■ Python
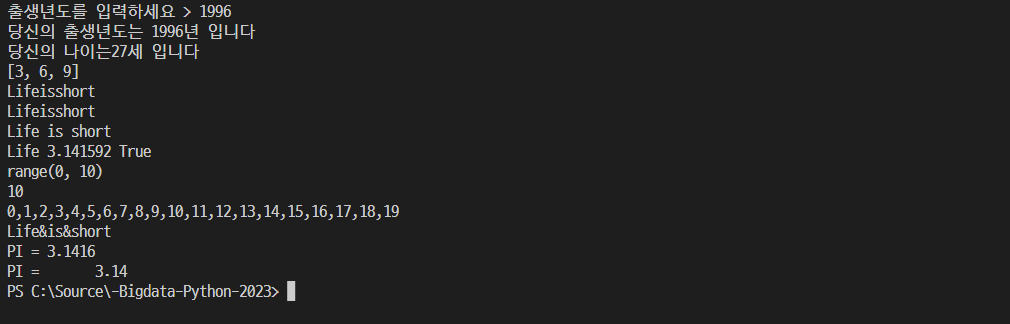
01. 입출력
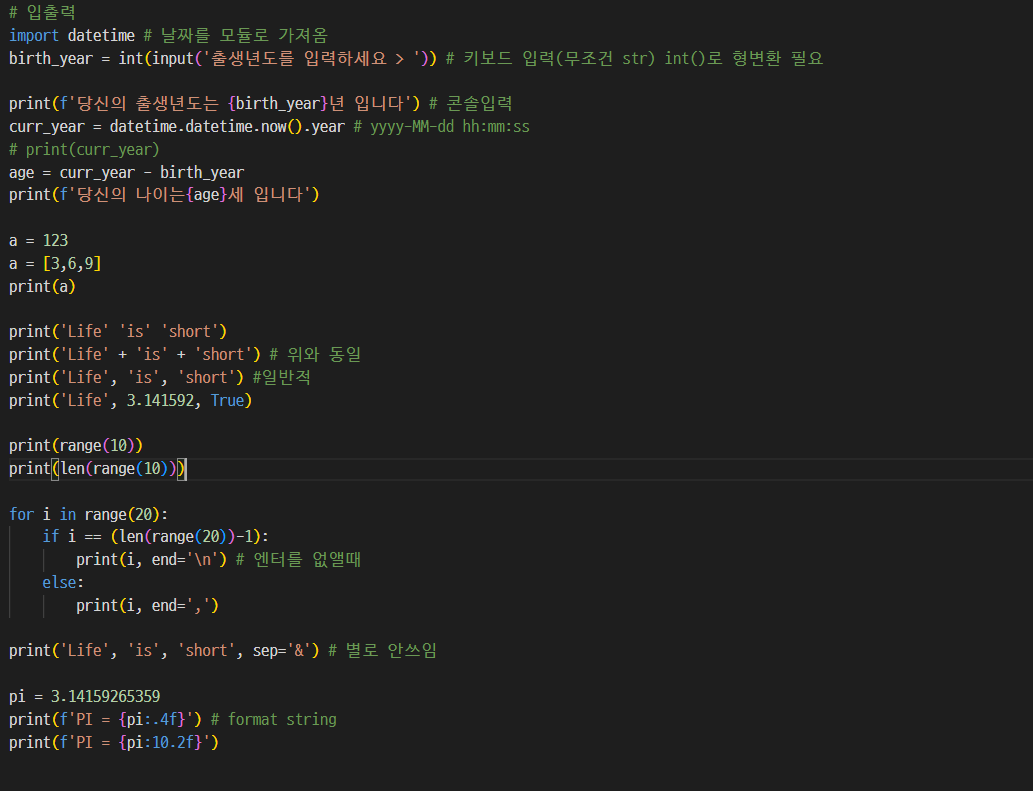
- 결과값
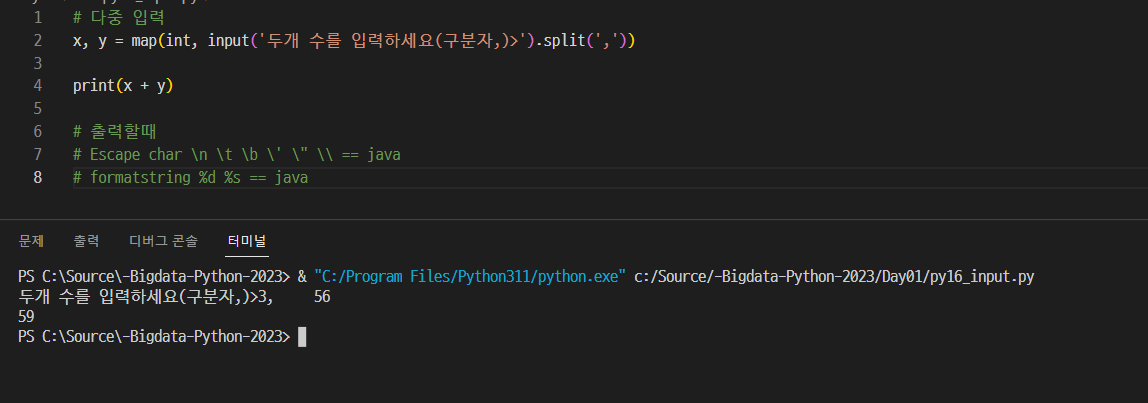
02. 다중입력
03. 파일 입출력, 파일 읽기
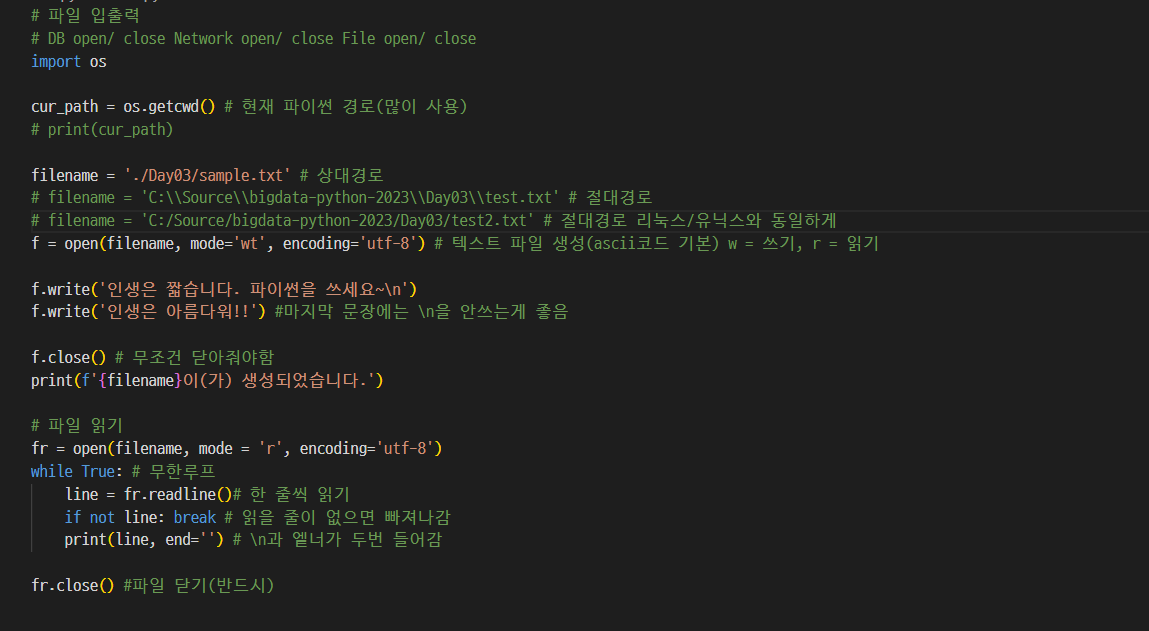
- 결과값
04. csv 파일 일기
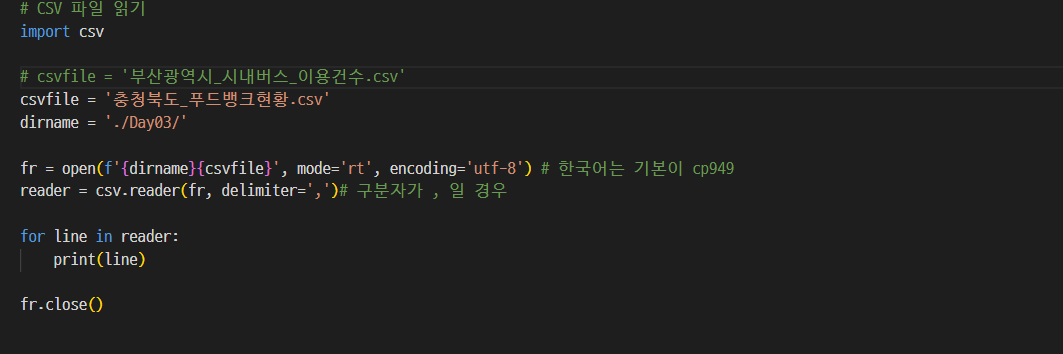
