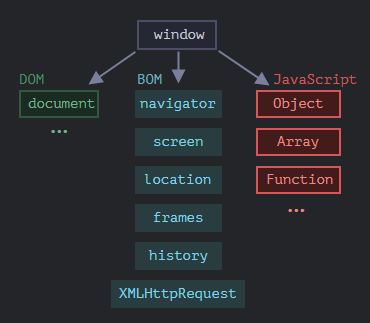
1.1 Browser environment, spacs
DOM(Document Object Model)
alert(window.innerHeight); // inner window height
// change the background color to red
document.body.style.background = "red";
// change it back after 1 second
setTimeout(() => document.body.style.background = "", 1000);BOM (Browser Object Model)
// i.g control BOM
alert(location.href); // shows current URL
if(confirm("Go to Wikipedia")) {
location.href = "https://wikipedia.org"; // redirect the browser to another URL
}- The functions alert/confirm/prompt are also part of the BOM
1.2 DOM tree
Other node type
- There are 12 node types. In practice we usually work with 4 of them:
- document - the “entry point” into DOM
- element nodes - HTML-tags, the tree building block.
- text nodes - contain text.
- cocmments - sometimes we can put information there, it won’t be shown, but JS can read it from the DOM.
Development tool in browser
- Subtab of Elements in development tools
- Styles: the current element
- Computed: the element by property
- Event Listeners: to see event listeners attached to DOM elements
Interaction with console
Now the last selected element is available as $0, the previously selected is $1 etc.
We can run commands on them. For instance, $0.style.background = 'red' makes the selected list item red, like this:
That’s how to get a node from Elements in Console.
There’s also a road back. If there’s a variable referencing a DOM node, then we can use the command inspect(node) in Console to see it in the Elements pane.