이 글에서는 diffusers 라이브러리를 이용한 pretrained 사용예시와 Fine-Tuning을 다뤄보고자 한다.
라이브러리 가져오기
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision
from datasets import load_dataset
from diffusers import DDIMScheduler, DDPMPipeline
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
from tqdm.auto import tqdmpretrained 모델 받기
- 모델들은 허깅페이스에 있다.
image_pipe = DDPMPipeline.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-celebahq-256")
image_pipe.to(device);- 이후로는 다음과 같이 매우 간단하게 이미지를 생성할 수 있다.
images = image_pipe().images
images[0]

Scheduler 받기
- scheduler에는 input x의 scale 방법과 diffusion 프로세스의 step에 따른 x와 noise 비율 계산 방법 등이 담겨 있다.
- 아래 코드를 통해 scheduler를 받을 수 있다.
scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-celebahq-256")
scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps=40)- 아래 코드는 새로운 스케줄러 적용방법과 steps 조절 방법이다.
image_pipe.scheduler = scheduler
images = image_pipe(num_inference_steps=40).images
images[0]

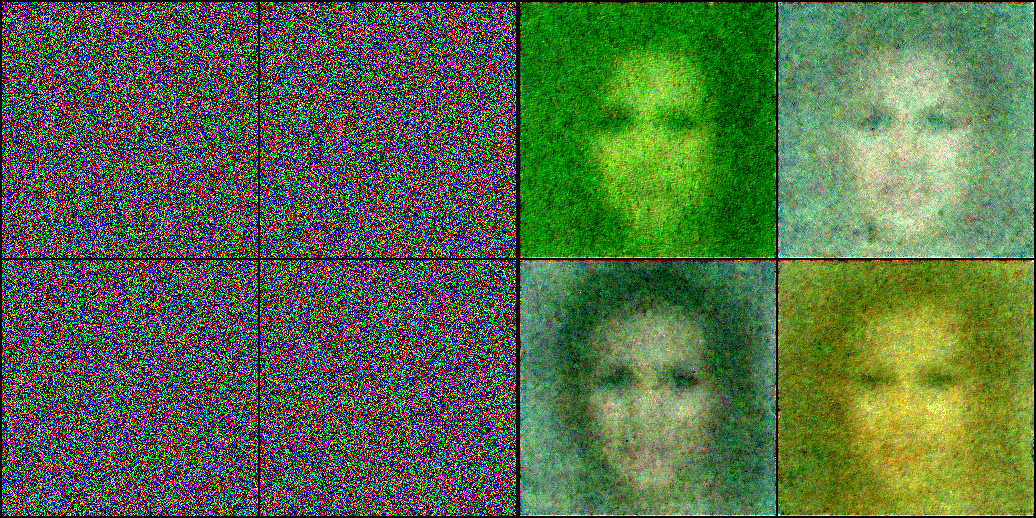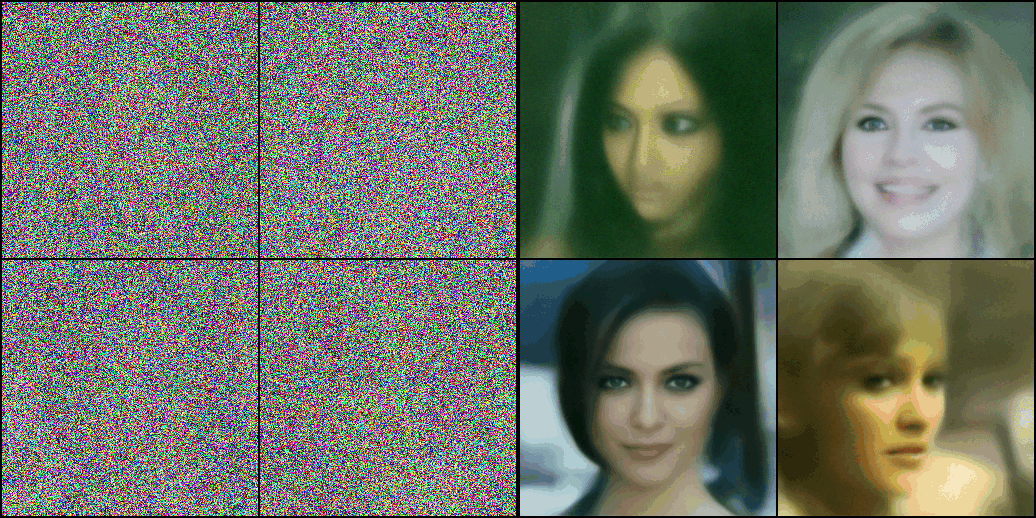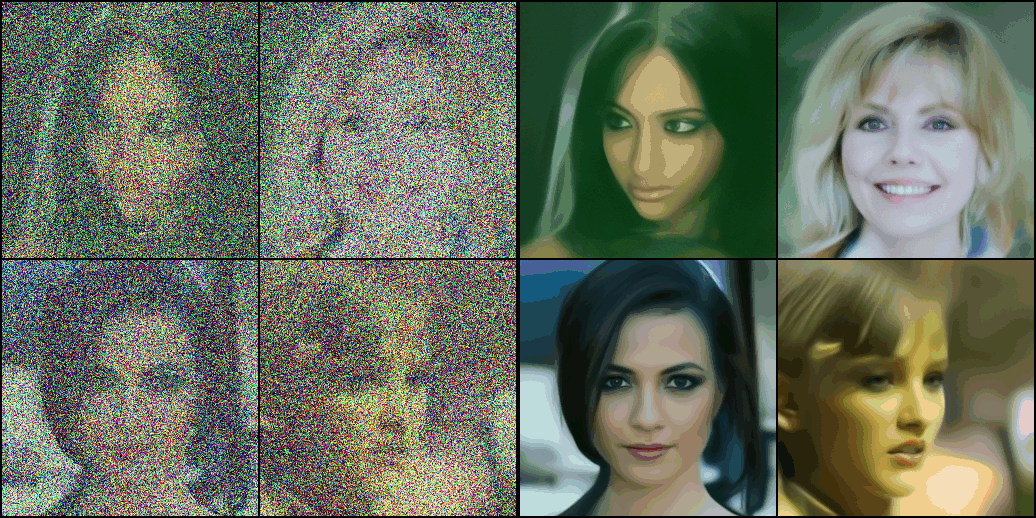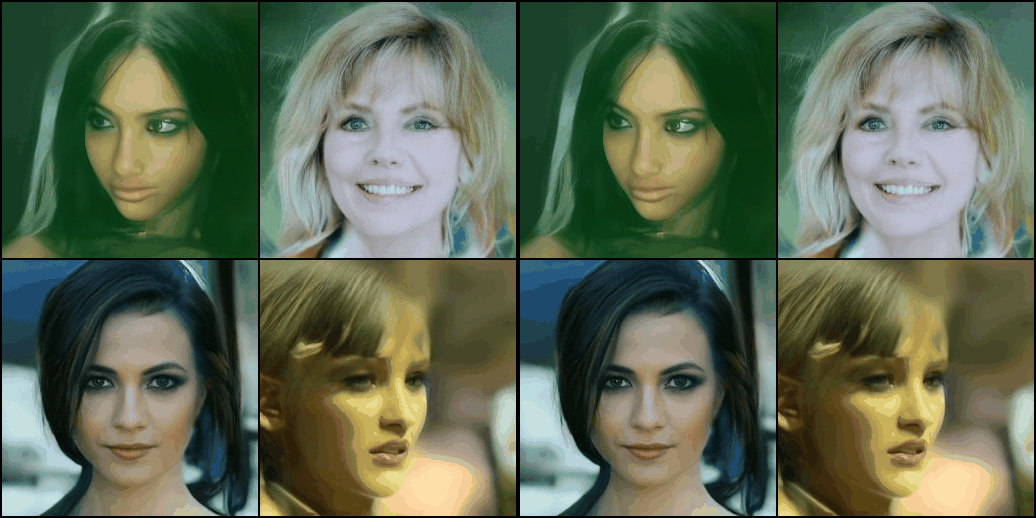
step()을 이용한 Diffusion 프로세스
- 핵심 코드 부분만 확인해보자.