- 결과값

■ 연습문제
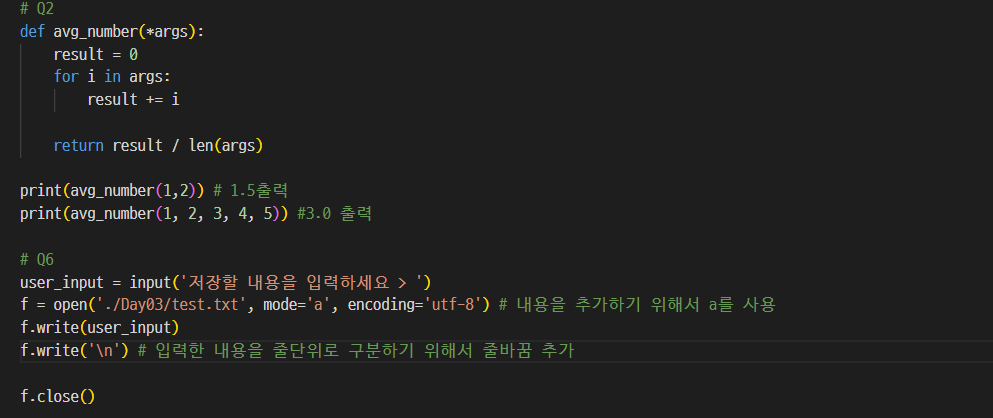
- 결과값
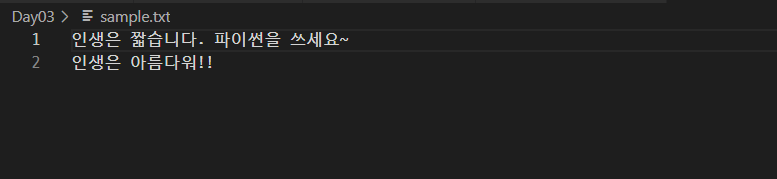
05. 클레스, 묘듈사용
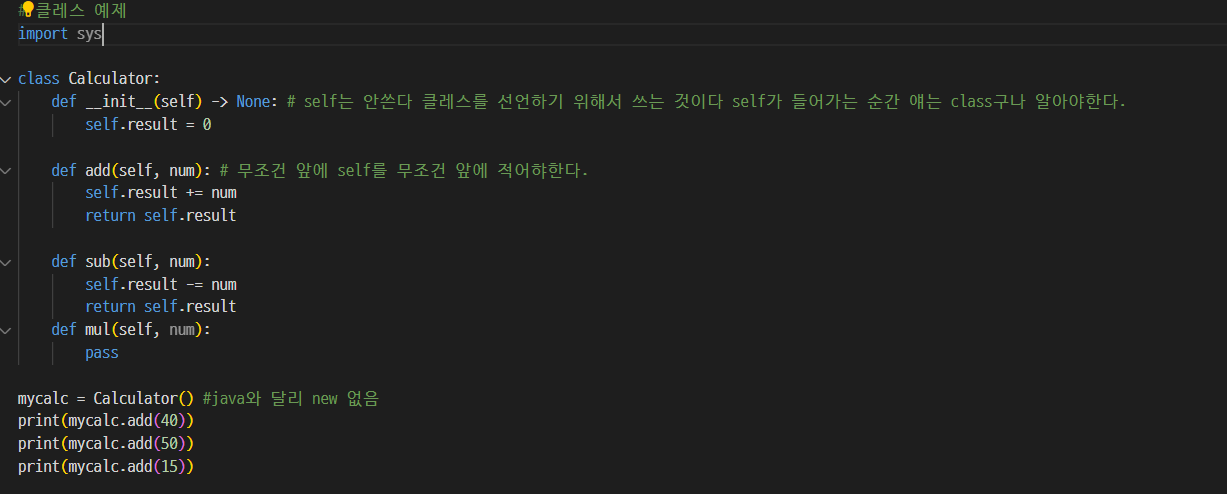
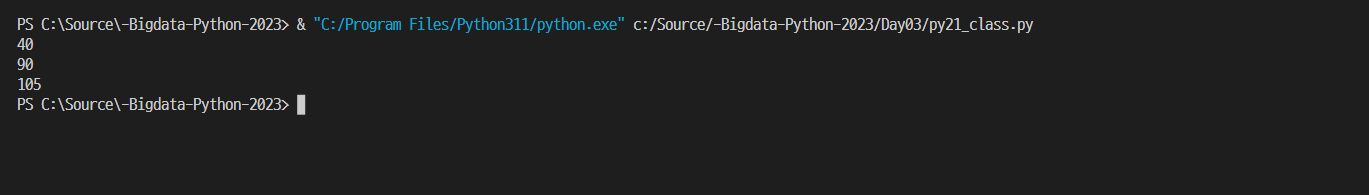
- 결과
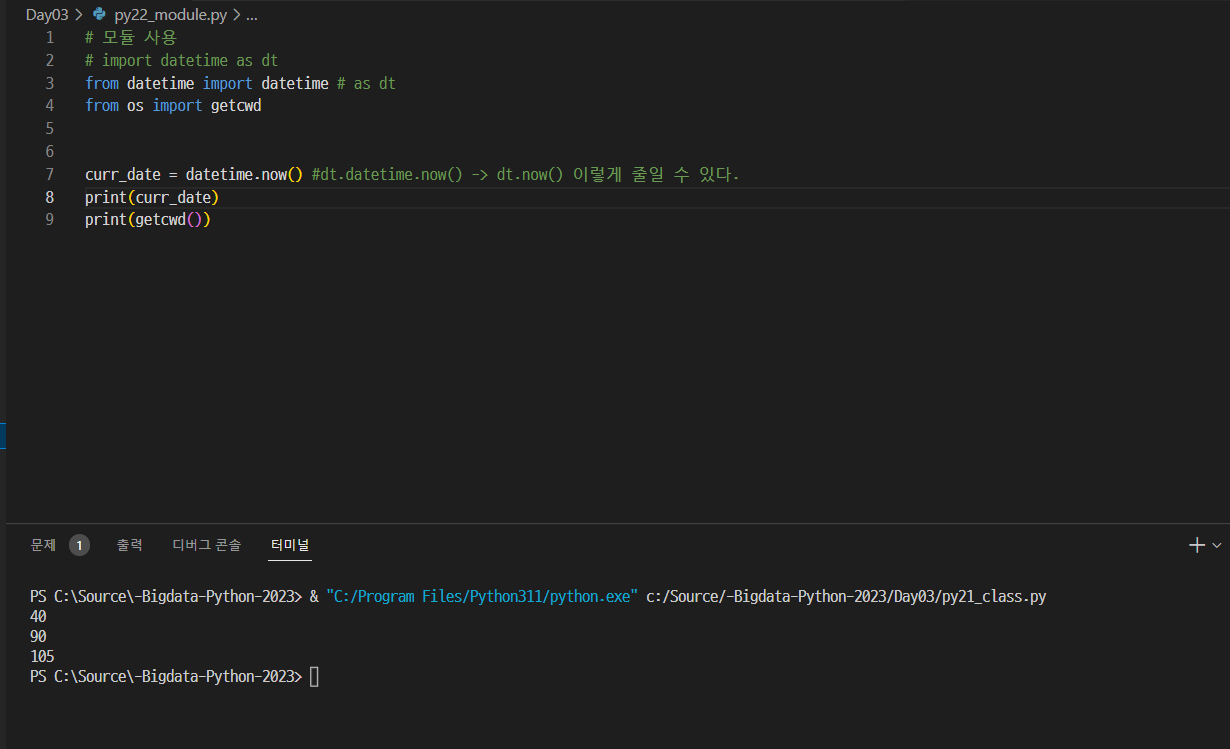
묘듈
