배열
- 실제 게임의 경우 플레이어나 몬스터가 한 필드에서 하나만 존재하지 않기 때문에 배열이 필요하다
- 일종의 바구니 역할
- 배열 또한 형태를 설정해야 한다.
- int[] array = new int[5]; 형태로 배열을 생성하고 배열 크기는 결정되면 변경할 수 없다.
using System;
namespace CSarp
{
class Progrma
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] scores = new int[5];
scores[0] = 10;
scores[1] = 20;
scores[2] = 30;
scores[3] = 40;
scores[4] = 50;
for (int i = 0; i < scores.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(scores[i]);
}
}
}
}-
하나의 변수로 다양한 변수를 다룰 수 있다.
-
foreach문을 활용할 수도 있다.
-
배열 하나씩 순회해 가며 변수들을 탐색할 수 있다.
using System;
namespace CSarp
{
class Progrma
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] scores = new int[5] { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
for (int i = 0; i < scores.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(scores[i]);
}
foreach (int score in scores)
{
Console.WriteLine(score);
}
}
}
}- 직접 인덱스에 접근하여 입력해도 되고 배열 크기에 맞게 데이터를 넣어도 된다.
using System;
namespace CSarp
{
class Progrma
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] scores = new int[] { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
for (int i = 0; i < scores.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(scores[i]);
}
foreach (int score in scores)
{
Console.WriteLine(score);
}
}
}
}- 동적으로 할당될 수 있다. (참조 타입)
다차원 배열
-
다층 구조 건물 같은 개념
-
층 / 호실을 표시하는 느낌
-
상하좌우 움직임을 맵 타일을 2차원 배열로 표현하여 이동시키면 편함
using System;
namespace CSarp
{
class Progrma
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] scores = new int[5] { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
int[,] arr = new int[2, 3] { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i ++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(arr[i, j]);
}
}
}
}}
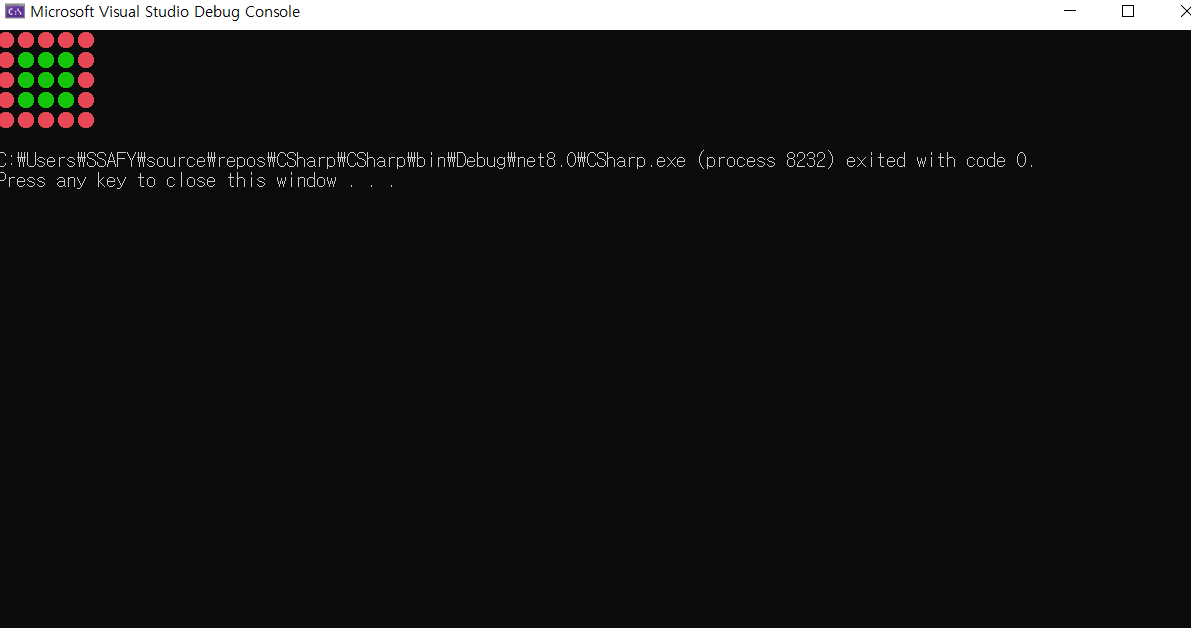
- 1이 적힌 곳은 못가고 0이 적힌 곳만 이동할 수 있는 맵 간단하게 구현
```C#
using System;
namespace CSarp
{
class Map
{
int[,] tiles = {
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
};
public void Render()
{
ConsoleColor defaultColor = Console.ForegroundColor;
for (int y = 0; y < tiles.GetLength(1); y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < tiles.GetLength(0); x++)
{
if (tiles[x, y] == 1)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
}
else
{
Console.ForegroundColor= ConsoleColor.Green;
}
Console.Write("\u25cf");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.ForegroundColor = defaultColor;
}
}
class Progrma
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Map map = new Map();
map.Render();
}
}
}
List
- 배열은 크기가 고정된다는 한계점이 있음
- 배열의 크기를 크게 만들 수도 있지만 메모리 낭비의 가능성이 있음
- 동적 배열인 List를 활용하는 방안이 있다.
