객체생성 과정
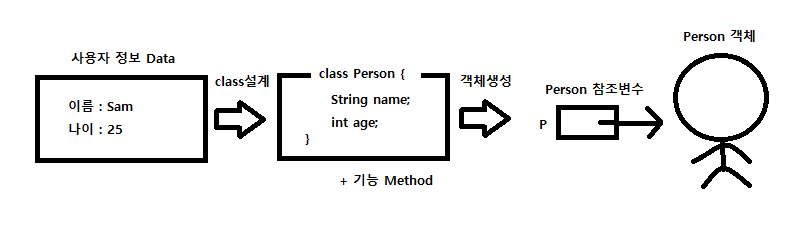
1. 연관있는 것 끼리 묶어 클래스를 설계
2. class에 변수(필드)와 기능(method)를 설계함
3. heap에 new키워드를 사용해 객체를 생성해야 비로소 만들어짐
4 heap영역에 있는 것은 이름을 붙일 수 없음 참조변수를 사용해 만든 객체를 제어함 (객체를 만들면 기본적으로 0에 해당하는 값으로 자동 초기화 된다)
변수 이름 구분
멤버변수 : class 안에 변수 / 0에 해당하는 값
매개변수 : 값을 전달 해 주는 파라미터
지역변수 : 함수 안에 변수 / 쓰레기값
생성자 [Constructor]
- 객체가 생성(new)될 때 딱 한번 자동으로 실행되는 아주 특별한 메소드
- 생성자의 목적은 멤버값의 초기화를 위해서 존재함
생성자 생성 규칙
1. 메소드의 이름은 클래스의 이름과 같다
2. 리턴 타입을 명시하지 않는다
생성자 동작하는 모습
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//객체 생성
First f = new First();// ()가 생성자를 부르고 있는것
//생성자 메소드에 값을 파라미터로 전달해보기
First f3 = new First(10);
}
}
public class First {
//생성자 [Constructor]
First(){
System.out.println("First 생성자!");
}
//생성자 오버로딩
public First(int num) {
System.out.println("num = "+ num);
}
}

객체 생성하면 자동으로 호출되는 걸 볼 수 있다
생성자 메소드는 객체를 생성할 때 마다 발동
생성자 활용
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 초기값 설정해보기
Person p = new Person();
p.show();
//2. 생성하며 초기화
Person p3 = new Person("kim",25);
p3.show();
}
}
public class Person {
//멤버변수는 private 접근제한 권장
private String name; //기본값 : null
private int age; //기본값 : 0
//멤버함수는 public 접근제한자 권장
public void show() {
System.out.println("이름 : "+ name);
System.out.println("나이 : "+ age);
System.out.println();
}
public void set(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {
System.out.println("Person 객체 생성~");
//1. 멤버변수에 전달할 값이 없을때의 초기값 설정
name = "익명";
age = 0;
}
//2. 생성자 오버로딩
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//오버로딩은 개수제한이 없기 때문에 몇개라도 추가로 만둘 수 있다
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
age = 0;
}
public Person(int age) {
this.name = "익명";
this.age = age;
}
}
this
자신의 주솟값을 가르키는 키워드 this!
- 클래스의 멤버를 거리킬 때
- 생성자를 호출할 때
- 자신의 주솟값을 전달 할 때 사용
- this 생략 가능 : this는 본인 안에서 식별이 안될 때 씀
클래스 멤버를 가리킬때
- 생성자 내에서 매개변수와 멤버변수를 구분하기 위해 this를 쓴다
-> this. 이 붙은 것이 멤버변수를 가르키는것
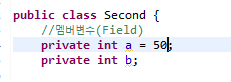
public class Second {
//멤버변수(Field)
private int a;
private int b;
//멤버변수를 초기화하는 생성자메소드
public Second(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
}this() 생성자 호출 문법
- 생성자에서 자신의 다른 생성자를 호출할 때 쓰는 문법
- 멤버변수가 많을 때 값대입(초기화)을 매번하기 번거로워서 사용하는 문법
- 멤버변수를 전부 부르는 생성자 하나를 만들고 그 생성자를 this()로 호출해 값을 전달함
- this() 생성자 호출은 생성자 내에서 반드시 첫번째 줄에 써야함
public class Second {
//멤버변수(Field)
private int a;
private int b;
//멤버변수를 초기화하는 생성자메소드
public Second(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
System.out.println("세컨드 호출");
}
public Second() {
this(0,0);
}
public Second(int a) {
this(a,0);
System.out.println("");
}
}

this()를 사용함으로써 다른 생성자에서 위임함을 볼 수 있다
자바에서 초기화 하는 4단계
- 기본값 초기화 (0에 해당하는 값으로)
- 명시적 초기화
=> class를 설계할 때 초기화
- 초기화를 위한 block
블럭 사용 이유 -> 실행문을 쓸수 있음, class에는 method와 필드만 쓸수 있는데 블럭을 사용함으로써 연산이 가능
3-1) 인스턴스 초기화 블럭
3-2) static 초기화 블럭 - 생성자
생성자 또한 {} 가 있기 때문에 프로그래밍적 초기화 가능
초기화 블럭이 있어도 만든 이유 : 파라미터를 받을 수 있는 장점이 있음
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//초기화 4단계
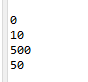
//1.
InitialTest obj = new InitialTest();
System.out.println(obj.a);
//2.
System.out.println(obj.b);
//3.
System.out.println(obj.c);
//4.
System.out.println(obj.d);
}
}
public class InitialTest {
//1. 기본값 초기화 - 0에 해당하는 값
int a;
//2. 명시적 초기화
int b = 10;
//3. 초기화 블럭
int c=0;
{//인스턴스 초기화 블럭
c = 20;
c++;
if(c > 19) c = 500;
}
//4. 생성자 초기화
int d;
public InitialTest() {
d=50;
}
}