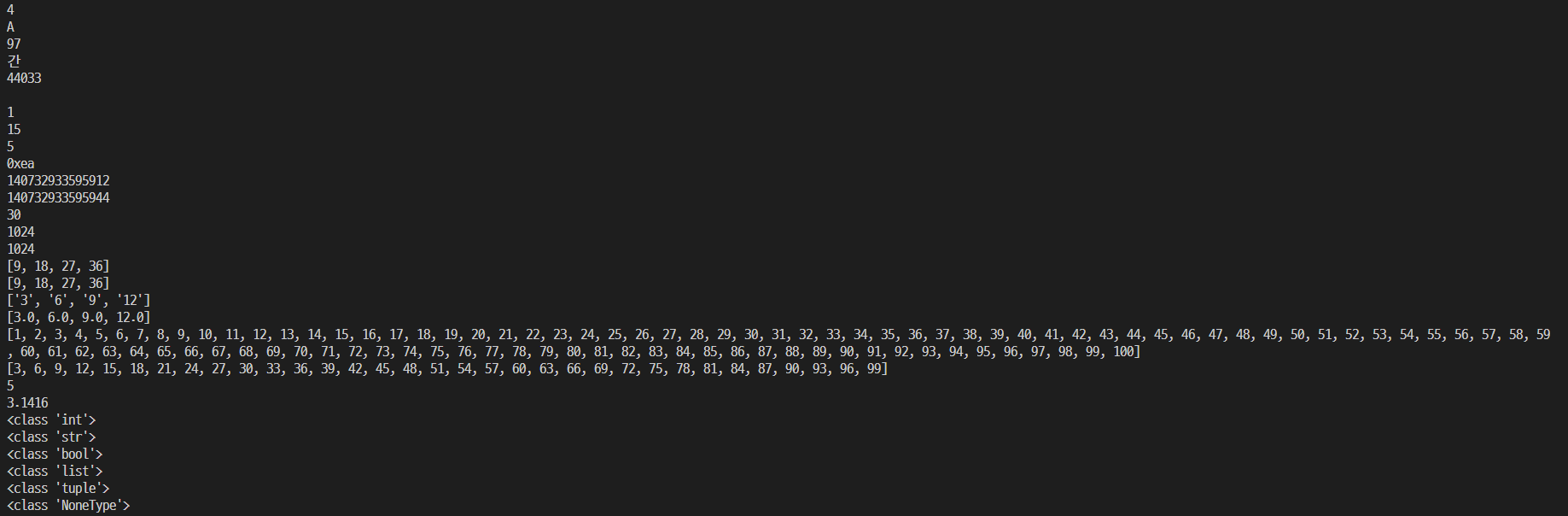
06. 내장함수
print(abs(-4))
print(chr(65))
print(ord('a'))
print(chr(44036))
print(ord('각'))
print(chr(13))
print(min(1,4))
print(max(15,2))
print(eval('1 + 4'))
print(hex(234))
a = 0
b = 1
print(id(a))
print(id(b))
print(int('30'))
print(pow(2,10))
print(2 ** 10)
def three_times(numberlist):
result = []
for n in numberlist:
result.append(n * 3)
return result
l1 =[3, 6, 9, 12]
print(three_times(l1))
def threetimes(x):
return x * 3
print(list(map(threetimes,l1)))
print(list(map(str,l1)))
print(list(map(float,l1)))
print(list(range(1,101)))
print(list(range(3, 100, 3)))
print(round(4.6))
print(round(3.141592,4))
l1.sort()
sorted(l1)
print(type(21))
print(type('21'))
print(type(True))
print(type([1,2,3]))
print(type((1,2,3)))
print(type(None))
- 결과값