=== Synchronization: Basics ===
1. Shared Variables in Threaded C Programs
Threaded C Program에서 공유 변수에 대해서 이야기 해보자. concurrent web server 개발시 3가지 방법이 존재하는 것은 저번에 배웠다. 이중 Thread 기반의 경우 address space를 공유한다.
OS의 도움을 받아야지만 application 끼리 공유를 받을 수 있다.
Thread기반은 process와 유사하지만 contect switching도 적고 reaping도 적다는 것을 배웠다.
어떤 변수들이 shared인가? global 변수들은 shared이다. stack 변수들은 private이다.
실재로는 이렇게 간단하지가 않다.
정의에 따라 어떤 변수가 shared라는 것은 여러 thread가 x의 값을 다 참조할 수 있는 경우를 이야기 한다. 반대인 경우도 이야기 한다.
-
Question: Which variables in a threaded C program are shared?
- The answer is not as simple as “global variables are shared” and “stack variables are private”
-
Def: A variable x is shared if and only if multiple threads reference some instance of x.
-
Requires answers to the following questions:
- What is the memory model for threads?
- How are instances of variables mapped to memory?
- How many threads might reference each of these instances?
메모리에 변수들이 어떻게 mapping이 되냐
변수들의 instance들을 어떻게 reference하는가
Threads Memory Model
-
Conceptual model:
- Multiple threads run within the context of a single process : 개념적으로는 context 내에서 여러 thread가 돌아가는 중이다.
- Each thread has its own separate thread context : thread는 각자의 context를 가지고 있다
- Thread ID, stack, stack pointer, PC, condition codes, and GP registers
- All threads share the remaining process context : 모든 thread들은 context의 나머지 것들을 모두 공유한다.
- Code, data, heap, and shared library segments of the process virtual address space
- Open files and installed handlers
-
Operationally, this model is not strictly enforced:
- Register values are truly separate and protected, but…
- Any thread can read and write the stack of any other thread
실재로는 GP register들은 완전히 분리되어서 protected된다. 어떤 스레드가 다른 스레드의 stack을 읽고 쓸 수 있는 경우가 발생할 수 있다.
The mismatch between the conceptual and operation model is a source of confusion and errors
Example Program to Illustrate Sharing
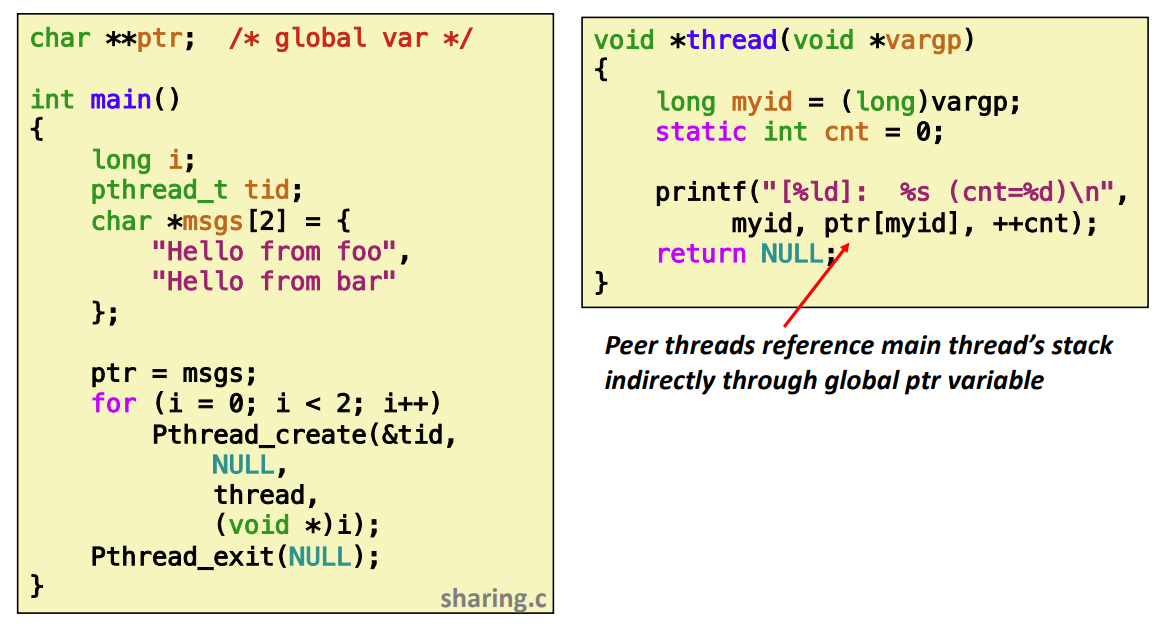
char **ptr; /* global var */
int main()
{
long i;
pthread_t tid;
char *msgs[2] = {
"Hello from foo",
"Hello from bar"
};
ptr = msgs;
for (i = 0; i < 2; i++)
Pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread, (void *)i);
Pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *thread(void *vargp)
{
long myid = (long)vargp;
// local 변수이지만 global과 동일하게 stack에 할당된다. 차이는 thread안에서만 생존한다.
