🔔기하1 - 어린 왕자
흥미로웠던 문제...어려워보이지만 생각보다 간단하다.
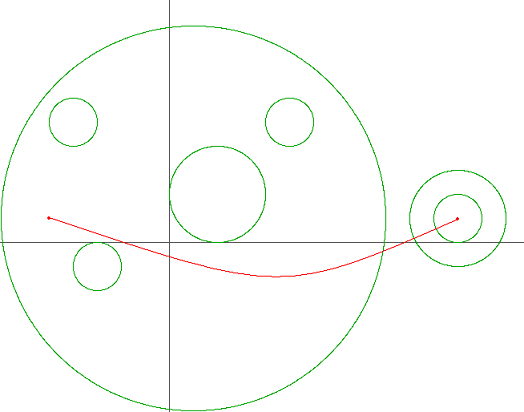
행성의 최소 진입,이탈 횟수를 구해야한다.
즉 출발점에서 도착점을 잇는 빨간 선이 원의 경계에 최소로 닿아야한다.
그림을 보면, 원이 여러 개가 있지만 출발점에서 출발할 때 출발점이 속한 큰 원 하나만 뚫고 나가면 된다.
마찬가지로, 도착점으로 도착할 때 도착점이 속한 원 2개를 뚫고 들어가야한다.
- 원의 방정식을 이용하여 출발점이 속한 원의 개수와 도착점이 속한 원의 개수를 구해야한다.
(x - a)² + (y - b)² <= r²
이때, 단순히 출발점과 도착점이 원에 속한다고 무조건 세면 안된다. 항상 반례가 있는지를 살펴야한다.
- 하나의 원 안에 출발점과 도착점이 동시에 속하면 세지 않는다.
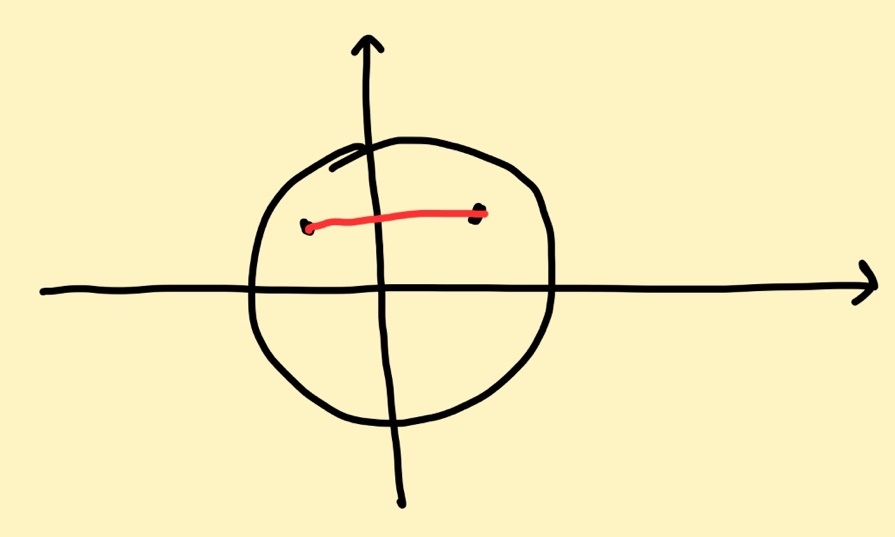
그림과 같이 한 원안에 출발점과 도착점이 동시에 있으면 최소 진입,이탈 횟수는 0이되므로 세면 안된다. 이 점을 유의해야한다.
🔑 java 풀이
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int T = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int start[] = new int[2];//출발점 입력
int end[] = new int[2];//도착점 입력
int circle[]=new int[3];//원 입력
for(int i=0; i<T; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
start[0]=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());//출발 x
start[1]=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());//출발 y
end[0]=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());//도착 x
end[1]=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());//도착 y
int n=Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int cnt=0;//최소의 행성계 진입,이탈 횟수
for(int j=0; j<n; j++) {
boolean startPoint=false;
boolean endPoint=false;
st=new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
circle[0]=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());//원 중심 x
circle[1]=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());//원 중심 y
circle[2]=Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());//원의 반지름
//(x-a)^2 + (y-b)^2 <= r^2
//출발점, 도착점이 행성계(원) 안에 있는지를 판단함
if(Math.pow(start[0]-circle[0], 2)+Math.pow(start[1]-circle[1], 2)<=Math.pow(circle[2], 2)) {
startPoint=true;
cnt++;
}
if(Math.pow(end[0]-circle[0], 2)+Math.pow(end[1]-circle[1], 2)<=Math.pow(circle[2], 2)) {
endPoint=true;
cnt++;
}
//한 원안에 출발점,도착점이 동시에 속하면 cnt증가를 취소함
if(startPoint==true && endPoint==true)
cnt-=2;
}
sb.append(cnt+"\n");
}
System.out.print(sb);
br.close();
}
}