1. 입출력 버퍼
- 프로그래밍에서 가장 속도가 느린 작업 = 입출력.
- 입출력 속도 및 효율성 향상을 위해 버퍼 사용.
- 버퍼(Buffer) = 입력이나 출력을 모아두는 공간.(Memory)
- 입력이나 출력을 한번에 모은 뒤 수행하기 위해 사용.
- 버퍼를 사용하지 않으면, 값이 입력 되자마자 바로 출력.
- 버퍼를 사용하면 입력한 값을 버퍼에 모아두었다가, 특정 조건 만족시 한번에 출력.
💡 버퍼에 저장된 값을 출력하는 조건
1. `\`(백슬래시)가 포함된 값(Escape Sequence)이 입력되었을 때. (줄바꿈(\n) 등..)
2. 버퍼가 가득 찼을 때.
- 버퍼 사이즈는 가장 효율적인 크기로 정해져 있으며, 변경도 가능.버퍼 사용, 미사용 비교
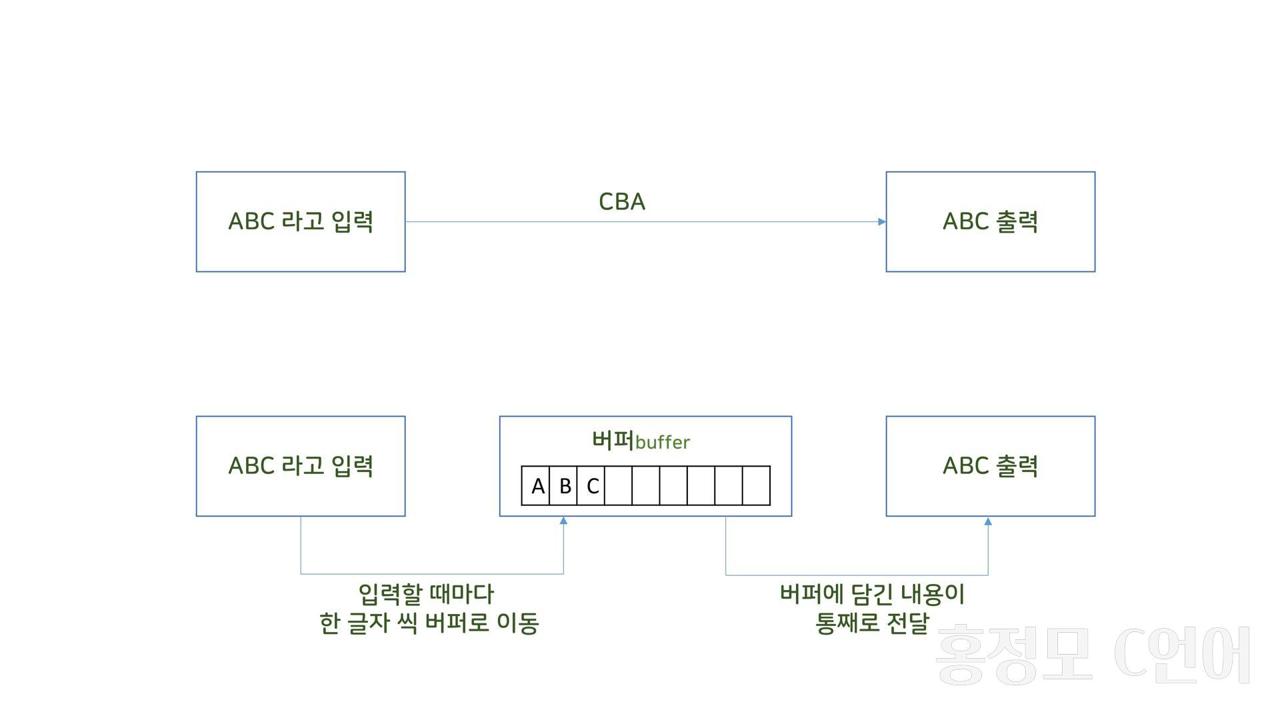
버퍼 사용
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char c;
while ((c = getchar()) != '.') // '.'을 입력받을 때까지 while문 실행. (getchar() = 버퍼 사용)
putchar(c); // putchar() = 값을 출력해주는 표준 입출력 함수.
return 0;
}결과
- 입력된 문자를 버퍼에 모아둔 후, 엔터(\n) 입력시 모아둔 값 한번에 출력.
