비동기 처리
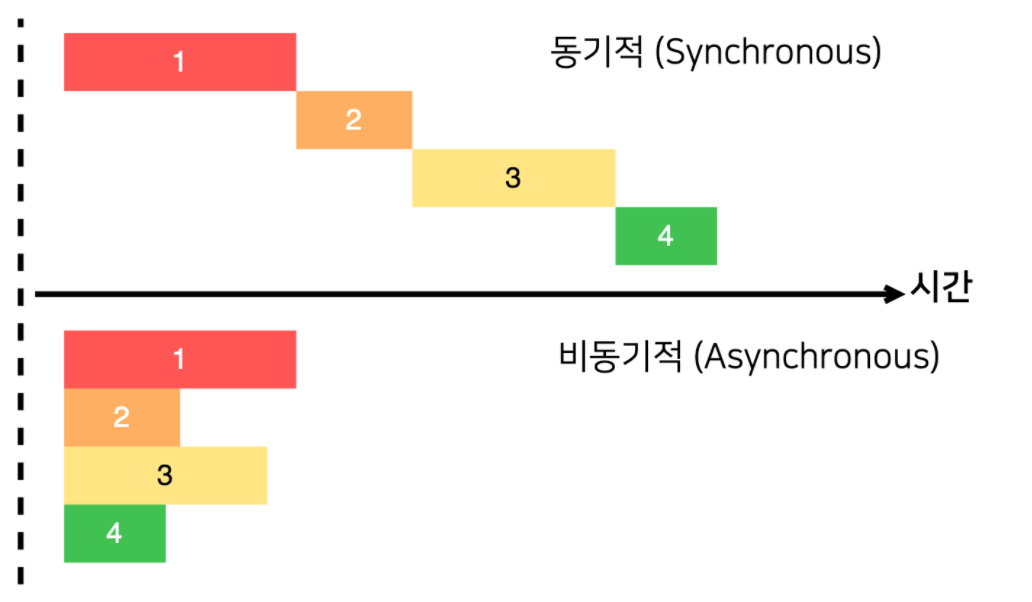
1.동기적 방식(Syncronous)
-
요청을 보낸 후 해당 요청의 응답을 받아야 다음 동작을 실행하는 방식
-
예시) 은행 업무를 보러가면 번호표를 뽑고 기다린 후에 차례가 되었을 때 내 업무를 볼 수 있고, 내 업무가 끝나야 다음 사람이 업무를 진행할 수 있다, 내가 업무를 보고 있는 동안 다른 업무를 보지못한다.
2.비동기적 방식(Asynchronous)
-
요청을 보낸 후 응답과 관계없이 다음 동작을 실행할 수 있는 방식
-
예시) 커피숍에서 커피를 주문할 때, 한사람 주문을 받고 커피를 내리고 커피를 완성해서 커피를 주고 다음 손님을 받는게 아니라, 한꺼번에 주문을 받고 한꺼번에 커피가 나간다, 그렇게 함으로 뒤에 사람이 기다리는 시간이 좀 더 줄어든다, 좀 더 효율적인 처리가 가능해진다
-
요청에 대한 결과를 바로 반환하는게 아니라, delay한 후 반환
알아야할 개념
1. 콜백
- 다른 함수의 전달인자로 넘겨주는 함수
- parameter를 넘겨받은 함수는 callback 함수를 필요에 따라 즉시 실행(동기적)할 수도 있고, 나중에 (비동기적) 실행할 수도 있음
function B() {
console.log("callback!")
}
function A(callback) {
callback(); // callback === B
}
A(B)Async를 다루기 위해서 콜백이 필요
const printString = (string, callback) => {
setTimeout (
() => {
console.log(string)
callback()
},
Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) +1
)
}
const printAll = () => {
printString("A", () => { // 콜백 함수 실행 //콜백 안에서 콜백함수를 실행하는 것
printString("B", () => {
printString("C", () => {})
})
})
}2. 블로킹(blocking)과 논플로킹(Non-Blocking)
Blocking
- 동기적으로 수행
- 현재 컨텍스트에서 다음의 javascript 코드가 수행되기 위해 현재의 연산이 끝날 떄까지 기다려야하는 상황
function waitSync(ms) {
var start = Date.now();
var now = start;
while(now - start < ms) {
now = Date.now();
}
} // 현재 시각과 시작 시각을 비교하며 ms 범위 내에서 무한 루프를 도는 blocking 함수입니다
function drink(person, coffee) {
console.log(person + '는 ' + coffee + '를 마십니다');
}
function orderCoffeeSync(coffee) {
console.log(coffee + '가 접수되었습니다');
waitSync(2000);
return coffee;
}
let customers = [{
name: 'Steve',
request: '카페라떼'
}, {
name: 'John',
request: '아메리카노'
}];
// call synchronously
customers.forEach(function(customer) {
let coffee = orderCoffeeSync(customer.request);
drink(customer.name, coffee);
});Non-Blocking
- 비동기적 수행
- 다음의 javasciprt코드가 수행되기 위해 현재의 연산이 끝나는 것을 기다리지않아도 되는 상황
function watiAsync (callback, ms) {
setTimeout(callback, ms); //특정 시간 이후에 callback 함수가 실행되게끔 하는 내장 기능
}
function drink (person, coffee) {
console.log(person + '는 ' + coffe + '를 마십니다');
}
function orderCoffeeSync(coffee) {
console.log(coffee + "가 접수되었습니다");
waitSync(2000);
return coffee
}
let custoers = [{
name : "Steve",
request : "카페라떼"
}, {
name : "John",
request : "아메리카노"
}]
function orderCoffeeAsync(menu, callback) {
console.log(menu + '가 접수되었습니다');
waitAsync(function() {
callback(menu);
}, 2000);
}
// call asynchronously
customers.forEach(function(customer) {
orderCoffeeAsync(customer.request, function(coffee) {
drink(customer.name, coffee);
});
});실행시키면 주문을 다받고, 커피가 나오는 걸 볼 수 있음
3. 비동기 주요 사례
DOM Element의 이벤트 핸들러
- 마우스 , 키보드 입력
- 페이지 로딩
타이머
- 타이머 API
- 애니메이션 API
서버에 자원 요칭 및 응답
- fetch API
- AJAX(XHR)
