Hash
데이터를 빠르게 저장하고 검색하기 위한 방법
Hash Function을 사용하여 데이터를 특정 위치(해시값)로 매핑
Hash Function
Key값을 받아 고정된 크기의 정수(Hash Code)로 변환하는 함수
Collision: 서로 다른 Key값이 같은 해시값을 갖는 경우
Hash Table
Hash 기반으로 데이터를 저장하는 자료구조
구성: Key-Value 쌍으로 데이터를 저장
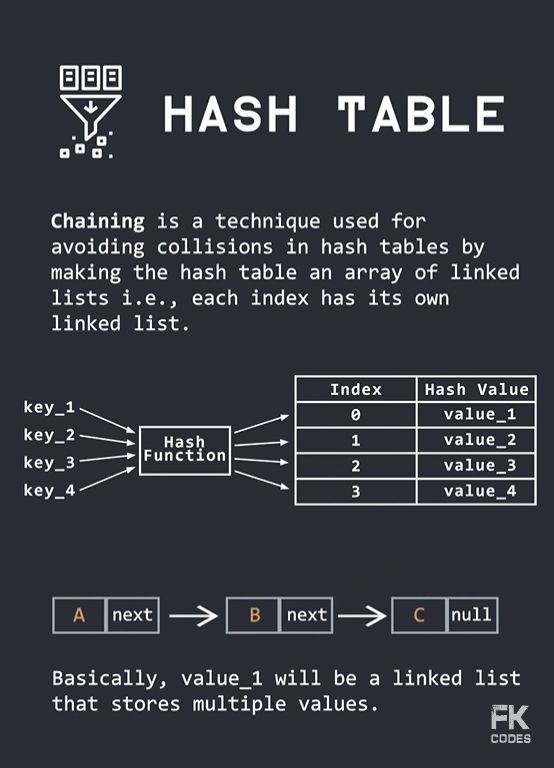
Solution Collision
Chaining: 같은 해시값의 데이터를 연결 리스트로 관리
Open Addressing: 충돌이 발생하면 테이블의 다른 빈 공간을 찾아 저장
Implementation
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
class HashTable {
private:
vector<list<pair<string, int>>> table;
int size;
int hashFunction(const string& key) {
int hash = 0;
for(char ch:key) {
hash = (hash * 31 + ch) % size;
}
return hash;
}
public:
HashTable(int s) : size(s) {
table.resize(size);
}
void insert(const string& key, int value) {
int hash = hashFunction(key);
for(auto& pair : table[hash]) {
if(pair.first == key) {
pair.second = value;
return;
}
}
table[hash].emplace_back(key, value);
}
bool search(const string& key) {
int hash = hashFunction(key);
for(const auto& pair : table[hash]) {
if(pair.first == key) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void remove(const string& key) {
int hash = hashFunction(key);
auto& bucket = table[hash];
for(auto it = bucket.begin(); it != bucket.end(); ++it) {
if(it->first == key) {
bucket.erase(it);
return;
}
}
}
void display() {
for(int i=0; i<size; i++) {
for(const auto& pair : table[i]) {
cout<<"["<<pair.first<<": "<<pair.second<<"]";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
};
Complexity
| average | worst |
|---|
| Insert | O(1) | O(n) |
| Search | O(1) | O(n) |
| Deletion | O(1) | O(n) |
Summary
빠른 검색/삽입이 필요할 때 효율적
정렬, 범위 검색이 필요하거나 메모리가 제한된 환경은 비효율적
STL
std::unordered_map
Key-Value 쌍을 저장한는 해시 기반 맵
std::unordered_set
중복되지 않는 데이터를 저장하는 해시 기반 집합