Doubly Linked List
각 노드가 이전 노드와 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터 두 개를 가지고, 양방향으로 탐색이 가능한 리스트
Implementation
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node *prev;
Node *next;
explicit Node(int data) : data(data), prev(nullptr), next(nullptr) {
}
};
class DoublyLinkedList {
private:
Node *head;
Node *tail;
public:
DoublyLinkedList() : head(nullptr), tail(nullptr) {
}
void append(int data) {
Node *newNode = new Node(data);
if (tail == nullptr) {
head = tail = newNode;
} else {
tail->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = tail;
tail = newNode;
}
}
void prepend(int data) {
Node *newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == nullptr) {
head = tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode->next = head;
head->prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
}
}
void deleteNode(int key) {
Node *cur = head;
while (cur != nullptr && cur->data != key) {
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur == nullptr) return;
if (cur == head) {
head = cur->next;
if (head != nullptr) head->prev = nullptr;
} else if (cur == tail) {
tail = cur->prev;
if (tail != nullptr) tail->next = nullptr;
} else {
cur->prev->next = cur->next;
cur->next->prev = cur->prev;
}
delete cur;
}
void displayForward() const {
Node* temp = head;
cout<<"nullptr <-> ";
while(temp != nullptr) {
cout<<temp->data<<" <-> ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout<<"nullptr"<<endl;
}
void displayBackward() const {
Node* temp = tail;
cout<<"nullptr <-> ";
while(temp != nullptr) {
cout<<temp->data<<" <-> ";
temp = temp->prev;
}
cout<<"nullptr"<<endl;
}
};
int main() {
DoublyLinkedList list;
list.append(10);
list.append(20);
list.prepend(5);
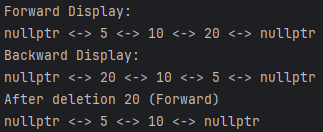
cout<<"Forward Display: "<<endl;
list.displayForward();
cout<<"Backward Display: "<<endl;
list.displayBackward();
list.deleteNode(20);
cout<<"After deletion 20 (Forward)"<<endl;
list.displayForward();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Output
Efficiency
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Explaination |
|---|
| Search | O(n) | O(1) | 특정 데이터를 찾기 위해 리스트의 시작 또는 끝에서 순차적으로 탐색해야 함. 선형 시간 소요. 빈번한 랜덤 접근이 필요할 경우 부적절. |
| Insertion | O(1)(처음/끝), O(n)(중간) | O(1) | 리스트의 처음이나 끝에 삽입 시 상수 시간. 중간 위치에 삽입은 해당 위치까지 탐색이 필요하므로 선형시간 소요. |
| Deletion | O(1)(처음), O(n)(중간/끝) | O(1) | 리스트의 처음이나 끝에 삭제 시 상수 시간. 중간 위치에 삭제는 해당 위치까지 탐색이 필요하므로 선형시간 소요. |
Efficiency Summary
양방향 탐색이 필요한 경우, 앞뒤로 탐색 가능 적합
빈번한 중간 삽입/삭제가 필요한 경우 적합
양쪽 끝에서 요소 추가/삭제가 필요한 경우 적합
빠른 임의 접근이 필요한 경우 부적합
정렬이 빈번하게 필요한 경우 부적합
단방향 탐색만으로 충분한 경우, Singly Linked List가 더 효율적
STL
std::list
Doubly Linked List로 구현됨