GeoPandas
📌 GeoPandas
: 지리 데이터를 읽을 때 필요한 라이브러리
import geopandas as gpd- GeoPandas 의 자료형은 pandas와 흡사하게 GeoSeries, GeoDataFrame로 나뉜다.
- gpd로 임포트하는 것이 관례이다.
지리데이터의 형식
- shapefile :
- 가장 흔한 지리 데이터 타입
- 점, 다각형 등의 지리정보를 담고 있다.
- 지리정보의 타입은 혼용되지 않는다.
(점과 다각형이 같은 파일에 저장 될 수 없다는 뜻이다.)
- GeoJSON
- KML
- GPKG
Geo 데이터 읽기
- 데이터 읽기
pgd.read_file()- url을 불러와서 데이터 읽기
countries = gpd.read_file(gpd.datasets.get_path('naturalearth_lowres'))
cities = gpd.read_file(gpd.datasets.get_path('naturalearth_cities'))
countries.tail(3)- New York의 지리 데이터를 이용한 예시(Department of Environmental Conservation)
# Read in the data
full_data = gpd.read_file("../input/geospatial-learn-course-data/DEC_lands/DEC_lands/DEC_lands.shp")
# View the first five rows of the data
full_data.head()Pandas와 Geo 데이터
-
Geo 데이터를 가공 및 처리하기 위해서는 pandas 사용에 대해 알아야 한다.
-
데이터 타입
type(full_data)
# geopandas.geodataframe.GeoDataFrame- subset추출 (일부 칼럼만 추출하기)
data = full_data.loc[:, ["CLASS", "COUNTY", "geometry"]].copy()- 칼럼별 데이터 종류의 갯수
# How many lands of each type are there?
data.CLASS.value_counts()WILD FOREST 965
INTENSIVE USE 108
PRIMITIVE 60
WILDERNESS 52
ADMINISTRATIVE 17
UNCLASSIFIED 7
HISTORIC 5
PRIMITIVE BICYCLE CORRIDOR 4
CANOE AREA 1
Name: CLASS, dtype: int64
- 특정 데이터가 있는 데이터셋 추출하기
wild_lands = data.loc[data.CLASS.isin(['WILD FOREST', 'WILDERNESS'])].copy()
wild_lands.head()맵 생성하기
- plot()로 맵 생성하기
wild_lands.plot()Geometry
📌 Geometry
: 모든 geoDataFrame(지리정보를 표현하는 다각형, 선, 점)이 포함되어 있는 데이터이다.
- GeoPandas는 내부적으로 다각형, 선, 점을 Shapely 패키지를 사용하여 처리
- 지리데이터에 대한 정보를 담고 있다.
- geometry칼럼은 plot() 사용시 geometric objects를 보여준다
- head()를 통해 데이터를 간단하게 확인할 수 있다.
# View the first five entries in the "geometry" column
wild_lands.geometry.head()Geometry 타입
- Shapely 패키지를 통해 Geometry 데이터 처리
- 대표적으로 point, linestring, ploygen이 있다
- 각각 지점, 경로, 경계 데이터에 사용할 수 있다.
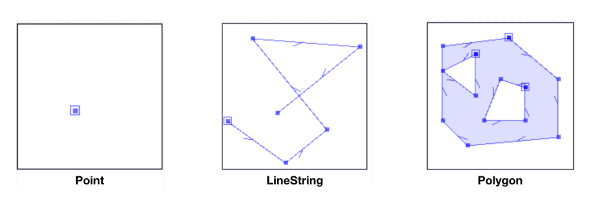
# Campsites in New York state (Point)
POI_data = gpd.read_file("../input/geospatial-learn-course-data/DEC_pointsinterest/DEC_pointsinterest/Decptsofinterest.shp")
campsites = POI_data.loc[POI_data.ASSET=='PRIMITIVE CAMPSITE'].copy()
