객체지향 프로그래밍이란?
객체를 상태와 행위로 이루어진 객체로 만드는 것이다.
객체들의 모험은 객체들이 스스로 결정한다.
객체들은 캡슐화를 통해 자신이 어떤 모험을 떠날것인지 스스로 결정하므로 매우 자유롭다.
객체들끼리의 하나의 약속을 통해 공동의 목표를 메세지를 주고받으며 협력하여 처리해 나간다.
오늘 내가 짠 코드에서는 아래와 같은 객체들의 모험이 있었다.
public interface UserInputInterface {
public String userInput() throws IOException;
public String[] parsingLocation(String input);
public int howManyCountOfLocations() throws IllegalAccessException;
}국왕은 컴퓨터를 통해 사용자의 입력값등을 받을 필요가 생겨, 위의 미션을 구현해보라고 지령을 내린다.
위 처럼 특정 행위에 대한 내용을 서술한 미션(Interface)을 A 객체가 난 이일을 내방식대로 해보겠어! 라고 말하고 해당 객체를 구현해낸다.
public class AUserInputInterface implements UserInputInterface {
String[] inputArray;
String userInput;
@Override
public String userInput() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String inputLocation = br.readLine();
return inputLocation;
}
@Override
public String[] parsingLocation(String input) {
String locationManufacturing = locationManufacturing(input);
this.inputArray = locationManufacturing.split(" ");
return inputArray;
}
@Override
public int howManyCountOfLocations() throws IllegalAccessException {
if(inputArray.length == 0){
throw new IllegalAccessException("아직 좌표를 입력하지 않았습니다. 잘못된 접근입니다.");
}
return inputArray.length;
}
private String locationManufacturing(String input) {
String one = input.replaceAll("[^0-9,)]","");
String two = one.replaceAll("[)]"," ");
String three = two.replaceAll("[,]", " ");
return three;
}
}A 객체는 해당 일을 성공적으로 구현해내며, 내가 구현했다는 것을 알리기위해 AUserInputInterface 라는 이름을 붙여준다!
우리는 이제 AUserInputInterface 를 사용하여 입력값을 받는 일들을 진행할 것이다.
그리고 국왕은 사람들에게 우리가 성공적으로 구현해 내는걸 보여줘야 한다며, Graph 를 그리는 Class 에 대한 미션도 준다.
public interface Graph {
/*
* Render to Graph
* */
public void render(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2);
public void render(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int x3, int y3);
public void render(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int x3, int y3, int x4, int y4);
}그래서 B 객체가 이를 구현해보겠다고 도전하며, 이를 구현해내는데 성공한다.
package Week2.Rendering;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BGraph implements Graph{
String[][] graphMap;
int maxHeight;
int maxWidth;
int idx = 0;
public void render(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2){
maxHeight = Math.max(y1, y2);
maxWidth = x2;
int max = Math.max(maxHeight, maxWidth)+1;
graphMap = new String[max][max];
initializingArray(max);
graphMap[max-y1][x1-1] = "🌝";
graphMap[max-y2][x2-1] = "🌕";
printGraph(max);
}
public void render(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int x3, int y3){
maxHeight = Math.max(Math.max(y1, y2),y3);
maxWidth = Math.max(Math.max(x1, x2),x3);
int max = Math.max(maxHeight, maxWidth)+1;
graphMap = new String[max][max];
initializingArray(max);
graphMap[max-y1][x1-1] = "🌝";
graphMap[max-y2][x2-1] = "🌕";
graphMap[max-y3][x3-1] = "🌚";
printGraph(max);
}
public void render(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int x3, int y3, int x4, int y4){
maxHeight = Math.max(Math.max(y1, y2),Math.max(y3,y4));
maxWidth = Math.max(Math.max(x1, x2),Math.max(x3,x4));
int max = Math.max(maxHeight, maxWidth);
graphMap = new String[max][max];
initializingArray(max);
graphMap[max-y1][x1-1] = "🌝";
graphMap[max-y2][x2-1] = "🌕";
graphMap[max-y3][x3-1] = "🌚";
graphMap[max-y4][x4-1] = "🌍";
printGraph(max);
}
private void initializingArray(int size){
for(int i = 0; i<size; i++){
for(int j=0; j<size; j++){
graphMap[i][j] = " ";
}
}
}
private void printGraph(int max) {
max += 1;
for (String[] line : graphMap) {
max--;
System.out.println(max + " " + Arrays.toString(line));
}
}
}
평소 천체를 좋아하던 B 객체는 자신이 이렇게 천체를 넣어 그래프를 그리도록한다.