static int cnt = 0;
// 여기에서 ptr을 통해서 다른 local 변수 값을 읽거나 쓰려고 한다
// cnt의 경우는 local 이지만 static이라 global 접근이 가능해진다.
// 그래서 또 다른 thread도 cnt에 접근이 가능해진다.
printf("[%ld]: %s (cnt=%d)\n",
myid, ptr[myid], ++cnt);
return NULL;
}- ptr[myid]
Peer threads reference main thread’s stack indirectly through global ptr variable
Mapping Variable Instances to Memory
메모리의 변수들이 mapping이 될때 변수의 특징들
- Global variables
- Def: Variable declared outside of a function
- Virtual memory contains exactly one instance of any global variable : 가상메모리 공간상에서 하나만 존재한다.
- Local variables
- Def: Variable declared inside function without static attribute : static으로 선언되지 않은 함수 안에서 선언된 변수를 이야기 한다.
- Each thread stack contains one instance of each local variable : 각 thread가 하나의 instance를 가질 수 있다. 그래서 중복되는 local 변수들을 가지고 있을 수 있다.
- Local static variables
- Def: Variable declared inside function with the static attribute : static으로 함수 안에 선언된 변수이다.
- Virtual memory contains exactly one instance of any local static variable. : 가상 메모리 공간안에서 하나만 있을 수 있다.
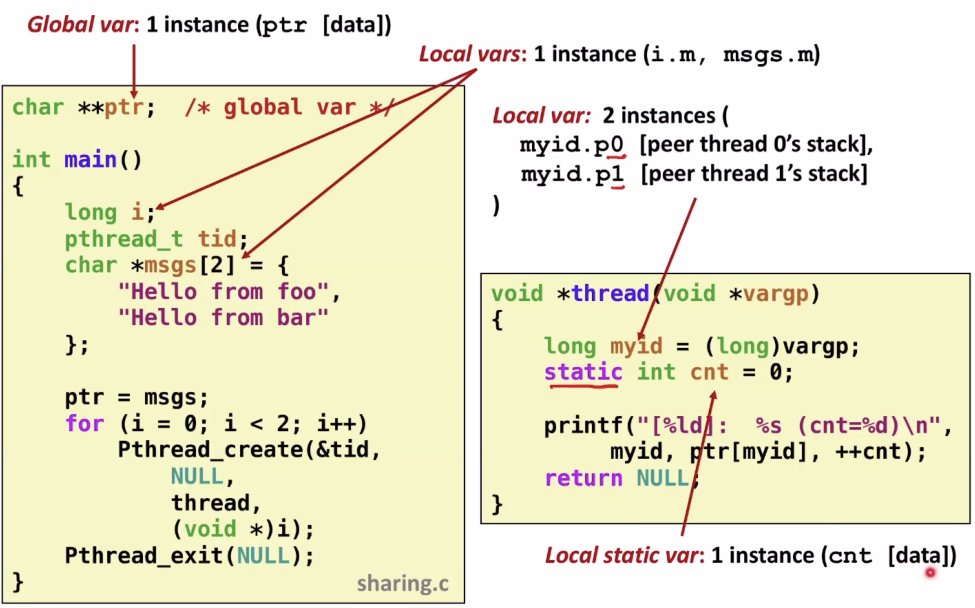
앞에서 배워던 global, local, static에 대해 검토해보자. ptr이라는 것은 global 변수이다. 이 변수는 data 영역에 들어가 있는 변수이다.
