Array
- 리스트 형태의 고수준 객체인 배열을 생성할 때 사용하는 전역 객체이다.
- 배열을 구성하는 각각의 값을 배열요소(element)라고 하며, 배열에서의 위치를 가리키는 숫자를 인덱스(index)라고 한다.
✅ 자주 사용하는 배열 함수들.
1. join()
- 배열의 모든 요소를 연결해 하나의 문자열로 만들어 준다.
- array.join([separator])
- array.length 가 0 이라면, 빈 문자열을 반환한다.
{
const fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"];
console.log(fruits.join());
console.log(fruits.join(""));
console.log(fruits.join("-"));
}
✔︎ 결과값

2. split()
- String 객체를 지정한 구분자를 이용하여 여러개의 문자열로 나누어준다.
- str.split([separator[, limit]])
- limit : 끊어진 문자열의 최대 개수를 나타내는 정수.
{
const str = "Hello this is Tinubee's blog";
console.log(str.split(" "));
}✔︎ 결과값

3. forEach()
- 주어진 함수를 배열 요소 각각에 대해 실행한다.
- arr.forEach(callback(currentValue[, index[, array]])[, thisArg]
- callback : 요소에 대해 실행할 함수.
- currentValue : 처리할 현재 요소.
- index : 처리할 현재 요소의 인덱스. ( Optional )
- array : forEach()를 호출한 배열. ( Optional )
- thisArg : callback을 실행할 때 this로 사용할 값. ( Optional )
{
const items = ["item1", "item2", "item3"];
const copy = [];
items.forEach((item) => copy.push(item));
console.log(copy);
}✔︎ 결과값

4. slice()
- 어떤 배열의 begin부터 end까지(end 미포함) 에 대한 얕은 복사본을 새로운 배열 객체로 반환한다. ( ✔︎ 원본 배열은 바뀌지 않는다.)
- arr.slice([begin[, end]])
{ const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; const sliceArray = array.slice(1, 3); console.log("array : " + array); console.log("slice array : " + sliceArray); }
✔︎ 결과값

5. find()
- 주어진 판별 함수를 만족하는 첫 번째 요소의 값을 반환한다. 요소가 없다면 undefined 를 반환한다.
- arr.find(callback[, thisArg])
- callback : 배열의 각 값에 대해 실행할 함수. 3개의 인자를 받는다.
- element : callback 함수에서 처리할 현재 요소.
- index : callback 함수에서 처리할 현재 요소의 인덱스.
- array : find 함수를 호출한 배열.
- thisArg : callback이 호출될 때, this로 사용할 객체.
class Number {
constructor(name, num) {
this.name = name;
this.num = num;
}
}
const numbers = [
new Number("one", 1),
new Number("two", 2),
new Number("three", 3),
new Number("four", 4),
new Number("five", 5),
];
{
const findNumber = numbers.find((element) => element.num == 3);
console.log(findNumber);
}✔︎ 결과값

6. filter()
- 주어진 함수의 테스트를 통과하는 모든 요소를 모아 새로운 배열로 반환한다.
- arr.filter(callback(element[, index[, array]])[, thisArg]
- 어떤 요소도 테스트를 통과하지 못했으면 빈배열을 반환한다.
class Number {
constructor(name, num) {
this.name = name;
this.num = num;
}
}
const numbers = [
new Number("one", 1),
new Number("two", 2),
new Number("three", 3),
new Number("four", 4),
new Number("five", 5),
];
{
const filterNumber = numbers.filter((element) => element.num > 3);
console.log(filterNumber);
}✔︎ 결과값

7. map()
- 배열 내의 모든 요소 각각에 대하여 주어진 함수를 호출한 결과를 모아 새로운 배열을 반환한다.
- arr.map(callback(currentValue[, index[, array]])[, thisArg]
class Number {
constructor(name, num) {
this.name = name;
this.num = num;
}
}
const numbers = [
new Number("one", 1),
new Number("two", 2),
new Number("three", 3),
new Number("four", 4),
new Number("five", 5),
];
{
const mapNumber = numbers.map((items) => items.num + items.num);
console.log(mapNumber);
}✔︎ 결과값

