논문 제목: Correlations between Word Vector Sets
"Correlations between Word Vector Sets" 논문은 자연어 처리에서 흔히 사용되는 단어 임베딩(word embeddings)을 이용하여 비지도적 의미론적 텍스트 유사성(unsupervised semantic textual similarity, STS) 작업에 접근하는 방법에 대해 탐구합니다. 주요 내용은 다음과 같습니다:
"Correlations between Word Vector Sets" 논문은 자연어 처리에서 흔히 사용되는 단어 임베딩(word embeddings)을 이용하여 비지도적 의미론적 텍스트 유사성(STS) 작업에 접근하는 방법에 대해 탐구합니다.
- 단어 임베딩 사용: 논문은 간단한 풀링(pooling) 연산과 전통적인 상관 계수(correlation coefficients)를 사용하여 단어 임베딩 간의 유사성을 측정하는 방법을 탐구합니다. 이 방법들은 표준 STS 벤치마크에서 우수한 결과를 보여줍니다.
단어 임베딩은 자연어 이해, 문서 분류, 기계 번역, 감정 분석 등 다양한 NLP 작업에 중요한 역할을 합니다.
단어 임베딩(Word Embedding)은 자연어 처리(Natural Language Processing, NLP) 분야에서 사용되는 기술로, 단어나 구절을 벡터의 형태로 표현하는 방법입니다. 이 벡터는 컴퓨터가 이해할 수 있는 형태로, 단어의 의미, 문맥, 동의어 관계 등을 수치적으로 나타냅니다. 주요 특징과 목적은 다음과 같습니다:
1. 고차원에서 저차원으로의 변환: 전통적으로, 단어는 고차원의 원-핫 벡터(One-Hot Vector)로 표현되었습니다. 원-핫 벡터는 각 단어를 대응하는 위치의 값이 1이고 나머지는 모두 0인 벡터로 표현합니다. 이 방식은 매우 비효율적이며, 단어 간의 의미적 관계를 전혀 표현할 수 없습니다. 단어 임베딩은 이러한 고차원 벡터를 저차원이면서도 정보가 풍부한 벡터로 변환합니다.
2. 단어 간 의미적 관계 표현: 임베딩된 벡터는 단어 간의 의미적 관계를 표현할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, "왕"과 "여왕"이나 "파리"와 "런던" 같은 단어 쌍은 벡터 공간에서 서로 가까운 위치에 있게 됩니다.
3. 효율적인 연산: 저차원의 임베딩 벡터는 기계 학습 모델에서 더 효율적으로 처리될 수 있습니다. 이는 연산 비용을 줄이고, 더 복잡한 언어 모델을 가능하게 합니다.
4. 사전 학습된 임베딩: 많은 단어 임베딩 모델(예: Word2Vec, GloVe, FastText)은 대규모 텍스트 데이터셋을 사용하여 사전에 학습됩니다. 이렇게 사전에 학습된 임베딩 벡터들은 다양한 NLP 작업에 적용될 수 있습니다.
-
Centered Kernel Alignment (CKA)의 새로운 적용: 논문은 CKA를 제곱 코사인 유사도(squared cosine similarity)의 일반화로 소개하며, 이는 단어 벡터 세트 간의 비교를 위한 방법으로 제안됩니다. CKA는 재생 커널 힐베르트 공간(reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces) 간의 상관 연산자를 통해 단어 임베딩 세트를 직접 비교할 수 있게 합니다. 이 방법은 고차원 특징 공간에서 작동하며, 다양한 응용 프로그램에 적합하고 구현이 쉽다는 장점이 있습니다. 또한, 표준 STS 벤치마크에서 기존 방법들보다 더 우수한 성능을 보여줍니다.
-
실제 평가: 논문은 fastText가 훈련된 Common Crawl 데이터를 사용하여 STS 작업 시리즈에 대한 평가를 통해 제안한 방법과 통계적 분석의 효과를 입증합니다. 성공 지표는 사람 평가자가 제공한 문장 유사성 점수와 후보 알고리즘이 생성한 점수 간의 피어슨 상관관계(Pearson correlation)입니다.
FastText
FastText는 컴퓨터가 단어를 이해하고, 그 단어들이 어떻게 서로 연관되어 있는지 배울 수 있게 도와주는 프로그램입니다. 예를 들어, 컴퓨터에게 '사과'와 '바나나'가 둘 다 과일이라는 것을 알려주는 것과 비슷해요. 이 프로그램은 특히 '단어의 조각들'을 사용해서 배웁니다.
