1. 깊이 우선 탐색
1) 개념
재귀함수+스택자료구조 이용
시간 복잡도 O(V+E) : V:노드 수, E: 에지 수
한번 방문한 노드는 다시 방문하면 안됨 -> 방문 여부를 체크할 배열 필요
2) 대표코드
- 재귀 -> 깊이 우선 탐색
- 문제에 따라 백트랙킹을 할 수도 있고 안할 수도 있음
아래의 코드는 백트랙킹 없는 코드
void DFS(int v) {
if (tf[v]) {
return;
}
tf[v] = true;
for (int p : arr[v]) { //** arr[v]와 연결된 모든 정점 p에 대해 반복문을 실행
if (tf[p] == false) {
DFS(p);
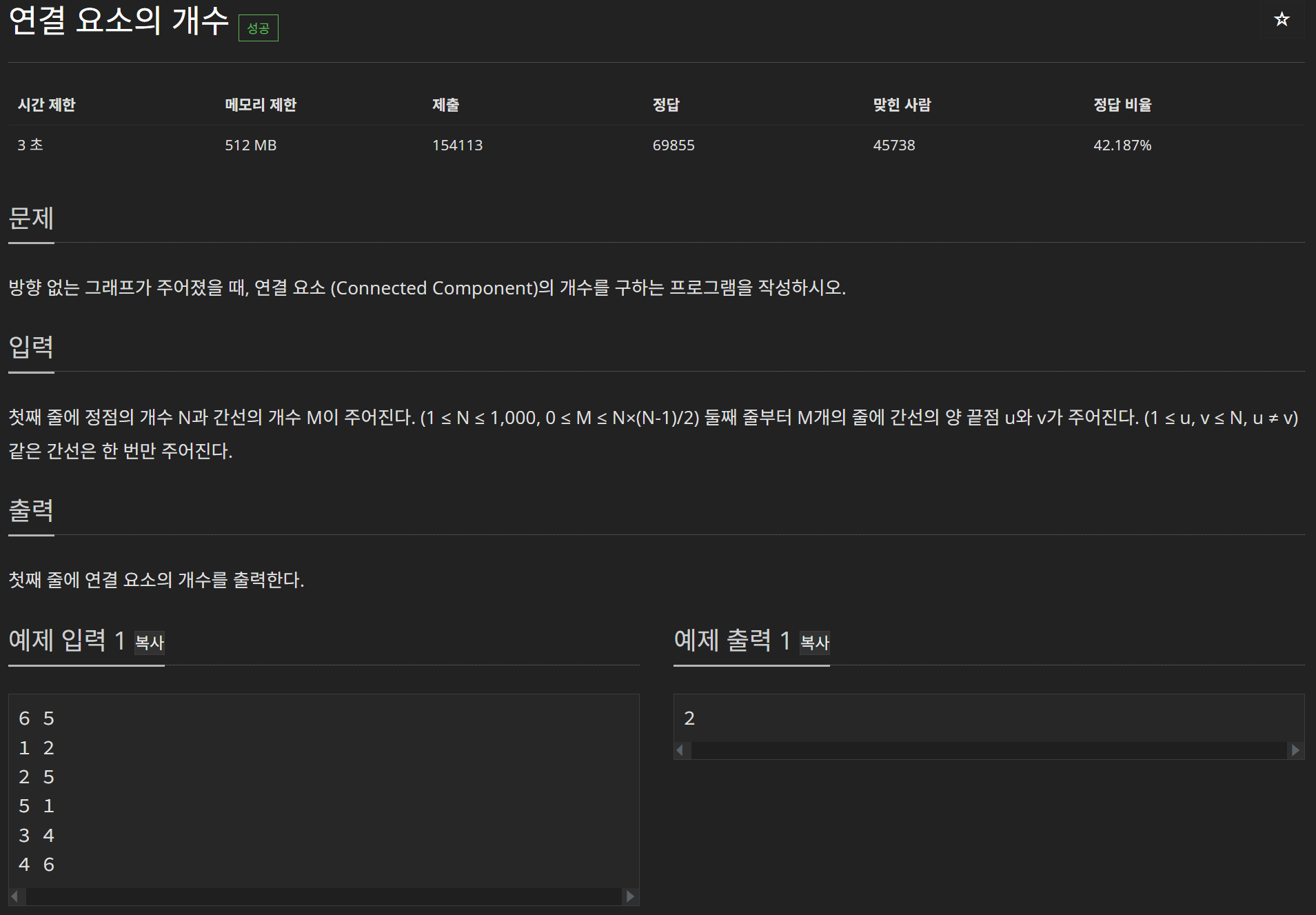
}}}3) 문제: 연결 요소의 개수 11724번
- 코드
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
//방향 없는 그래프가 주어졌을 때, 연결 요소 (Connected Component)의 개수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
static vector <vector <int>>arr;
static vector <bool> tf;
void DFS(int v);
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int n, e;
cin >> n >> e;
arr.resize(n + 1);
tf.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < e; i++) {
int n1,n2;
cin >> n1>>n2;
arr[n1].push_back(n2);
arr[n2].push_back(n1);
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!tf[i]) {
cnt++;
DFS(i);
}
}
cout << cnt;
return 0;