8. some()
- 배열 안의 어떤 요소라도 주어진 판별 함수를 통과하는지 테스트 한다. ( 빈 배열에서 호출하면 무조건 false를 반환한다.)
- arr.some(callback[, thisArg])
class Number {
constructor(name, num) {
this.name = name;
this.num = num;
}
}
const numbers = [
new Number("one", 1),
new Number("two", 2),
new Number("three", 3),
new Number("four", 4),
new Number("five", 5),
];
{
const someNumber = numbers.some((items) => items.num > 5);
const someNumber2 = numbers.some((items) => items.num > 3);
console.log(someNumber);
console.log(someNumber2);
}✔︎ 결과값

9. reduce()
- 배열의 각 요소에 대해 주어진 reducer 함수를 실행하고, 하나의 결과값을 반환한다.
- arr.reduce(callback[, initialValue])
class Number {
constructor(name, num) {
this.name = name;
this.num = num;
}
}
const numbers = [
new Number("one", 1),
new Number("two", 2),
new Number("three", 3),
new Number("four", 4),
];
{
const reduceNumber = numbers.reduce((acc, value) => acc + value.num, 0);
console.log(reduceNumber);
}✔︎ 결과값

ℹ️ 동작과정
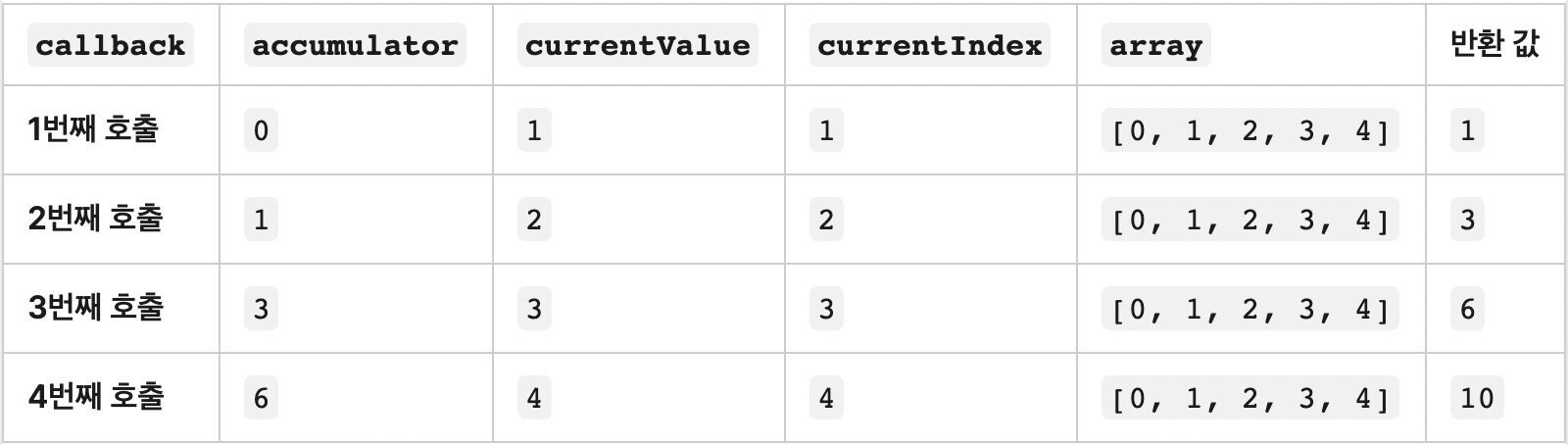
10. sort()
- 배열의 요소를 적절한 위치에 정렬한 후 그 배열을 반환한다.
- 정렬은 stable sort가 아닐 수 있다.
- 기본 정렬 순서는 문자열의 유니코드 코드 포인트를 따른다.
- arr.sort([compareFunction])
{
const array = [18, 2, 13, 4, 9, 1, 48, 120, 45, 67, 89, 100];
const sortedArray = array.sort((a, b) => a - b);
console.log(sortedArray);
}✔︎ 결과값

✅ 음수의 값을 return 하게 되면 첫번째 값이 두번째 값보다 작다고 판단하여 정렬을 시킨다.