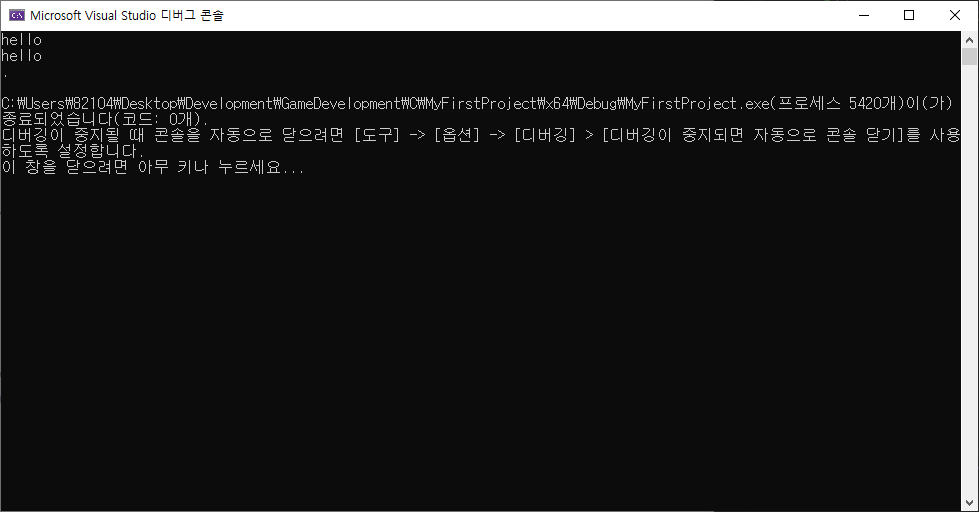
버퍼 미사용
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h> // 버퍼를 사용하지 않는 _getche 함수가 포함된 라이브러리. (윈도우 전용)
int main()
{
char c;
while ((c = _getche()) != '.') // '.'을 입력받을 때까지 while문 실행. (_getche() = 버퍼 사용 X)
putchar(c);
return 0;
}결과
- 입력된 문자를 버퍼에 모아두지 않고 입력 되자마자 바로 출력.
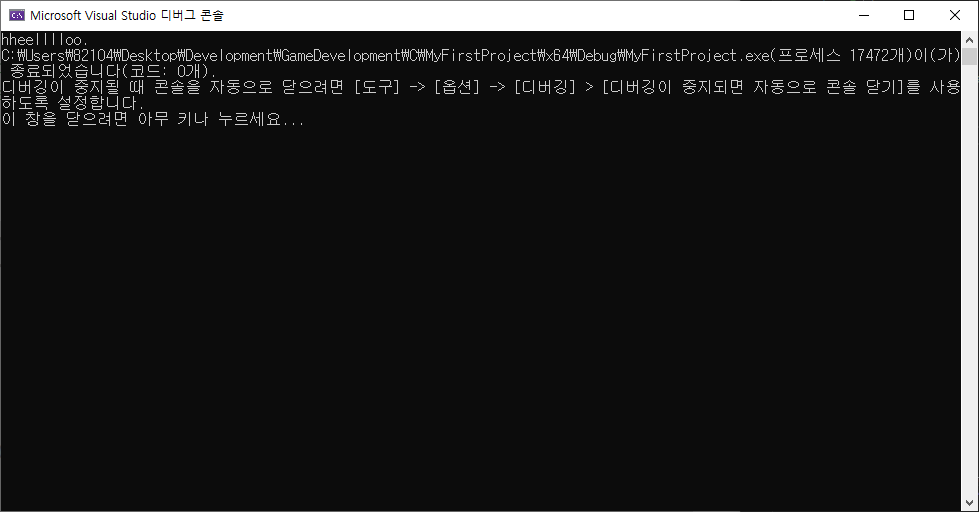
버퍼 비우기
- while (getchar() != '\n') 코드 사용.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int count = 0;
while (1) // while문 반복 실행.
{
printf("Current count is %d. Continue? (n = exit)\n", count);
if (getchar() == 'n') // 'n'을 입력받으면 while문 빠져나옴.
break;
while (getchar() != '\n') // '\n'(줄바꿈) 입력 받을 때까지 while문 실행.
continue; // 없어도 되나, 가독성을 위해 사용.
count++;
}
return 0;
}2. 파일의 끝(EOF - End Of File)
- EOF는 입력의 끝을 나타냄.
- 사용자의 입력이 끝났다는 것을 알려줄 때 사용한다.
- "Ctrl + z"를 누르면 운영체제가 프로그램에게 EOF를 보낸다.
- C 언어에서 EOF의 값 = -1.