}
void DFS(int v) {
if (tf[v]) {
return;
}
tf[v] = true;
for (int p : arr[v]) { //** arr[v]와 연결된 모든 정점 p에 대해 반복문을 실행
if (tf[p] == false) {
DFS(p);
}
}
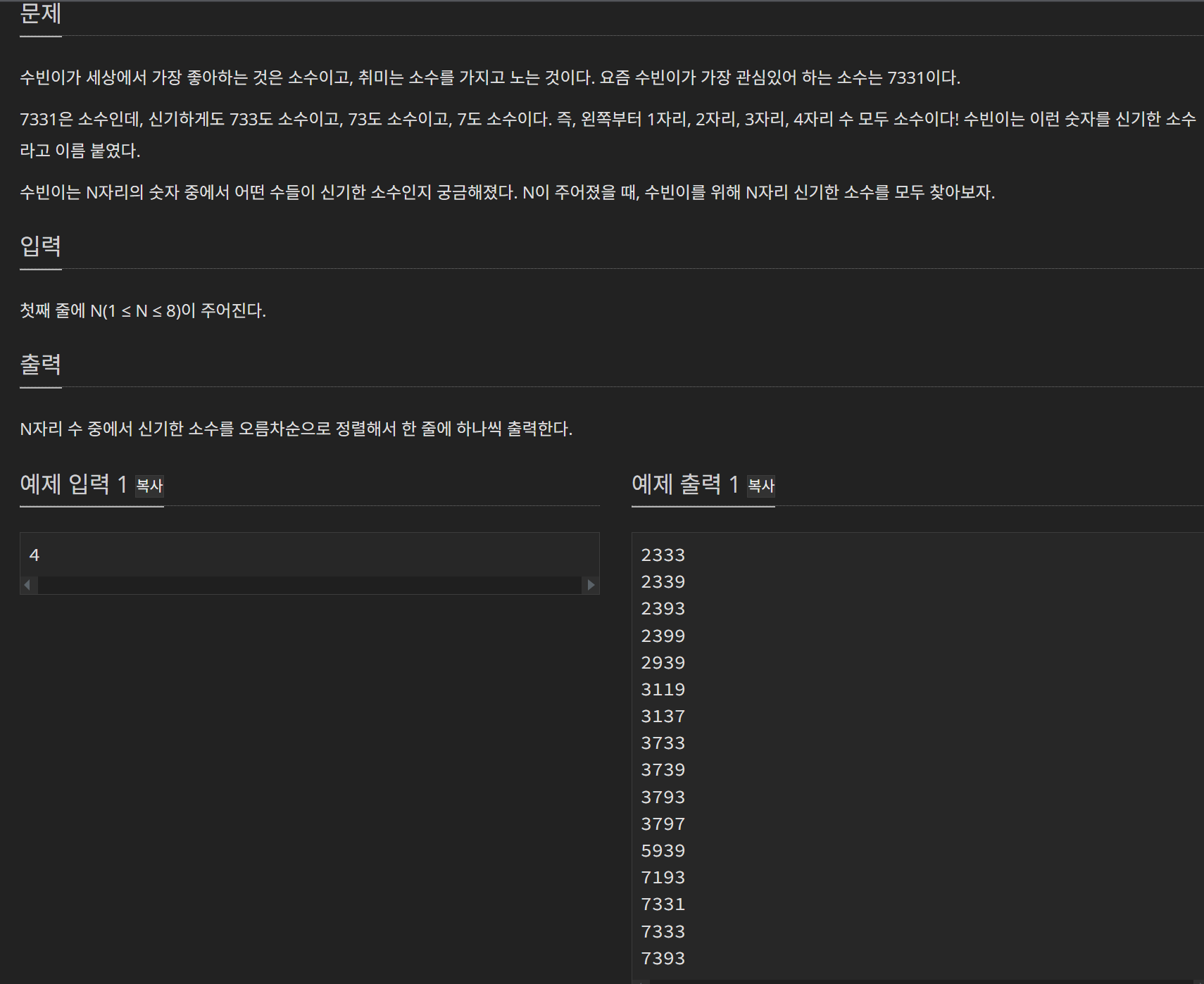
}4) 문제: 신기한 소수 2023번
- 코드
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void DFS(int);
bool isPrime(int);
int n;
//n자리 각각의 자리수가 모두 소수인 것 ex) 7331(4자리) 733(3자리) 73(2자리) 7(1자리)
//소수판별
bool isPrime(int num) {
for (int i = 2; i <= (num / 2); i++) {
if (num % i == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
//DFS
void DFS(int number, int jarisu) {
if (jarisu == n) {
if (isPrime(number)) {
cout << number << "\n";
return;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i += 2) {
if (isPrime(number * 10 + i)) {
DFS(number * 10 + i, jarisu + 1);
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
cin >> n;
DFS(2,1);
DFS(3, 1);
DFS(5, 1);
DFS(7, 1);
return 0;
}- vector를 안써도 충분히 풀 수 있는 문제였다.