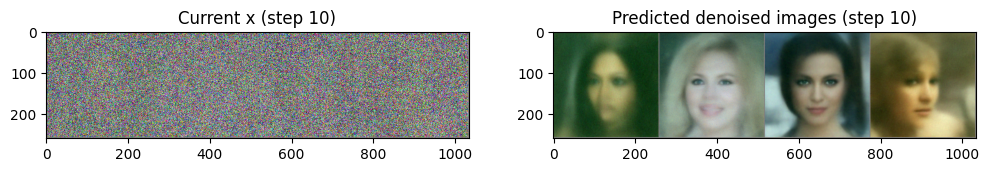
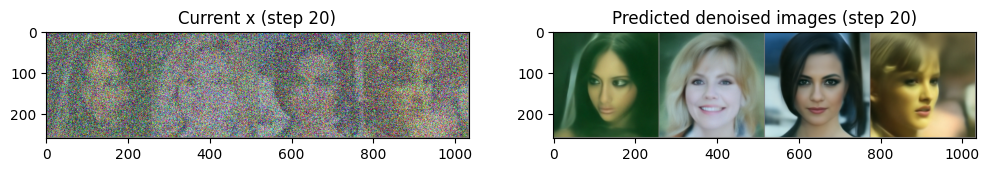
# 랜덤 정규분포 : N(0, 1)
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 256, 256).to(device)
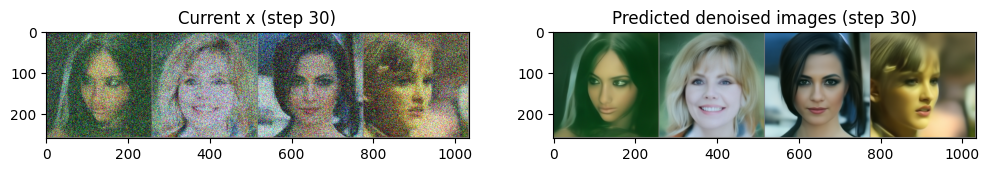
for i, t in tqdm(enumerate(scheduler.timesteps)):
# 이미지 전처리
model_input = scheduler.scale_model_input(x, t)
with torch.no_grad():
noise_pred = image_pipe.unet(model_input, t)["sample"]
scheduler_output = scheduler.step(noise_pred, t, x)
# Update x
x = scheduler_output.prev_sample- 여기서는 x의 값 범위를 (-1, 1)로 본다.
- 초기값으로 randn을 주더라도 크게 영향을 끼치지는 않는다.
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 256, 256).to(device)- scheduler.timesteps는 다음 값들을 가지고 있다.
- 최대 steps를 1000까지 나눌 수 있을 것이다.
scheduler.timestepstensor([975, 950, 925, 900, 875, 850, 825, 800, 775, 750, 725, 700, 675, 650,
625, 600, 575, 550, 525, 500, 475, 450, 425, 400, 375, 350, 325, 300,
275, 250, 225, 200, 175, 150, 125, 100, 75, 50, 25, 0])- U-Net에 t라는 input이 추가되었는데 model_input의 noise 강도를 알려주어 학습 및 예측에 유리하다.
