로 정수가 저장 됨.
- 가독성을 높여줌.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
enum spectrum { red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet };
// 열거형 spectrum 선언.
enum spectrum color; // 열거형 spectrum의 변수 color 선언.
color = blue;
if (color == yellow) // color 값이 yellow일 경우.
printf("yellow\n");
for (color = red; color <= violet; color++)
printf("%d\n", color);
printf("red = %d, orange = %d\n", red, orange);
return 0;
}10. 함수 포인터(Function Pointer)
- 함수가 저장되어 있는 memory의 주소 값을 저장.
코드
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h> // toupper(), tolower() 함수 사용.
void ToUpper(char* str) // ToUpper 함수 정의.
{
while (*str) // = while (*str != NULL)
{
*str = toupper(*str); // *str 에 해당하는 문자를 대문자로 변경.
str++; // 포인터 산술연산.
}
}
void ToLower(char* str) // ToLower 함수 정의.
{
while (*str) // = while (*str != NULL)
{
*str = tolower(*str); // *str 에 해당하는 문자를 소문자로 변경.
str++; // 포인터 산술연산.
}
}
int main()
{
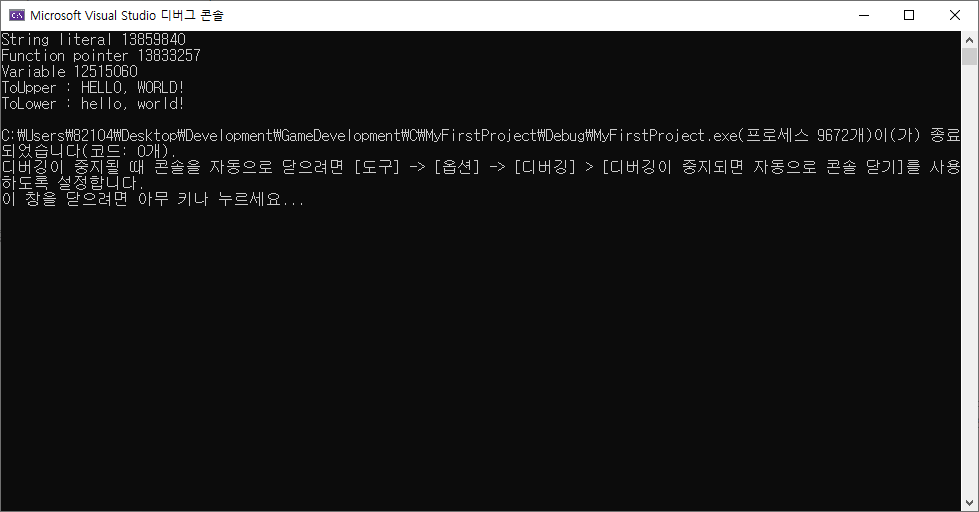
char str[] = "Hello, World!"; // 배열 str에 문자열 저장.
void (*pf)(char*); // 자료형 = void, 매개변수 자료형 = char 함수의 포인터 pf 선언.
pf = ToUpper; // 함수 포인터 pf에 함수 ToUpper 대입.
printf("String literal %lld\n", (long long)("Hello, World!")); // 문자열 자체의 memory 주소 출력. (TEXT Segment memory)
printf("Function pointer %lld\n", (long long)ToUpper); // 함수의 memory 주소 출력. (TEXT Segment memory)
printf("Variable %lld\n", (long long)str); // 배열의 memory 주소 출력. (Stack memory)
(*pf)(str); // = ToUpper(str);
printf("ToUpper : %s\n", str); // ToUpper 함수 실행 후 문자열 출력.
pf = ToLower; // 함수 포인터 pf에 ToLower 함수 대입.
pf(str); // = ToLower(str);
printf("ToLower : %s\n", str); // ToLower 함수 실행 후 문자열 출력.
return 0;
}결과
11. Typedef
- 자료형에 별명을 붙여줌.
- 새로운 자료형을 만드는 것이 아니라, 특정 자료형에 별명(Alias)을 붙여주는 것.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
typedef unsigned char unchar; // unsigned char 자료형에 unchar 라는 별명을 붙여줌.
unchar var = 'N'; // = unsigned char var = 'N';
return 0;
}🚩 출처 및 참고자료 : 홍정모의 따라하며 배우는 C 언어 (따배씨)