메인 스레드 안에 선언된 local 변수들
thread 실행시 myid는 스레드 생성시 p0,p1에 각각 스레드 스택에 존재하는 local 변수이다. myid의 경우 local 변수이지만 cnt는 static으로 globally 하나만 존재할 수 있다.
Shared Variable Analysis
앞에 있는 변수들 중에 어떤 변수들이 shared 변수인지 확인해보자
- Which variables are shared?
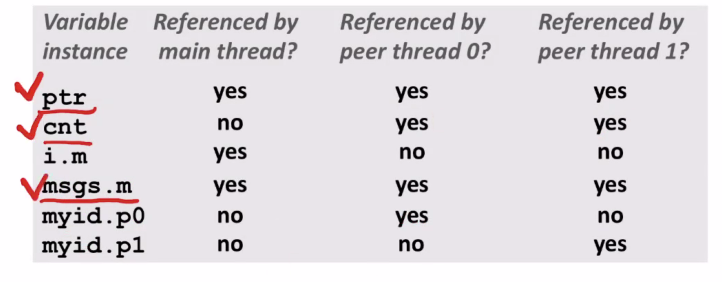
ptr은 스레드 3개에 의해서 reference 될 수 있기에 shared라고 이야기 한다.
cnt는 static local 변수로 globaly 하나만 존재할 수 있으며 thread에서만 접근할 수 있다. 그래서 shared이다.
i변수는 local 변수라서 main만 접근할 수 있다.
msgs local 변수는 main은 접근가능, thread0,1은 ptr로 접근이 가능하다. 그래서 shared이다.
myid.p0은 thread0에서만 접근 가능하다.
myid.p1은 thread1에서만 접근 가능하다.
shared는 3개이다.
- Answer: A variable x is shared iff multiple threads reference at least one instance of x. Thus:
- ptr, cnt, and msgs are shared n
- i and myid are not shared
어떤 변수가 shared라는 것은 다수의 thread가 local 변수에 접근할 수 있다는 것이다.
2. Synchronizing Threads
-
Shared variables are handy...
-
…but introduce the possibility of nasty synchronization
errors.
쓰레드 동기화하다보면 내가 예상 못한 상황이 생길 수 있다.
badcnt.c: Improper Synchronization(재정리)
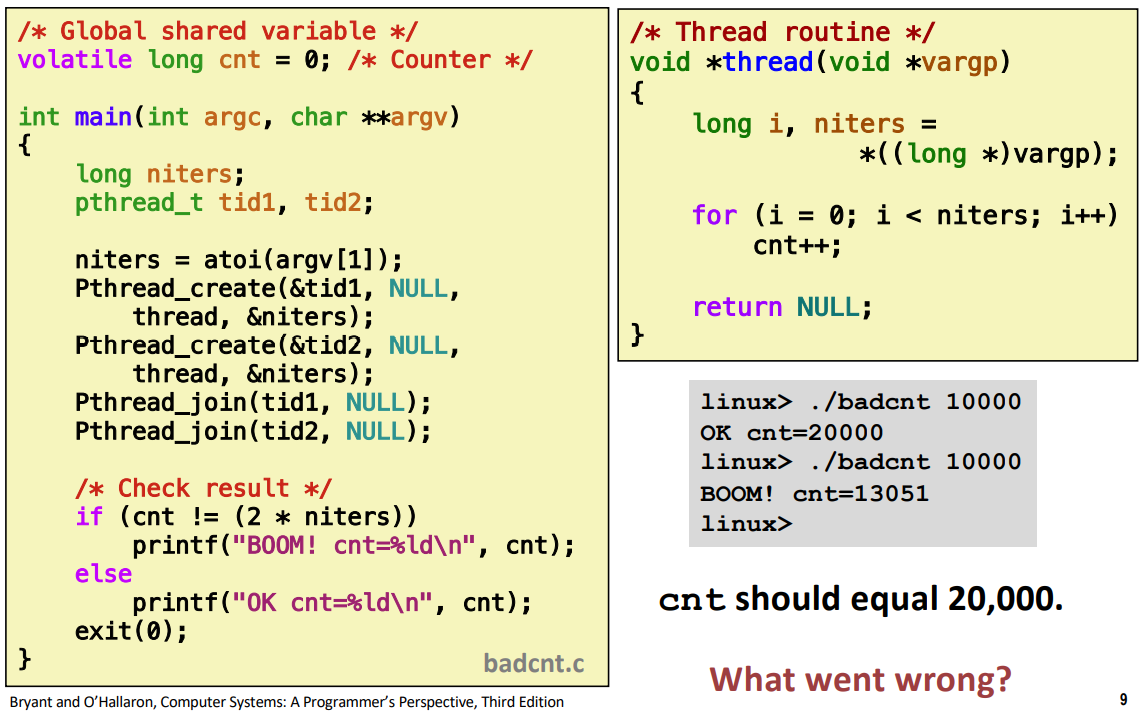
/* Global shared variable */