vector를 써야만 문제가 풀릴거라는 썩어빠진 생각은 버리자 - 첫번째 자릿수를 fixed한 상태에서 main함수에서 DFS를 4번 호출하는 방법을 생각하지 못했다. 굳이 DFS과정의 모든 것을 DFS함수내에서 시작하고 끝날 필요가 없다.
5) 문제: ABCD 13023번
- 문제: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/13023
DFS 깊이가 5이상 인것이 있으면 1출력, 없으면 0출력
- 코드
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
static vector <vector <int>> fri;
static vector <bool> tf;
static bool arrive;
void Friend_DFS(int v, int depth);
//DFS깊이가 5이상 인것이 있으면 1출력, 없으면 0출력
void Friend_DFS(int v, int depth) {
if (arrive || depth==5) {
arrive = true;
return;
}
tf[v] = true;
for (int i : fri[v]) {
if (!tf[i]) {
Friend_DFS(i, depth+1);
}
}
tf[v] = false; //백트랙킹 매우 중요!!!!!
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int n, e;
cin >> n >> e;
fri.resize(n + 1 );
tf.resize(n + 1 );
for (int i = 0; i < e; i++) {
int f1, f2;
cin >> f1 >> f2;
fri[f1].push_back(f2);
fri[f2].push_back(f1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Friend_DFS(i,1);
if (arrive) {
break;
}
}
if (arrive) cout << 1;
else cout << 0;
return 0;
}- !!!!백트랙킹의 중요성!!!!