Subword (단어의 조각)
'단어의 조각'이란, 큰 단어 안에 있는 작은 단어나 글자들의 조합을 의미해요. 예를 들어, 'apple'이라는 단어는 'ap', 'pp', 'pl', 'le'라는 조각들로 나눌 수 있어요. 이런 식으로 단어를 조각으로 나누면, 컴퓨터는 새로운 단어를 만나도 그 안에 있는 익숙한 조각들을 통해 그 단어를 이해할 수 있어요.
예를 들어, 'happiness'라는 단어는 'hap', 'app', 'pin', 'ine', 'nes', 'ess' 같은 조각들로 나눌 수 있어요. 이런 조각들을 통해 컴퓨터는 'happiness'라는 단어가 'happy'라는 단어와 관련이 있다는 걸 알 수 있죠.Pearson Correlation (피어슨 상관관계)
피어슨 상관관계는 두 가지 것이 얼마나 비슷한지, 즉 서로 얼마나 잘 따라가는지를 수치로 나타내는 방법이에요. 예를 들어, 여러분이 매일 운동하는 시간과 시험 점수 사이의 관계를 살펴볼 수 있어요. 만약 여러분이 많이 운동할수록 시험 점수가 높아진다면, 이 두 가지는 긍정적인 상관관계가 있다고 할 수 있어요.
- 1에 가까울수록: 두 변수는 강한 양의 선형 관계를 가집니다. 하나의 변수가 증가할 때 다른 하나도 증가합니다.
- -1에 가까울수록: 두 변수는 강한 음의 선형 관계를 가집니다. 하나의 변수가 증가할 때 다른 하나는 감소합니다.
- 0에 가까울수록: 두 변수 간에 선형 관계가 없습니다.
논문에서의 적용
논문에서는 FastText를 사용해서 단어들이 서로 어떻게 연관되어 있는지 컴퓨터가 배우게 하고, 이를 통해 문장들이 서로 얼마나 비슷한지를 평가해요. 그리고 이 평가 결과가 사람들이 생각하는 것과 얼마나 비슷한지를 피어슨 상관관계로 확인해요. 이렇게 하면, 컴퓨터가 사람처럼 문장의 유사성을 잘 판단하고 있는지 알 수 있어요.
- 결론: 이 논문은 단어 임베딩에 기반한 유사성 측정 방법, 예를 들어 기본 풀링 연산과 고전적 상관 계수가 표준 STS 벤치마크에서 우수한 결과를 제공한다는 것을 보여줍니다. 이러한 방법들은 최근 제안된 많은 방법들을 능가하면서도 더 빠르고 구현하기 쉽습니다. 논문은 또한 단어 벡터 분포에서의 이상치(outliers)를 처리하는 것의 중요성을 강조하며, 이를 통해 STS 연구의 새로운 기준을 제시합니다.
📕 Summary
Abstract
The paper explores the use of word embeddings for unsupervised semantic textual similarity (STS) tasks, showing that simple pooling operations and classic correlation coefficients can yield excellent results on standard benchmarks.
Additionally, the paper introduces a novel application of centered kernel alignment (CKA) as a generalization of squared cosine similarity for comparing sets of word vectors, which also demonstrates strong empirical results.
Novel application of CKA