그리고 B 객체도 마찬가지로 자신이 구현했다며, BGraph 라고 이름을 붙여주게 된다.
국왕은 이제 계산하는 과정만 있으면 된다며, 계산하는 과정에 대한 미션을 준다.
public interface Calculator {
public int add(int a, int b);
public int sub(int a, int b);
public int div(int a, int b);
public int mul(int a, int b);
public int mod(int a, int b);
public double getLineMeter(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2);
public double getTriangleArea(int width, int height);
//@Overload
public double getTriangleArea(double x1, double x2, double x3);
public double getSquadreArea(double width, double height);
}
국왕이 내린 미션을 처리하기 위해 이곳저곳에서 객체들이 몰려들고, 객체 중 C 객체가 이를 구현해 내는데 성공한다.
C 객체는 아래와 같이 구현한뒤, 자신의 이름을 붙여 CCalculator 라고 한다.
public class ACalculator implements Calculator{
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
@Override
public int sub(int a, int b) {
return a-b;
}
@Override
public int div(int a, int b) {
return a/b;
}
@Override
public int mul(int a, int b) {
return a*b;
}
@Override
public int mod(int a, int b) {
return a%b;
}
@Override
public double getLineMeter(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
if(x2 < x1){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("x2 의 값이 x1 보다 작습니다.");
}
int xMeter = x2 - x1;
int yMeter = y2 - y1;
double lineMeter = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(xMeter,2) + Math.pow(yMeter,2));
return lineMeter;
}
@Override
public double getTriangleArea(int width, int height) {
return (width*height) / 2 ;
}
@Override
public double getTriangleArea(double x1, double x2, double x3) {
double pow_x1 = Math.pow(x1, 2);
double pow_x2 = Math.pow(x2, 2);
double pow_x3 = Math.pow(x3, 2);
double area = Math.sqrt((4*pow_x1*pow_x2 - Math.pow((pow_x1+pow_x2-pow_x3),2)))/ 4;
return area;
}
@Override
public double getSquadreArea(double width, double height) {
return width*height;
}
}하지만 국왕은 너무 부품적으로 설계한탓에, 객체들을 협력 시키지 못했고 객체들을 협력시키기 위해 하나의 Main Logic 을 생성하라고 미션을 준다.
객체들 끼리 따로 놀지말고, 서로 협력해! 입력도 받은걸 그래프로 그려내고, 계산해!
평소 협력을 싫어하던 ABC 객체들은 한숨을 쉬며 서로 협력하기 마음다잡고, 국왕 객체가 구현해낸 MainLogic 을 통해 서로 메세지를 주고받으며 소통한다.
국왕은 객체들이 언제 자신을 배신할지 모른다며, 내가 가지고 있는 객체가 다른 객체로 바뀌어도 영향을 끼치지 않도록.. 아래와 같이 자신의 로직을 설계했다.
UserInputInterface userInputInterface;
Calculator calculator;
Graph graph;
int countOfLocation;
String[] locations;
public MainLogic(UserInputInterface userInputInterface, Calculator calculator, Graph graph) {
this.userInputInterface = userInputInterface;
this.calculator = calculator;
this.graph = graph;
}위와 같이 설계한 덕분에, 국왕은 아까 객체들에게 내린 미션용지만 있으면, 객체들을 바꿔버려도 자신의 로직에는 영향을 미치지 않게됬다..