- 백트랙킹 tf[v]=false 가 없으면
DFS가 끝나도 다시 방문을 못함
DFS 탐색 중 방문한 노드는 계속 true로 남아 있어서 다른 경로를 못 탐색함 >> DFS가 제대로 안됨 - 백준 예제코드 2번을 통해 백트랙킹의 필요성을 알 수 있음!!!
2. BFS: 너비 우선 탐색
1)대표코드
- while문+큐 이용
void BFS(int v) {
bfs.push(v);
tf2[v] = true;
while (!bfs.empty()) {
int node= bfs.front();
cout << node << ' ';
bfs.pop();
for (int p : arr[node]) {
if (!tf2[p]) {
tf2[p] = true;
bfs.push(p);
}
}
}
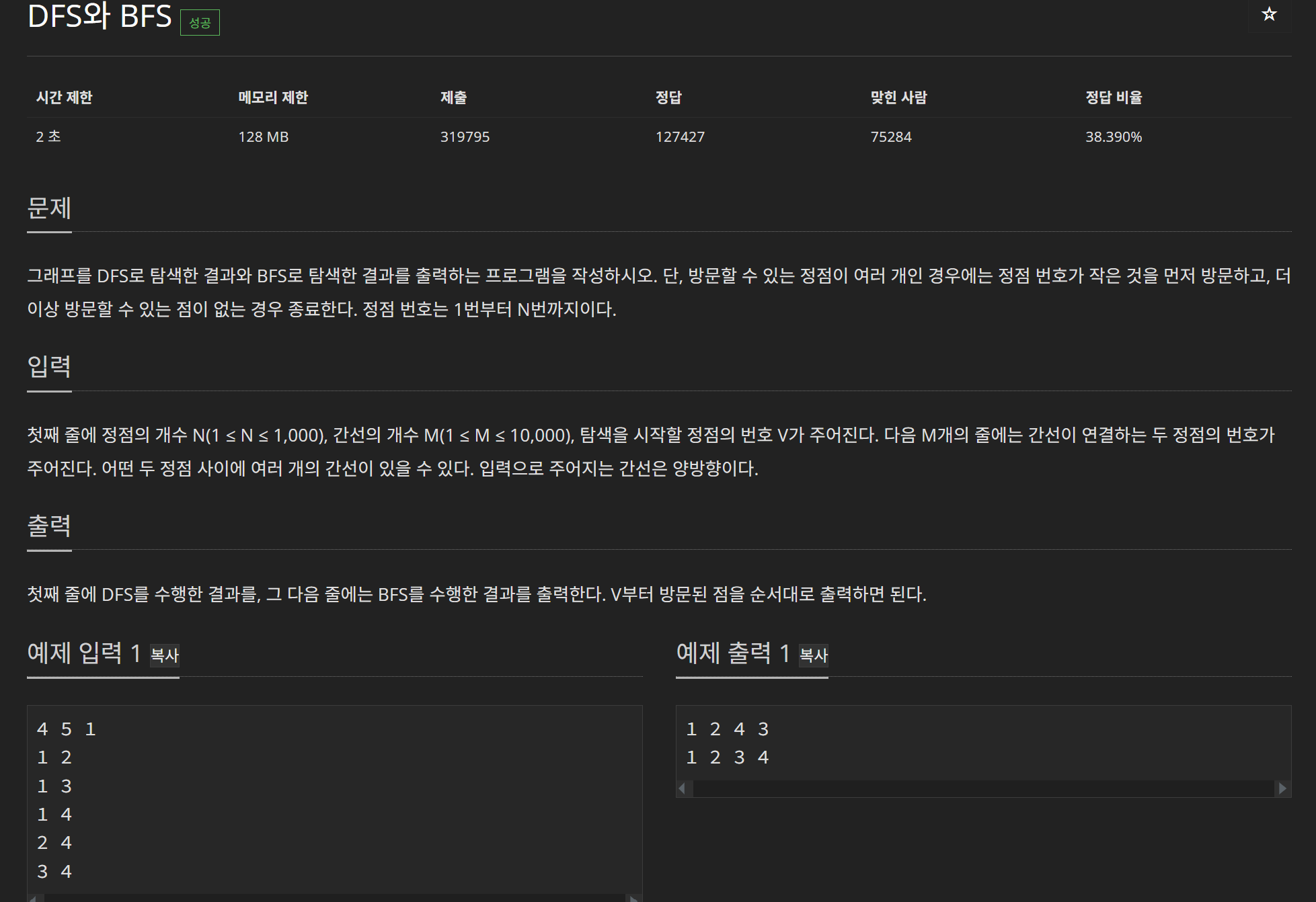
}2) 문제: DFS와BFS 1260번
- DFS는 위에서 다룬 대로 쓰면 됨
- BFS는 while+큐로 코드짜기
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
static vector<vector<int>> arr;
static queue<int> bfs;
static vector<bool> tf;
static vector<bool> tf2;
void DFS(int v);
void BFS(int v);
void DFS(int v) {
if (tf[v]) {
return;
}
tf[v] = true;
cout << v << " ";
sort(arr[v].begin(),arr[v].end());
for (int i : arr[v]) {
if (!tf[i]) {
cout << i << " ";
DFS(i);
}
}
}
//BFS는 while을 사용하는게 일반적
void BFS(int v) {
bfs.push(v);
tf2[v] = true;