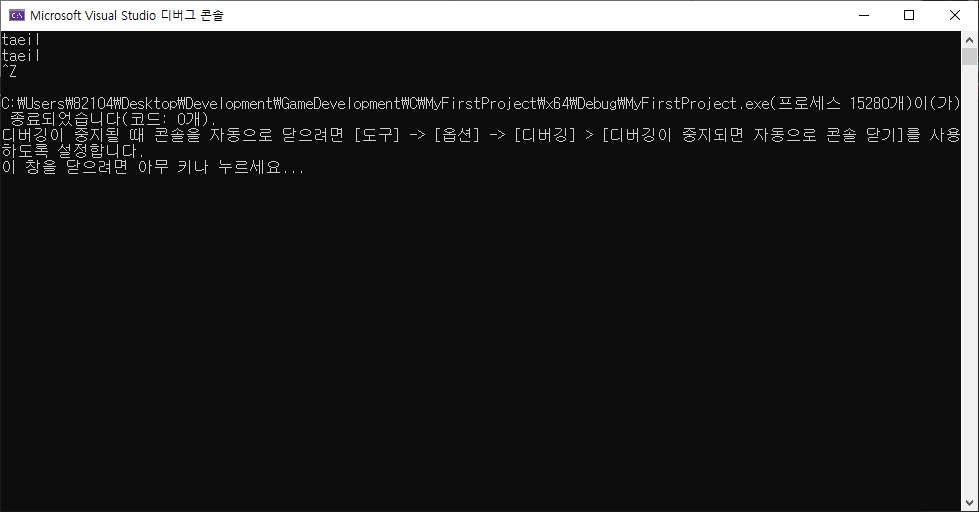
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int c;
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF) // "EOF"를 입력받을 때까지 while문 실행.
putchar(c);
return 0;
}결과
💡 Data Stream 에서 EOF.
- Data Stream : 데이터가 흐르는 것. (작성한 프로그램 <-> 파일간 데이터를 주고 받는 것)
- Data Stream 의 끝을 표시할 때에도 "EOF" 사용.3. 입력 값 확인하기 예제
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
long input;
char c;
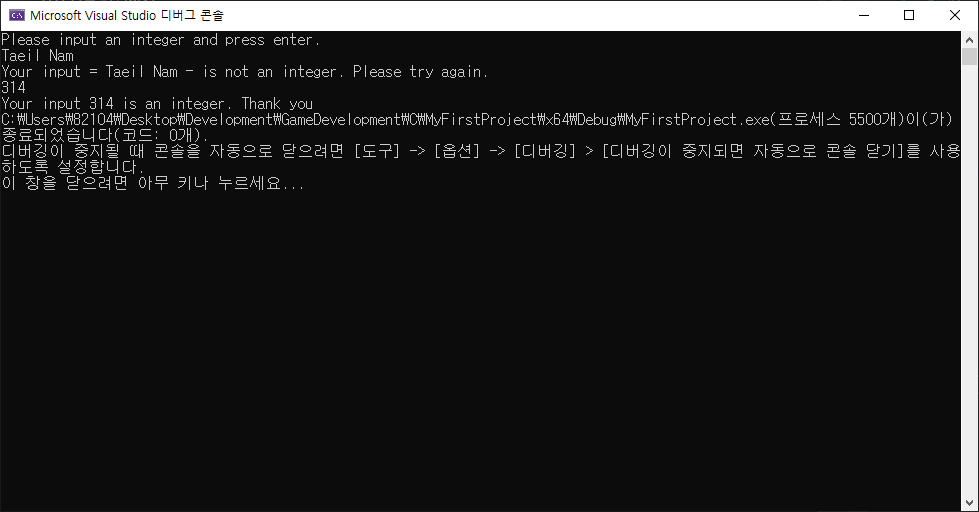
printf("Please input an integer and press enter.\n");
while (scanf("%ld", &input) != 1) // input에 입력 값이 저장되지 않은 경우. (입력 값이 정수가 아닌 경우)
{
printf("Your input = ");
while ((c = getchar()) != '\n') // '\n'(줄바꿈)이 나올 때까지 입력 버퍼에 저장된 문자를 변수 c에 저장.
putchar(c); // c의 값 출력.
printf(" - is not an integer. Please try again.\n");
}
printf("Your input %ld is an integer. Thank you", input);
return 0;
}결과
4. 메뉴 만들기 예제
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char c;
int num;
while (1) // while문 반복 실행.