- using System.Collections.Generic; 을 통해 사용
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace CSarp
{
class Progrma
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> list = new List<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
list.Add(i);
Console.WriteLine(list[i]);
}
}
}
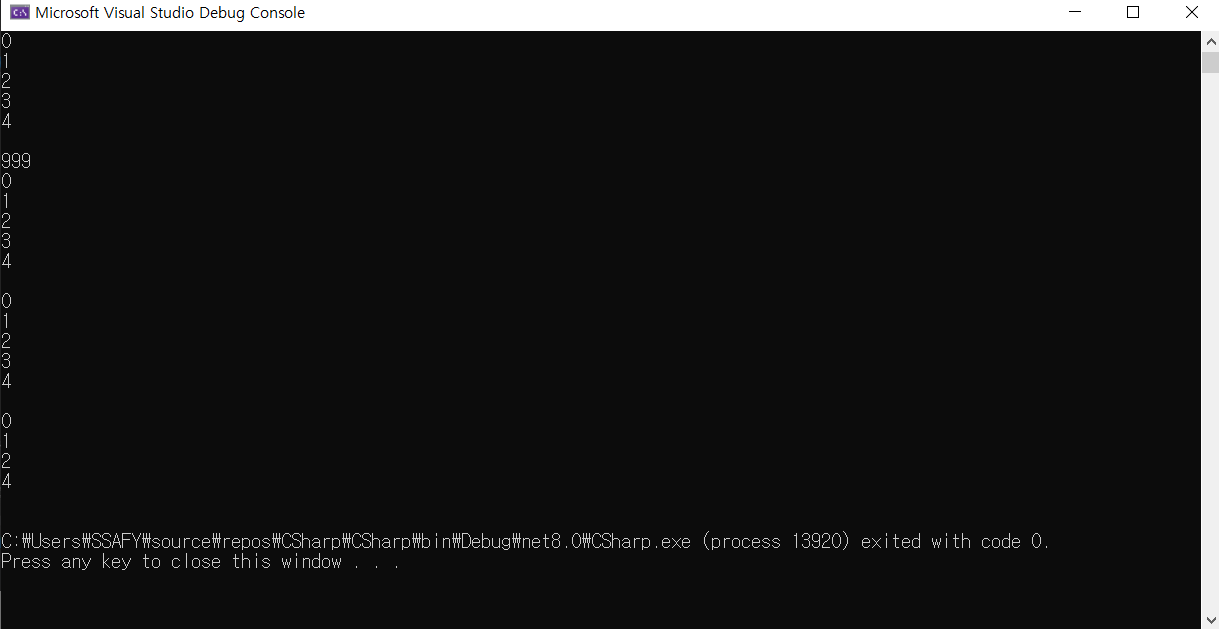
}- 삽입은 Insert / list의 크기는 Count로 측정 가능
- 제거는 Remove 등을 사용 가능
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace CSarp
{
class Progrma
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> list = new List<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
list.Add(i);
Console.WriteLine(list[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine();
// 삽입
list.Insert(0, 999);
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(list[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine();
// 값 삭제
list.Remove(999);
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(list[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine();
// 인덱스 접근 삭제
list.RemoveAt(3);
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(list[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine();
// 전체 삭제
list.Clear();
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(list[i]);
}
}
}
}
- 단, 중간에 값을 수정하거나 추가하는 건 메모리, 시간 복잡도 등의 이유로 비효율적이다.
Dictionary
- 리스트로만 데이터를 관리할 경우 특정 자료를 찾는 것은 어렵다
- Key Value 값을 가진 Dictionary를 통해서 관리 가능
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace CSarp
{
class Monster
{
public int id;
private int i;
public Monster(int i)
{
this.i = i;
}
}
class Progrma
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Dictionary<int, Monster> dic = new Dictionary<int, Monster>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
dic.Add(i, new Monster(i));
}
Monster mon;
bool found = dic.TryGetValue(7777, out mon);
dic.Remove(7777);
dic.Clear();
}
}
}- HashTable 기법으로 이루어진 dictionary