volatile 변수에 수행되는 load, store 명령어는
main 메모리에 직접 읽고 쓴다.
volatile long cnt = 0; /* Counter */
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
//niters은 받은 성분을 atoi로 바꾸어준다.
long niters;
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
// char to int
niters = atoi(argv[1]);
Pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread, &niters);
Pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread, &niters);
Pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
Pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
/* Check result */
if (cnt != (2 * niters))
printf("BOOM! cnt=%ld\n", cnt);
else
printf("OK cnt=%ld\n", cnt);
exit(0);
}/* Thread routine */
void *thread(void *vargp)
{
long i, niters = *((long *)vargp);
for (i = 0; i < niters; i++)
cnt++;
return NULL;
} cnt를 모두 접근할 수 있다. 서로 경쟁해서 cnt값을 바꾸고 있다. 그래서 각 스레드가 cnt값을 경쟁하면서 바꾸게 되는데 결과값이 niters의 2배가 되었는지 확인하는 것이다.

하지만 실행결과 20000이 안찍힐때가 존재한다.
Assembly Code for Counter Loop
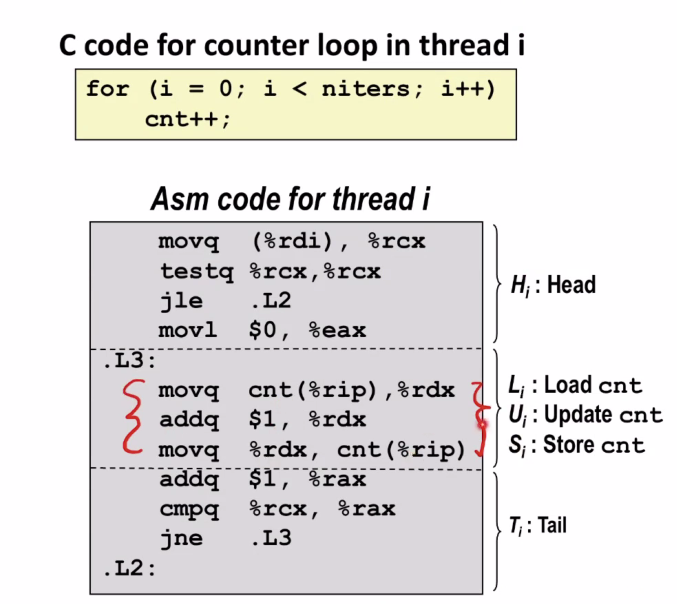
L3부터 3줄이 핵심적인 부분이다. Load, update, store 3가지의 instruction으로 코드를 실행하고 있다.