while (!bfs.empty()) {
int node= bfs.front();
cout << node << ' ';
bfs.pop();
sort(arr[node].begin(), arr[node].end());
for (int p : arr[node]) {
if (!tf2[p]) {
tf2[p] = true;
bfs.push(p);
}
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int n, m, V;
cin >> n >> m >> V;
arr.resize(n+1);
tf.resize(n+1,false);
tf2.resize(n+1, false);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int temp1, temp2;
cin >> temp1 >> temp2;
arr[temp1].push_back(temp2);
arr[temp2].push_back(temp1);
}
DFS(V);
cout << "\n";
BFS(V);
return 0;
}
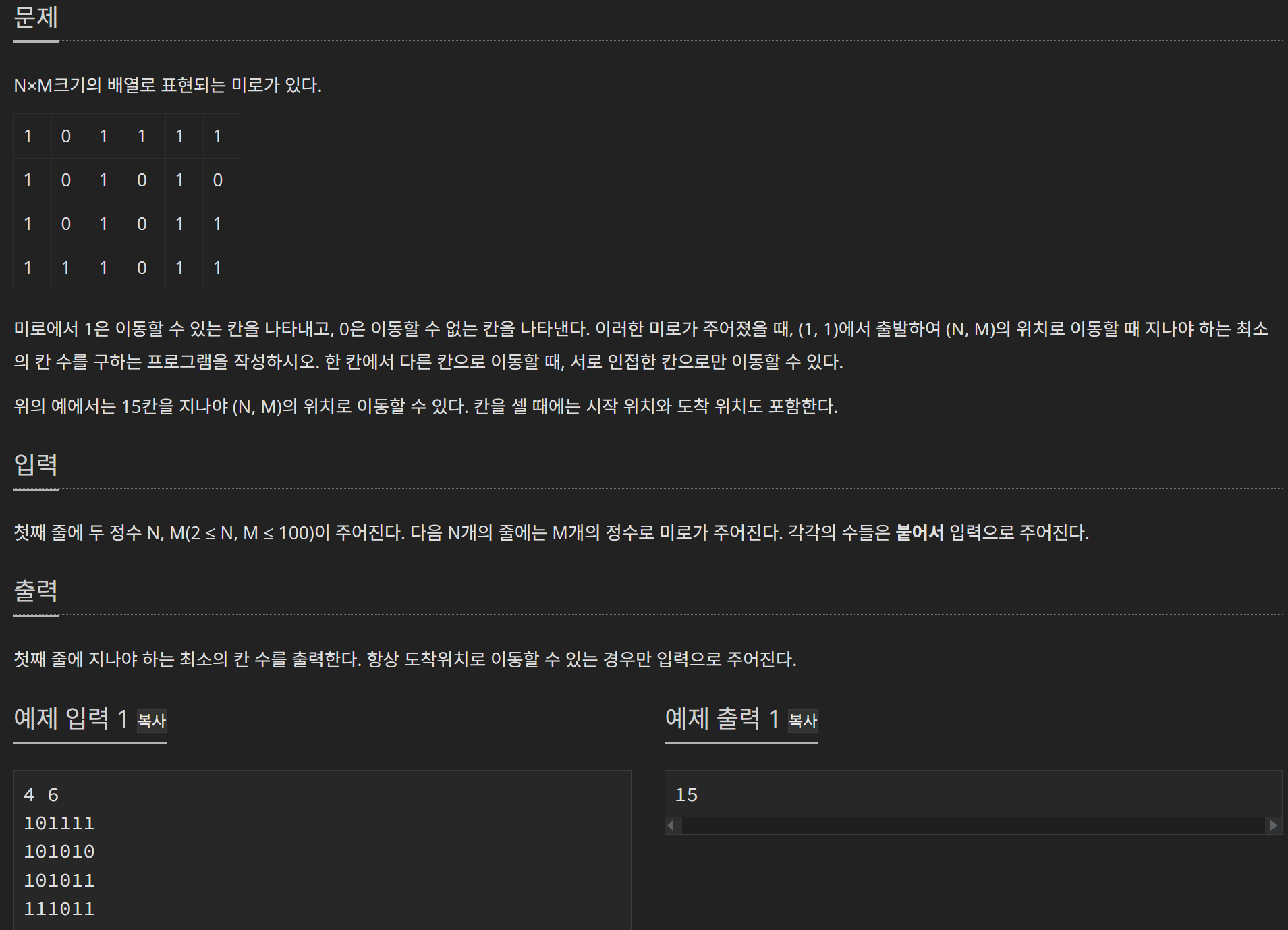
3) 문제: 미로탐색 2178번
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
//상하좌우 탐색
static int dx[] = { 0,1,0,-1 };
static int dy[] = { 1,0,-1,0 };
static int n, m;
static int A[101][101];
static bool visited[101][101] = { false };
void BFS(int i, int j);
void BFS(int i, int j) {
queue<pair<int, int>> myqueue; //(정수, 정수) 쌍을 저장하는 큐
myqueue.push(make_pair(i, j)); // (i, j)라는 한 쌍의 값을 만들어 push
while (!myqueue.empty()) {
int now[2];
now[0] = myqueue.front().first;
now[1] = myqueue.front().second;
myqueue.pop();
visited[i][j] = true;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = now[0] + dx[k];
int y = now[1] + dy[k];
if (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < n && y < m) {
if (A[x][y] != 0 && !visited[x][y]) {
visited[x][y] = true;
A[x][y] = A[now[0]][now[1]] + 1; //누적해가면서 숫자세기
myqueue.push(make_pair(x, y));
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
cin >> n >> m;
//문자열 받는 방식도 기억해두기!
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
A[i][j] = s[j] - '0';
}
}
BFS(0, 0);
cout << A[n - 1][m - 1];
return 0;
}
- 문자열을 2차원배열로 나누는 방식 알아두기!
- 미로 문제를 처음 접해봐서 당황,,, 기억해두고 비슷한 문제가 나오면 적용해볼 수 있도록 하자.
4) **문제: 트리의 지름 1167번
- 문제: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1167
- 시간이 없어서 못풀었음...ㅜㅜ 나중에 꼭 풀기..!