package Week2.Boot;
import Week2.Calc.Calculator;
import Week2.Rendering.Graph;
import Week2.UserInterface.UserInputInterface;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MainLogic {
UserInputInterface userInputInterface;
Calculator calculator;
Graph graph;
int countOfLocation;
String[] locations;
public MainLogic(UserInputInterface userInputInterface, Calculator calculator, Graph graph) {
this.userInputInterface = userInputInterface;
this.calculator = calculator;
this.graph = graph;
}
public void start() throws IOException, IllegalAccessException {
String userInputLocation = userInputInterface.userInput();
locations = userInputInterface.parsingLocation(userInputLocation);
this.countOfLocation = userInputInterface.howManyCountOfLocations();
selectCalcFromLocations(countOfLocation);
}
public void selectCalcFromLocations(int countOfLocation){
double area = 0;
if(countOfLocation == 4){
LineMeterLogic();
}else if(countOfLocation == 6){
TriangleLogic();
}else if(countOfLocation == 8){
SquareLogic();
}
}
private void SquareLogic() {
double area;
int x1 = Integer.parseInt(locations[0]);
int y1 = Integer.parseInt(locations[1]);
int x2 = Integer.parseInt(locations[2]);
int y2 = Integer.parseInt(locations[3]);
int x3 = Integer.parseInt(locations[4]);
int y3 = Integer.parseInt(locations[5]);
int x4 = Integer.parseInt(locations[6]);
int y4 = Integer.parseInt(locations[7]);
double lineOne = calculator.getLineMeter(x1,y1,x2,y2);
double lineTwo = calculator.getLineMeter(x2,y2,x3,y3);
graph.render(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4);
area = calculator.getSquadreArea(lineOne, lineTwo);
System.out.println("사각형의 넓이는 : " + area);
}
private void TriangleLogic() {
double area;
int x1 = Integer.parseInt(locations[0]);
int y1 = Integer.parseInt(locations[1]);
int x2 = Integer.parseInt(locations[2]);
int y2 = Integer.parseInt(locations[3]);
int x3 = Integer.parseInt(locations[4]);
int y3 = Integer.parseInt(locations[5]);
double lineOne = calculator.getLineMeter(x1,y1,x2,y2);
double lineTwo = calculator.getLineMeter(x2,y2,x3,y3);
double lineThree = calculator.getLineMeter(x1,y1,x3,y3);
area = calculator.getTriangleArea(lineOne, lineTwo, lineThree);
graph.render(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3);
System.out.println("삼각형의 넓이는 : " + area);
}
private void LineMeterLogic() {
double area;
int x1 = Integer.parseInt(locations[0]);
int y1 = Integer.parseInt(locations[1]);
int x2 = Integer.parseInt(locations[2]);
int y2 = Integer.parseInt(locations[3]);
area = calculator.getLineMeter(x1,y1,x2,y2);
graph.render(x1, y1, x2, y2);
System.out.println("두점 사이의 거리는 : " + area);
}
}국왕이 컴퓨터를 키자마자 너네들은 협력해야해! 라며 Boot 라는 녀석을 통해 강제로 한곳에 몰아넣는다.
public class Boot {
Calculator calculator = new ACalculator();
Graph graph = new BGraph();
UserInputInterface userInputInterface = new CUserInputInterface();
public void booting() throws IOException, IllegalAccessException {
MainLogic mainLogic = new MainLogic(userInputInterface, calculator, graph);
mainLogic.start();
}
}객체들은 서로 협력하기로 약속했고, 아래와 같이 일하기로 했다.
1. InputUserInterface 가 받아오는 값들을 좌표로 만들고, 해당 좌표를 메세지로 Calculator 와 Graph 에게 전달해준다.
2. Graph 는 해당 좌표값을 통해 Graph 를 그려낸다.
3. Calculator 도 해당 좌표값을 통해서 사용자가 원하는 값을 계산해 낸뒤, MainLogic 에 값을 전해준다.
그래서 객체들의 협력으로 아래와 같은 그래프를 만들어냈다.
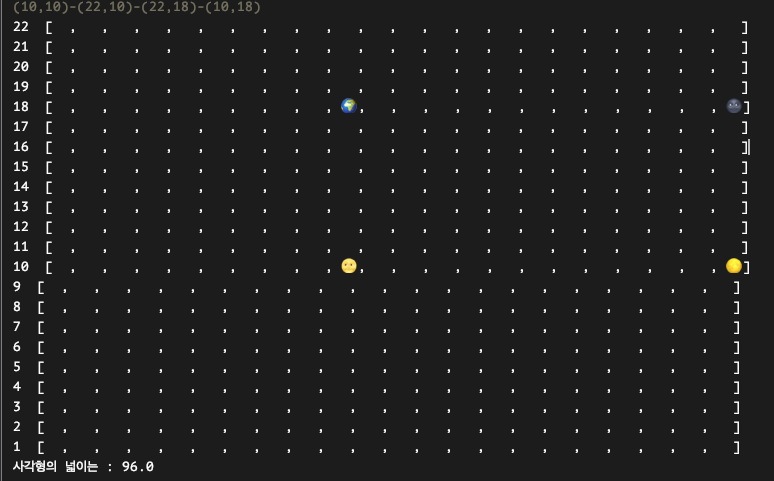
그런데 전 부터 천체를 맘에들지 않아했던 국왕은 공으로 Graph 를 바꾸라하지만, B 객체가 이를 듣지않아, D객체에게 너가 공으로 그려오면 B객체 대신 니 그래프를 쓸께 라고 말한다..