실재 cpu입장에서는 cnt 메모리에 있는 값을 바꾸고 있다.
Concurrent Execution
- Key idea: In general, any sequentially consistent interleaving is possible, but some give an unexpected result!
- Ii denotes that thread i executes instruction I
- %rdxi is the content of %rdx in thread i’s context
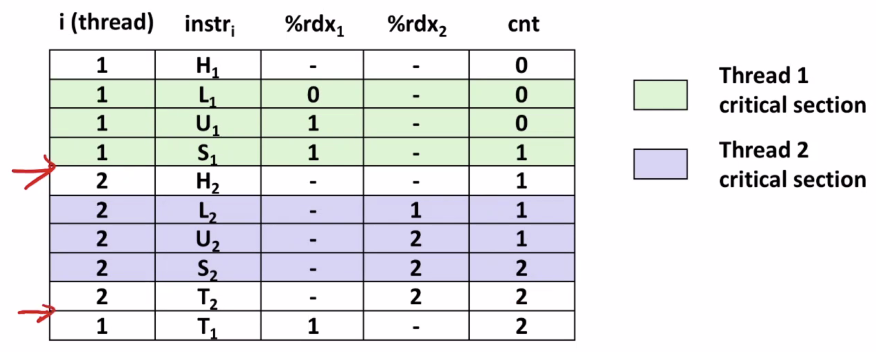
여기에서 문제가 발생한다. H->L->U->S->T 순으로 실행되기를 기대한다.
그래서 Thread1에서 cnt값을 바꾸어도 T 연산을 수행해야 하는데 여기에서 timer interrupt가 걸리어서 실재 cnt++를 다 수행못하고 context switch되어 Thread2로 제어권이 넘어간다.
그런데 우리의 예상과 다르게 작동하는 경우가 존재한다.
- Incorrect ordering: two threads increment the counter,
but the result is 1 instead of 2
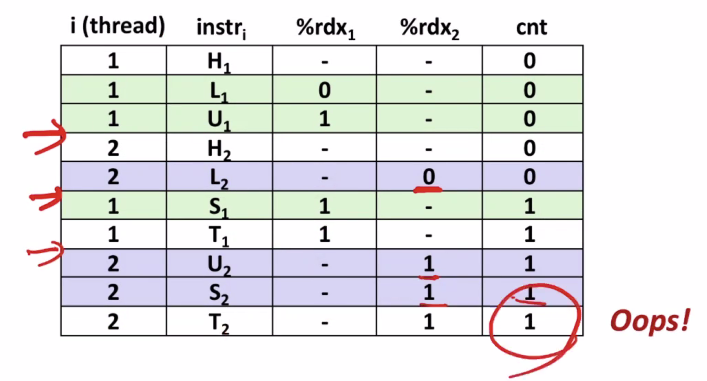
thread1이 s->l->u-> 하던중에 context switch가 일어난 경우이다. 두개의 thread가 실행되었지만 각각 ++하면 2가 되어야 하는데 1이 되어 있다.
-
How about this ordering?
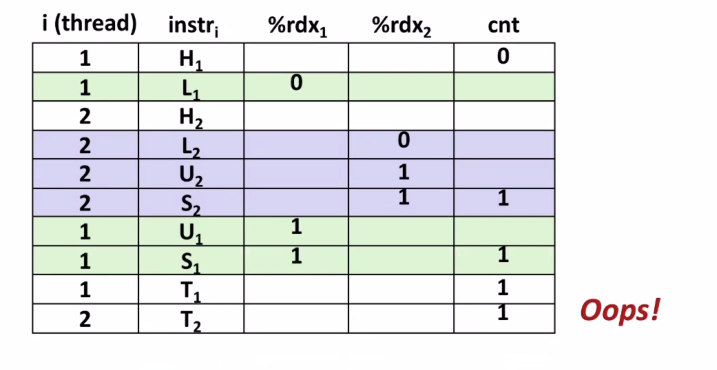
-
We can analyze the behavior using a progress graph
cnt++를 atomic하게 실행할 수 있다면 좋을거 같다.