The novel application of CKA (Centered Kernel Alignment) is as a natural generalization of squared cosine similarity for sets of word vectors. It allows for the comparison of sets of word embeddings directly via correlation operators between reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces. CKA operates in high-dimensional feature spaces, making it suitable for various applications. It is very easy to implement and has shown strong empirical results in comparing sets of word vectors, outperforming many recently proposed methods on standard semantic textual similarity (STS) benchmarks
📕 Solution
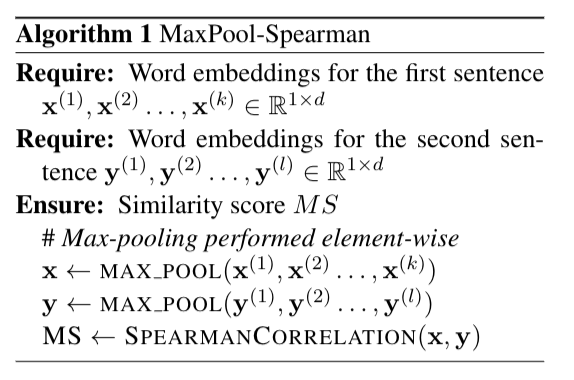
Algorithm 1
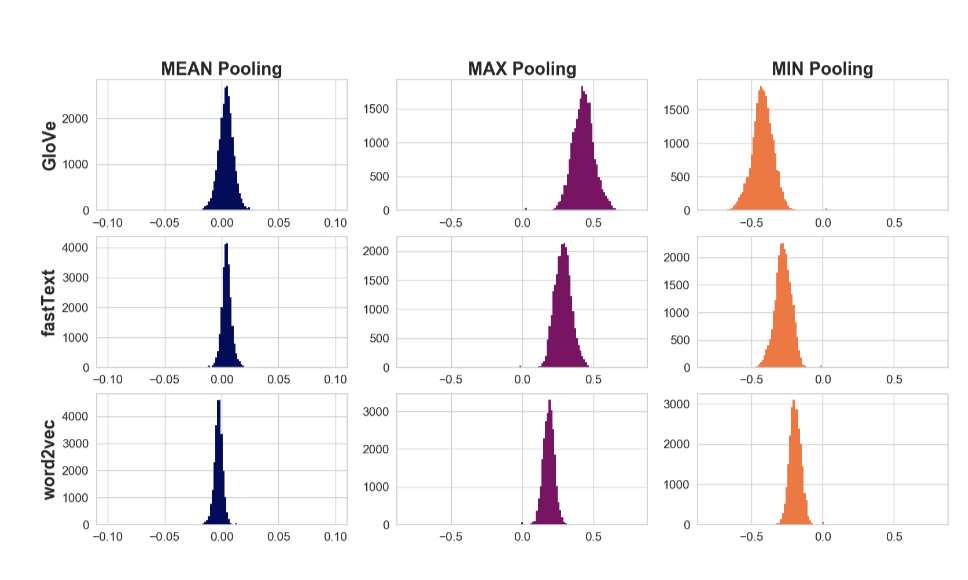
MEAN Pooling vs MAX Pooling VS MIN Pooling
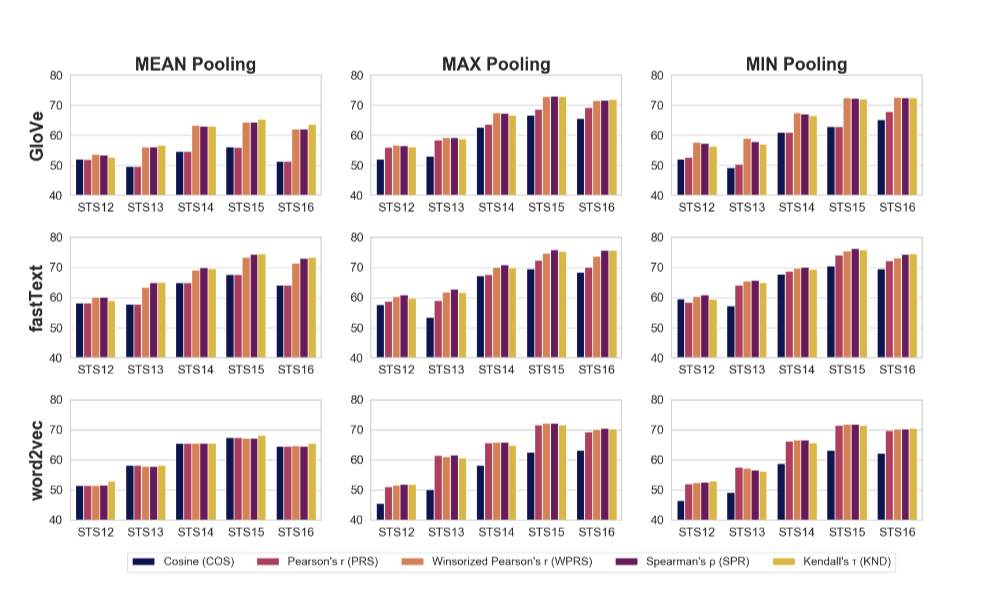
Method
The paper explores the use of elementary pooling operations and classic correlation coefficients to measure similarity between word embeddings, which yields excellent results on standard semantic textual similarity (STS) benchmarks.
The paper also introduces a novel application of centered kernel alignment (CKA) as a natural generalization of squared cosine similarity for comparing sets of word vectors. CKA allows for the comparison of sets of word embeddings directly via correlation operators between reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces. It is easy to implement and has shown strong empirical results.
The authors empirically demonstrate the power of the methods and statistical analysis presented in the paper through evaluations on the Semantic Textual Similarity (STS) tasks series. They use fastText trained on Common Crawl for methods involving pre-trained word embeddings.
The success metric for the STS tasks is the Pearson correlation between the sentence similarity scores provided by human annotators and the scores generated by a candidate algorithm.
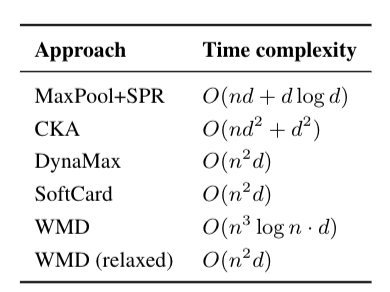
The paper also discusses the computational complexity of the set-based STS methods, including CKA, and compares it to other approaches. While CKA is more computationally expensive than pooling-based approaches, it can provide a performance boost on some tasks.