그래서 D 객체가 구현해내고 국왕은 자신의 로직에 D 객체를 주입하기 위해 컴퓨터를 켜줄때 주입을 다르게하도록 패치했다..
public class DGraph implements Graph{
String[][] graphMap;
int maxHeight;
int maxWidth;
int idx = 0;
public void render(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2){
maxHeight = Math.max(y1, y2);
maxWidth = x2;
int max = Math.max(maxHeight, maxWidth)+1;
graphMap = new String[max][max];
initializingArray(max);
graphMap[max-y1][x1-1] = "⚽️";
graphMap[max-y2][x2-1] = "🏀";
printGraph(max);
}
public void render(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int x3, int y3){
maxHeight = Math.max(Math.max(y1, y2),y3);
maxWidth = Math.max(Math.max(x1, x2),x3);
int max = Math.max(maxHeight, maxWidth)+1;
graphMap = new String[max][max];
initializingArray(max);
graphMap[max-y1][x1-1] = "⚽️";
graphMap[max-y2][x2-1] = "🏀";
graphMap[max-y3][x3-1] = "🥎";
printGraph(max);
}
public void render(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int x3, int y3, int x4, int y4){
maxHeight = Math.max(Math.max(y1, y2),Math.max(y3,y4));
maxWidth = Math.max(Math.max(x1, x2),Math.max(x3,x4));
int max = Math.max(maxHeight, maxWidth);
graphMap = new String[max][max];
initializingArray(max);
graphMap[max-y1][x1-1] = "⚽️";
graphMap[max-y2][x2-1] = "🏀";
graphMap[max-y3][x3-1] = "🥎";
graphMap[max-y4][x4-1] = "🏐";
printGraph(max);
}
private void initializingArray(int size){
for(int i = 0; i<size; i++){
for(int j=0; j<size; j++){
graphMap[i][j] = " ";
}
}
}
private void printGraph(int max) {
max += 1;
for (String[] line : graphMap) {
max--;
System.out.println(max + " " + Arrays.toString(line));
}
}
}
국왕은 D객체의 구현사항이 아주맘에 들었고, B 객체를 없애버리게된다.
public class Boot {
Calculator calculator = new ACalculator();
// Graph graph = new BGraph(); ㅜ_ㅜ
Graph graph = new DGraph();
UserInputInterface userInputInterface = new CUserInputInterface();
public void booting() throws IOException, IllegalAccessException {
MainLogic mainLogic = new MainLogic(userInputInterface, calculator, graph);
mainLogic.start();
}
}클래스 설계도
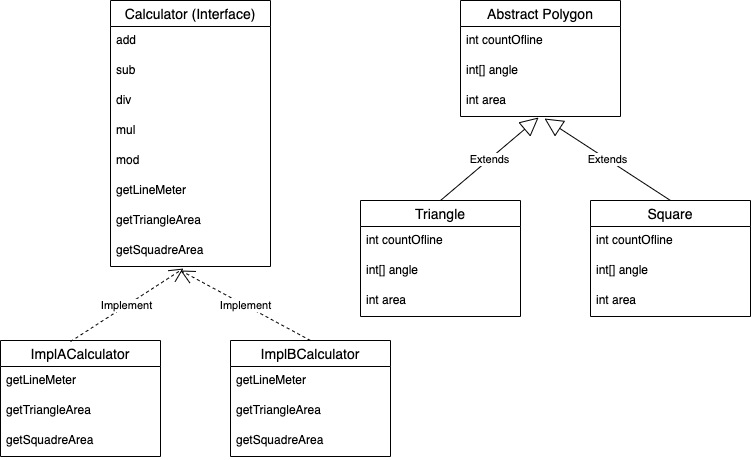
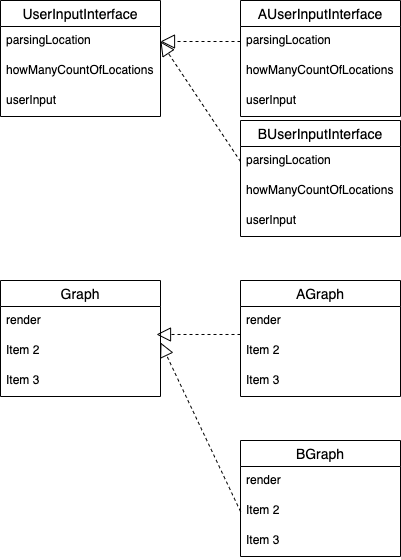
객체들의 모험처럼 최대한 재미있게 적어보려고 노력했다. 최대한 객체들이 자신의 역할과 책임 그리고 메세지를 통한 협력을 할 수 있도록 구성해보았다.
아직 공부하고 있는 만큼 틀린 내용도 있을 수 있으니 틀렸다면 피드백 부탁드립니다! 🌝


와 어려운 내용을 재밌게 풀어주셔서 감사합니다, 덕분에 이번 미션의 실마리를 찾을 수 있었습니다!!