- 이제 output은 denoised된 이미지가 아닌 어떤 노이즈가 씌워졌는지에 대한 output이다.
noise_pred = image_pipe.unet(model_input, t)["sample"]- step과정에서 denoised된 pred_original_sample과
다음 스텝에 넣을 x인 prev_sample가 계산된다. - 다음 스텝 x의 계산식은 이전과 다르지만 t가 0에 가까워질 수록
높은 denoise 비율을 적용한 다음 스텝 x가 계산 된다.
scheduler_output = scheduler.step(noise_pred, t, x)
x = scheduler_output.prev_sample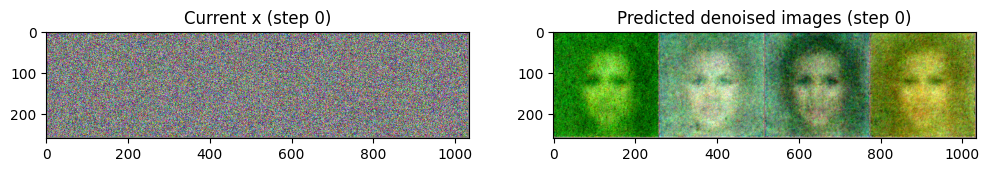
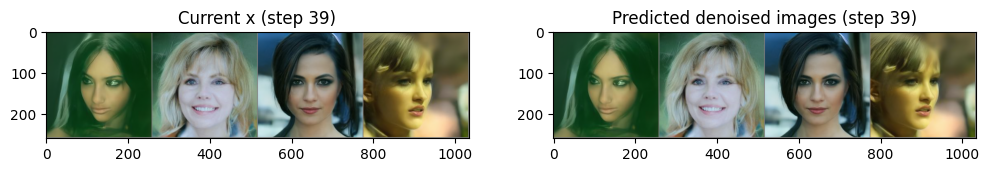
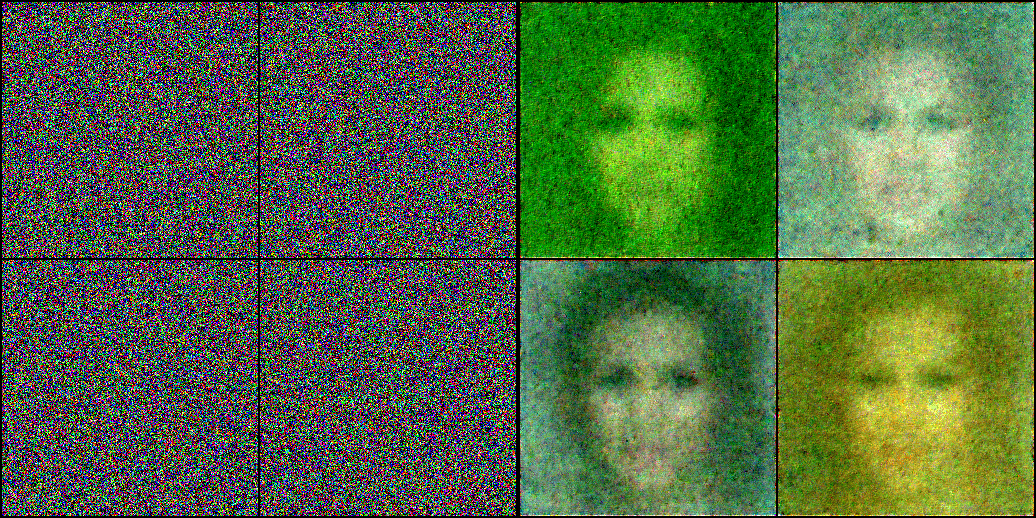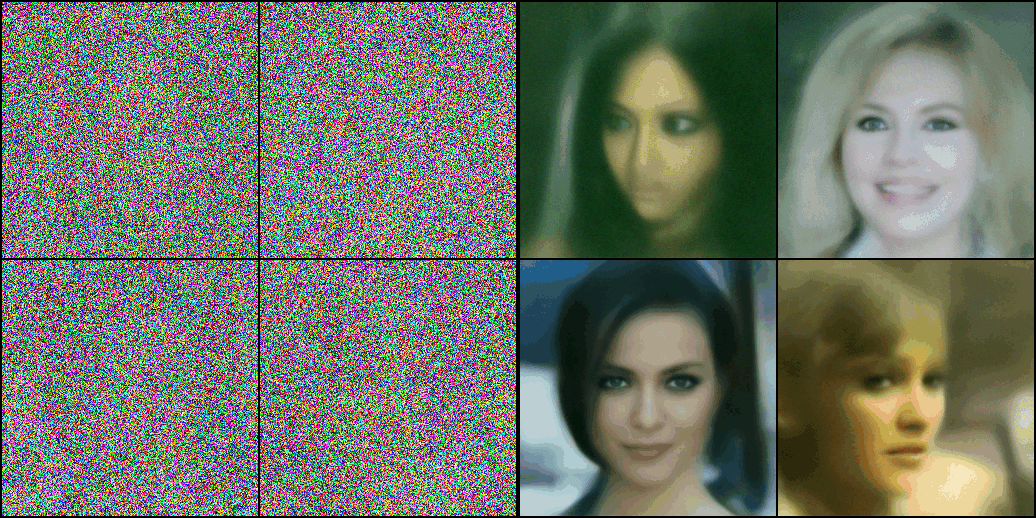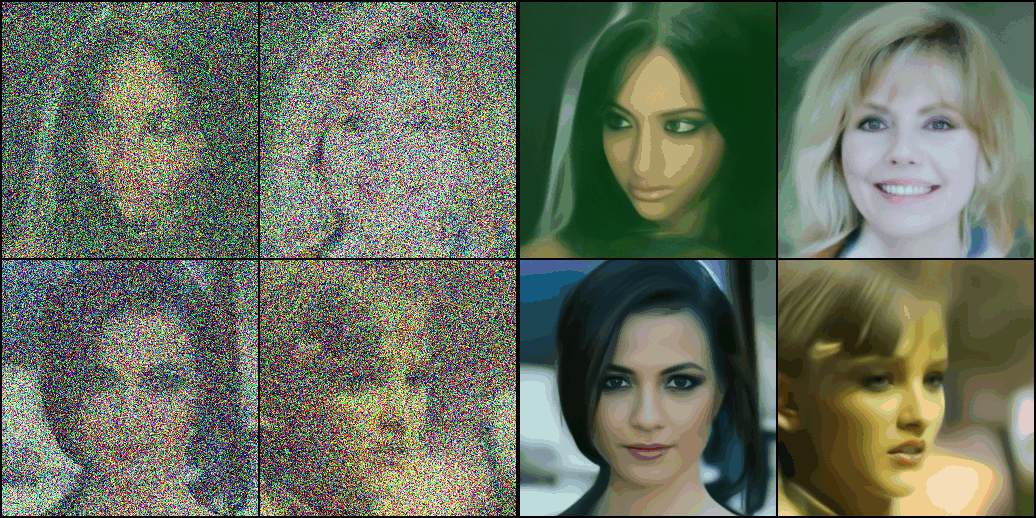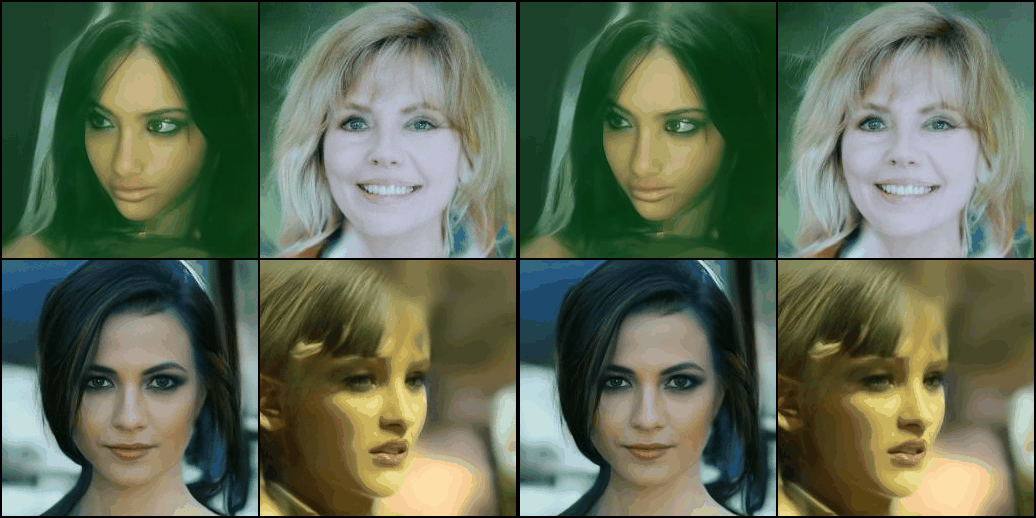
Fine-Tuning
- 아래 데이터셋을 위의 사전학습된 모델에 Fine-Tuning 시켜보자.

