Heap을 들어가기 전, 우선순위 큐를 알고 있어야 이해하기가 쉽다.
우선순위 큐 는 FIFO의 특징을 가지고 있는 일반적인 큐와 달리 우선 순위가 높은 요소가 먼저 나가는 큐다. 주의할 점은 우선순위 큐는 자료구조가 아닌 개념이라는 것이다.
우선순위 큐를 구현하는 방법은 다양한데, 그 중 heap 은 우선순위를 구현하기 가장 적합한 방법이다.
많은 사람들이 헷갈리는 부분이 우선순위와 큐가 같다고 생각하는 것인데 실제로는 다르다. 만약 배열은 매번 우선순위에 따라 정렬한다면, 우선순위 큐가 될 수있지만 힙보다 효율이 떨어진다.
힙(Heap)이란?
힙(Heap)은 이진 트리 형태를 가지며 우선순위가 높은 요소가 먼저 나가기 위해 요소가 삽입, 삭제 될 때 바로 정렬되는 특징이 있다.
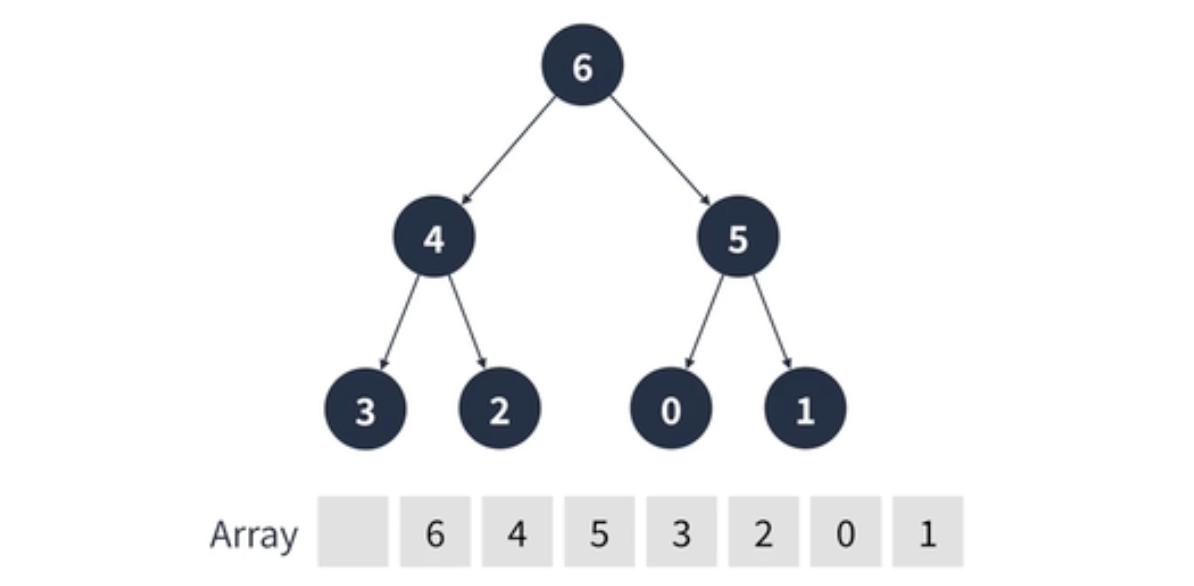
힙의 특징
- 우선순위가 높인 요소가 먼저 나가는 특징을 가진다.
- 루트가 가장 큰 값이 되는
최대 힙(Max Heap)과 루트가 가장 작은 값이 되는최소 힙(Min Heap)이 있다. - 다른 언어와 다르게 자바스크립트는 직접 구현해서 사용해야한다는 단점이 있다.
힙의 동작
힙의 동작은 추가/삭제 요소가 핵심이다.
Heap 요소 추가 알고리즘
- 요소가 추가될 때는 트리의 가장 마지막 정점에 위치한다.
- 추가 후 부모 정점보다 우선순위가 높다면, 부모 정점과 순서를 바꾼다.
- 이 과정을 반복하면 결국 가장 우선순위가 높은 정점이 루트가 된다.
- 완전 이진 트리의 높이는 이기에 힙의 요소 추가 알고리즘은 시간복잡도를 가진다.
Heap 요소 제거 알고리즘
- 요소 제거는 루트 정점만 가능하다.
- 루트 정점이 제거된 후 가장 마지막 정점이 루트에 위치한다.
- 루트 정점의 두 자식 정점 중 더 우선순위가 높은 정점과 바꾼다.
- 두 자식 정점이 우선순위가 더 낮을 때까지 반복한다.
- 완전 이진 트리의 높이는 이기에 힙의 요소 제거 알고리즘은 시간복잡도를 가진다.
JavaScript 힙 사용법
힙 요소의 추가/삭제 순서처럼 코드 구현 또한 순서가 동일하다.
class MaxHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [null]; // 편의를 위해 0번 index는 null로 비워놓기
}
/* 추가 로직 */
push(value) {
// 힙 마지막 요소의 추가한다.
this.heap.push(value);
let currentIndex = this.heap.length - 1;
let parentIndex = Math.floor(currentIndex / 2); // 부모 인덱스
// 부모가 루트가 아니고, 추가된 값보다 우선순위가 낮을 때 순서를 바꾼다.
while (parentIndex !== 0 && this.heap[parentIndex] < value) {
const temp = this.heap[parentIndex];
this.heap[parentIndex] = value;
this.heap[currentIndex] = temp;
currentIndex = parentIndex;
parentIndex = Math.floor(currentIndex / 2);
}
}
/* 삭제 로직 */
pop() {
const returnValue = this.heap[1]; // 루트 요소를 반환하기 위에 임시로 상수에 저장
this.heap[1] = this.heap.pop(); // 루트 정점은 마지막 요소로 대체
// root에서부터 아래로 내려갈 변수 선언
let currentIndex = 1;
let leftIndex = 2;
let rightIndex = 3;
// 하위 정점들이 현재 정점보다 우선순위가 낮을 때까지 반복한다.
while (
this.heap[currentIndex] < this.heap[leftIndex] ||
this.heap[currentIndex] < this.heap[rightIndex]
) {
if (this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[rightIndex]) {
const temp = this.heap[currentIndex];
this.heap[currentIndex] = this.heap[rightIndex];
this.heap[rightIndex] = temp;
currentIndex = rightIndex;
} else {
const temp = this.heap[currentIndex];
this.heap[currentIndex] = this.heap[leftIndex];
this.heap[leftIndex] = temp;
}
// 왼쪽 정점과 오른쪽 정점의 위치를 구한다.
leftIndex = currentIndex * 2;
rightIndex = currentIndex * 2 + 1;
}
return returnValue;
}
}
const heap = new MaxHeap();
heap.push(45);
heap.push(36);
heap.push(54);
heap.push(27);
heap.push(63);
console.log(heap.heap); // [ null, 63, 54, 36, 45, 27 ]
const array = [];
array.push(heap.pop()); // 63
array.push(heap.pop()); // 54
array.push(heap.pop()); // 45
array.push(heap.pop()); // 36
array.push(heap.pop()); // 27
console.log(array); // [ 63, 54, 45, 36, 27 ]참고사이트
프로그래머스 코딩 테스트 광탈 방지 A to Z : JavaScript
