ch6
Link layer
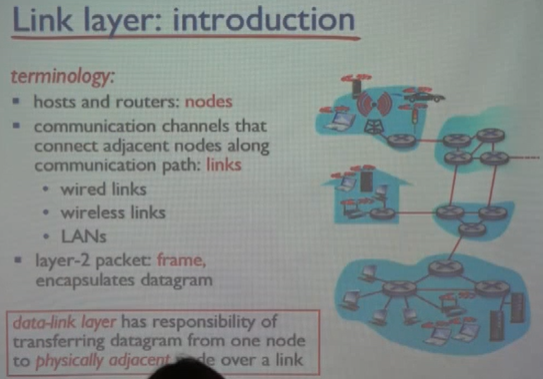
host, router = node
이웃한 노드를 연결하는 것을 link
layer-2 packet : frame
link-layer는 물리적으로 직접연결된 reliable transfer을 책임진다.
각각의 링크들에서 잘 전달되는지
link layer: context

어떤 데이터가 n to n으로 지날때 서로 다른 링크를 지날 수 있다.
각각의 링크 레이어 프로토콜은 다른 서비스를 이용한다.

framing : 데이터그램을 frame으로 encapsulation 하는 것이다. shared meduim이면 channel access control도 link layer이 결정한다.
MAC 주소도 이용해서 src, dest를 구분한다.
인접 노드사이의 data delivery를 책임진다. 에러를 확인하고 에러를 고치는 것이 link layer에 들어가 있다.
bit-error가 거의 일어나지 않는 fiber(광케이블), twisted pair에서는 거의 사용되지 않는다.
질문은 왜 link-level과 end-end reliability가 필요한가?
- link layer는 전달만해준다. 그럼 queing 이 일어날텐데 패킷 드랍이 link layer 문제가 아니기 때문에 n to n reliability가 필요해진 것이다.

- flow control
- error detection
- error correction
- half-duplex and full-duplex
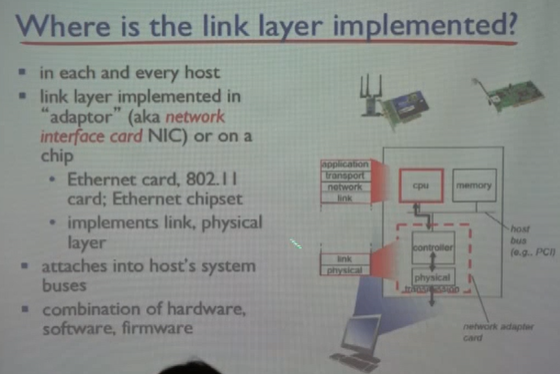
link layer는 NIC에 구현되어 있다.
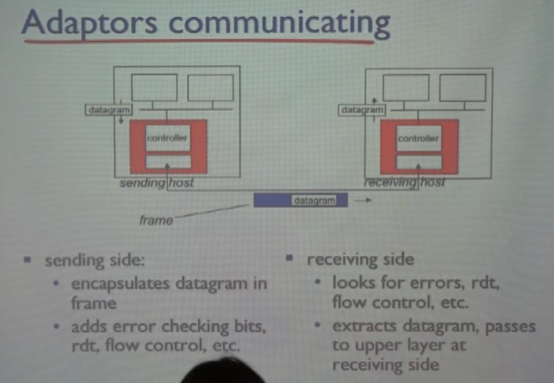
LAN 카드가 받은 프레임을 전달하고 receiving host에서 헤더를 제거하고 데이터만 받게 된다.
6.2 error detection, correction

EDC = error detection and correction bits
D = data protected by error checking
에러는 100% 믿을만 하지 않다. 100% detection 하는 것은 아니다.
EDC field가 크면 detection, correction을 보다 잘할 수 있지만 over head가 크다.

single bit parity는 한 비티를 검사하는 것이다.
single bit parity는 odd parity check와 even parity check가 존재한다.
odd면 1의 갯수가 홀수가 되도록 채워넣는 것이다.
한 비트만 에러 났으면 detect 가능하지만 두 비트가 났으면 불가능하다.
이 차원 비트 패리티에서는 row parity, column parity로 2차원으로 처리해버리는 것이다.
문제능 이렇게 하더라도 어디에서 에러가 났는지는 모른다. 그리고 overhead가 크다는 단점이 있다.

인터넷 체크썸

CRC
data bit = D, binary number
G = r + 1
목표 : r개의 CRC bit = R을 <D, R>
- CRC
- multiple access protocols - p2p, broadcast, MAC protocols(taxonomy), TDMA, FDMA, ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CA, CSMA/CD
- ARP, ethernet, switches, vlan
- MPLS
- data center networking