{
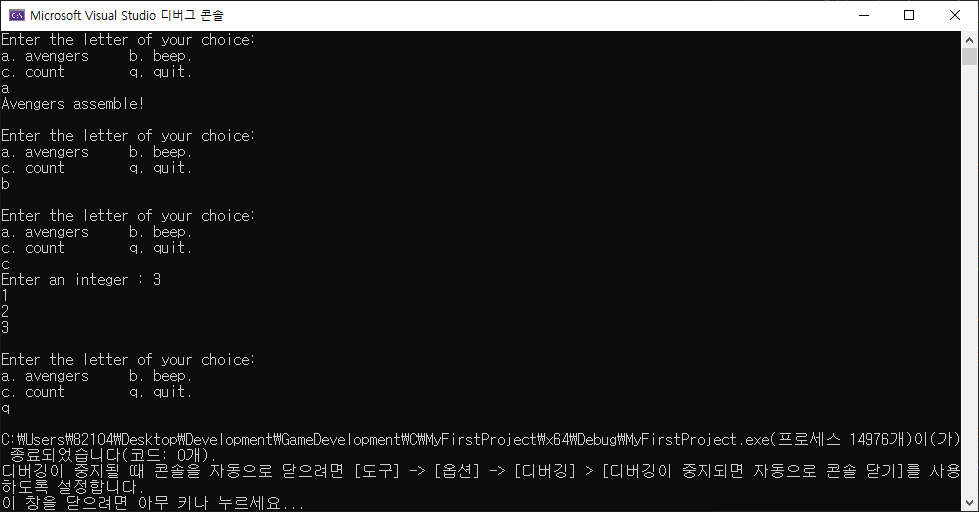
printf("Enter the letter of your choice:\n");
printf("a. avengers b. beep.\n");
printf("c. count q. quit.\n");
scanf("%c", &c); // 입력 값을 변수 c에 저장.
if (c == 'a') // 입력 받은 값이 'a'일 경우.
{
printf("Avengers assemble!\n\n"); // 'Avengers assemble!' 출력.
}
else if (c == 'b') // 입력 받은 값이 'b'일 경우.
{
printf("\a\n"); // 알림음 출력.
}
else if (c == 'c') // 입력 받은 값이 'c'일 경우.
{
printf("Enter an integer : ");
scanf("%d", &num); // 입력 값을 변수 num에 저장.
for (int i = 1; i <= num; ++i) // i = 1부터 num 값 까지.
{
printf("%d\n", i); // i 값 출력.
}
printf("\n");
}
else if (c == 'q') // 입력 받은 값이 'q'일 경우.
{
break; // while문 빠져 나옴.
}
while ((c = getchar()) != '\n') // c의 입력 버퍼 비우기.
continue;
}
return 0;
}결과
5. 텍스트 파일 읽기 예제
코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // exit() 함수 사용을 위한 라이브러리.
int main()
{
int c;
FILE *file = NULL; // 포인터 변수 file 선언.
char file_name[] = "my_file.txt";
file = fopen(file_name, "r"); // fopen()의 반환 값 = 파일 포인터 값을 포인터 변수 file에 저장.
if (file == NULL) // 변수 file의 값이 NULL인 경우. (파일이 존재하지 않는 경우)
{
printf("Failed to open file.\n");
exit(1); // 프로그램 종료. (code = 1)
}
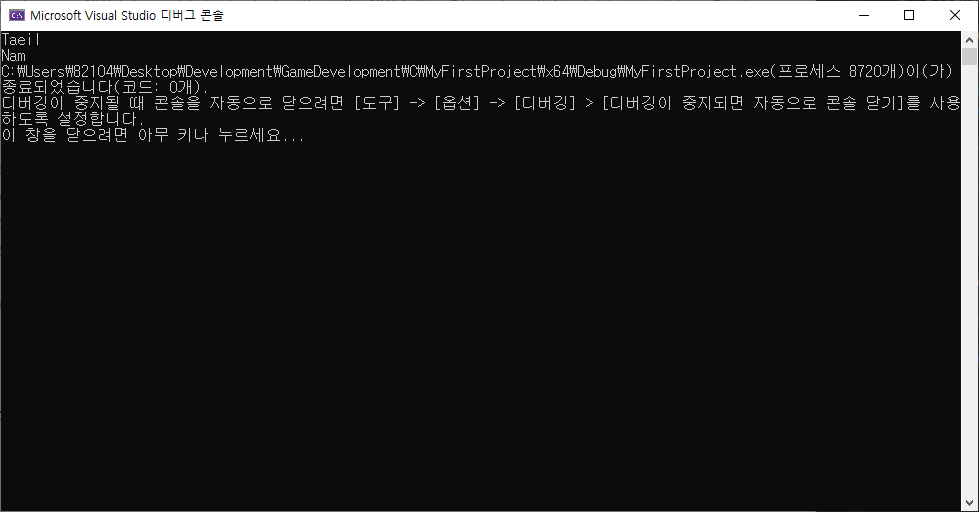
while ((c = getc(file)) != EOF) // "EOF" 문자가 나올 때까지 파일에 속해있는 문자를 변수 c에 저장.
putchar(c); // c의 값 출력.
fclose(file); // 파일 종료.
return 0;
}텍스트 파일 내용
Taeil
Nam
💡 경로 : C:/Users/82104/Desktop/Development/GameDevelopment/C/MyFirstProject/MyFirstProject/my_file.txt결과
🚩 출처 및 참고자료 : 홍정모의 따라하며 배우는 C 언어 (따배씨)