- 이번에도 학습 프로세스의 train step 부분만 살펴보고자 한다.
lr : 1e-5
optimizer : AdamW
grad_accumulation_steps : 2clean_images = batch["images"].to(device)
noise = torch.randn(clean_images.shape).to(device)
batch_size = clean_images.shape[0]
max_timestep = image_pipe.scheduler.num_train_timesteps
timesteps = torch.randint(0, max_timestep, (batch_size,), device=device).long()
noisy_images = image_pipe.scheduler.add_noise(clean_images, noise, timesteps)
noise_pred = image_pipe.unet(noisy_images, timesteps, return_dict=False)[0]
loss = F.mse_loss(noise_pred, noise)
loss.backward(loss)
if (step + 1) % grad_accumulation_steps == 0:
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()- 먼저 원본 이미지와 noise 이미지를 준비한다.
clean_images = batch["images"].to(device)
noise = torch.randn(clean_images.shape).to(device)- 무작위 timesteps를 이용하여 무작위 노이즈 비율이 적용된 noisy images를 만든다.
- 수식은 아래 수식이 될 수도 있고 다른 수식이 될 수도 있다.
- x : clean_images
- n : noise
- t : timesteps
- T : max_timestep
- noisy_images : x(1-t/T) + n(t/T)
timesteps = torch.randint(0, max_timestep, (batch_size,), device=device).long()
noisy_images = image_pipe.scheduler.add_noise(clean_images, noise, timesteps)- U-Net 출력은 어떤 노이즈가 씌워졌는지에 대한 예측이므로
MSE loss 함수에는 noise와 noise_pred가 들어간다.
noise_pred = image_pipe.unet(noisy_images, timesteps, return_dict=False)[0]
loss = F.mse_loss(noise_pred, noise)
loss.backward(loss)- 학습 안정성을 이유로 gradients를 몇 회 누적 후 파라미터에 적용한다.
if (step + 1) % grad_accumulation_steps == 0:
optimizer.step()
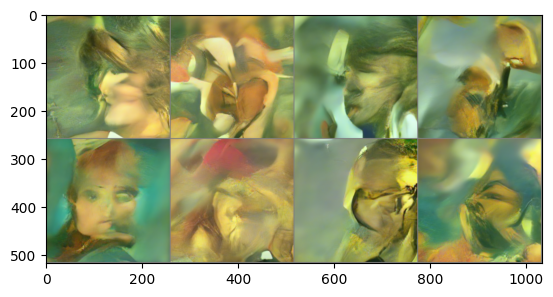
optimizer.zero_grad()- 학습 후 Diffusion 프로세스를 진행하여 이미지를 얻으면 다음과 같다.
- 짧은 epoch 동안만 학습하였기 때문에 괴상한 이미지가 나왔다.
- 더 긴 epoch 동안 학습 시키면 나비 모양을 확인할 수 있을 것이다.