# Foot trails in New York state (LineString)
roads_trails = gpd.read_file("../input/geospatial-learn-course-data/DEC_roadstrails/DEC_roadstrails/Decroadstrails.shp")
trails = roads_trails.loc[roads_trails.ASSET=='FOOT TRAIL'].copy()
# County boundaries in New York state (Polygon)
counties = gpd.read_file("../input/geospatial-learn-course-data/NY_county_boundaries/NY_county_boundaries/NY_county_boundaries.shp")- 시각화
# Define a base map with county boundaries
ax = counties.plot(figsize=(10,10), color='none', edgecolor='gainsboro', zorder=3)
# Add wild lands, campsites, and foot trails to the base map
wild_lands.plot(color='lightgreen', ax=ax)
campsites.plot(color='maroon', markersize=2, ax=ax)
trails.plot(color='black', markersize=1, ax=ax)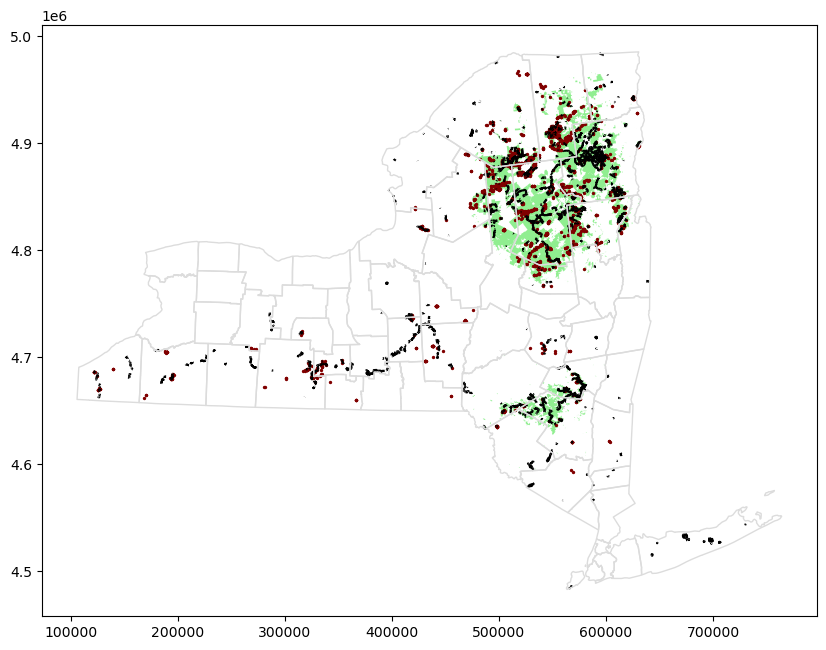
Geometry 데이터의 속성
-
지리정보의 속성 ( 아래의 속성값은 Point 데이터에서는 모두 0이다. )
-
area : 넓이
-
boundary : 테두리
-
centroid : 중앙지점
-
-
두 Geometry 간의 거리를 계산 해주는 함수 또한 유용하게 사용된다.
- distance : 두 점사이의 거리
Geometry 연산
- 관계를 연산한다는 말은, 두 데이터가 교차하는지, 하나가 다른 하나의 내부에 있는지 등을 말한다.
from shapely.geometry import Point, Polygon, LineString
northern_asia = countries.loc[countries['name'].isin(['Korea', 'China', 'Japan'])]
base = northern_asia.plot(figsize=(15, 15), color="w", edgecolor="m")
seoul = cities.loc[cities.name == "Seoul", "geometry"].squeeze()
beijing = cities.loc[cities.name == "Beijing", "geometry"].squeeze()
tokyo = cities.loc[cities.name == "Tokyo", "geometry"].squeeze()
line = LineString([beijing, seoul, tokyo])
ax = gpd.GeoSeries([seoul, beijing, tokyo, line]).plot(ax=base, color="k", edgecolor='k', lw=1)
ax.set_title("동북아시아 지도")
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show()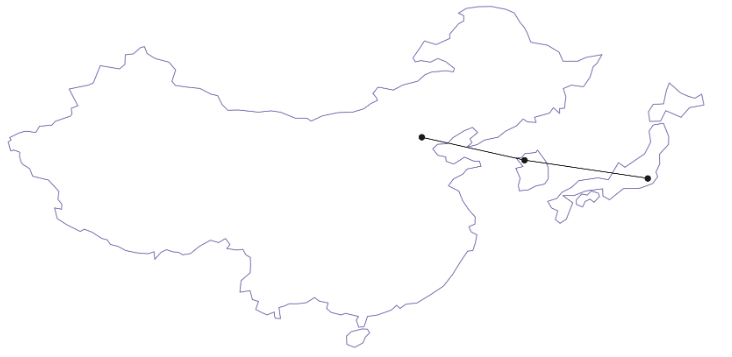
-
기본적인 관계연산함수 (출력은 boolean 값)
- within : 지리적으로 포함되는지 여부
seoul.within(korea)-
contains : 지리적으로 포함하고 있는지 여부
korea.contains(seoul) -
intersects : 지리적으로 교차하는지 여부, 두 지리가 경계선만 닿아있어도, True를 반환
china.intersects(korea) -
crosses : 지리적으로 교차하는지 여부, intersects와 차이점은 crosses는 내부를 지나가야만 True를 반환한다는 것이다.
line.crosses(korea) -
데이터 검색에 사용하기도 한다
countries[countries.crosses(line)]- 속성을 이ㅓ용한 연산
- 거리
seoul.distance(beijing)- 근접
countries[countries.geometry.distance(seoul) <= seoul.distance(beijing)]
참고
kaggle
geo pandas
지리정보 데이터 처리 - 데이터 사이언스 스쿨