The proposed methods in the paper serve as strong baselines for future research into STS and are efficient and simple to implement.
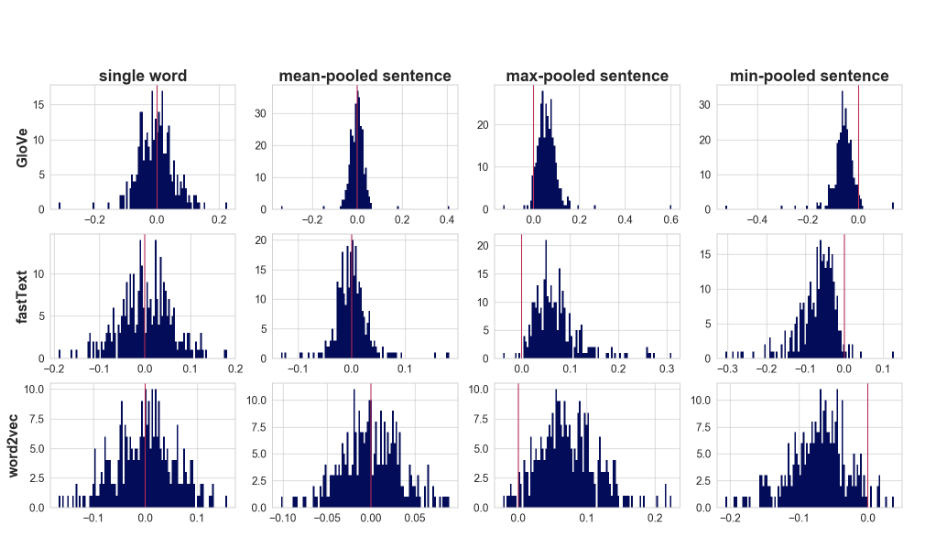
- Histograms for word embeddings of the word “cats” and pooled representations of the embeddings for
the words in the sentence “I like cats because they are very cute animals
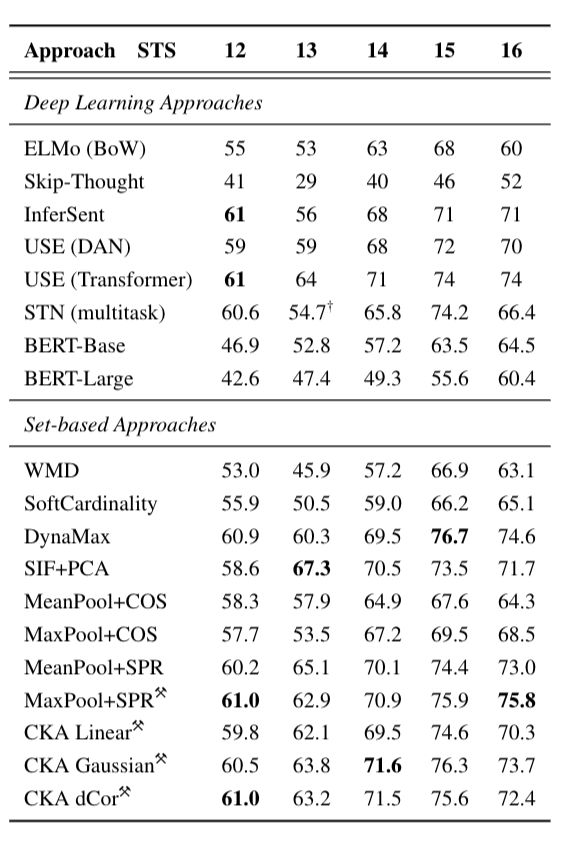
Mean Pearson correlation on STS tasks for
Deep Learning and Set-based methods using fastText
Computational Complexity
📕 Conclusion
The paper demonstrates that similarity measures based purely on word embeddings, such as elementary pooling operations and classic correlation coefficients, yield excellent results on standard semantic textual similarity (STS) benchmarks. These methods outperform many recently proposed methods while being faster and easier to implement .
The authors introduce a novel application of centered kernel alignment (CKA) as a natural generalization of squared cosine similarity for comparing sets of word vectors. CKA shows strong empirical results and is easy to implement
The paper highlights the importance of addressing outliers in word vector distributions, as they can disrupt the performance of set-based similarity metrics. The authors provide methods for solving or avoiding this issue through vector pooling operations, robust correlations, or winsorization .
The findings of the paper are supported by statistical analysis, practical examples, visualizations, and empirical evaluation on standard benchmark datasets. The proposed methods serve as strong baselines for future research into STS and are efficient and simple to implement