
edu day 34, 35
🚨이벤트 처리 (event handling)
js 이벤트 처리
- js 이벤트 모델
js 는 이벤트 드리븐(event-driven) 모델에 기반한다. 웹페이지 안에서 발생한 여러가지 사건(이벤트)에 따라 대응하는 방법을(이벤트 핸들러) 이용한 처리이다.
이벤트에 대응에 처리를 담당하는 함수를이벤트 핸들러😋라고 한다.
- 이벤트 발생 형태
- 애플리케이션 사용자가 발생시키는 이벤트
- 버튼클릭, 키보드 입력 등
- 애플리케이션 스스로가 발생시키는 이벤트
- 페이지 로드 등
- 애플리케이션 사용자가 발생시키는 이벤트
js 주요 이벤트 핸들러
모든 핸들러는 아니지만 주로 쓰이는 핸들러들만 작성했다.👍
| 이벤트 핸들러 | 기능 설명 |
|---|---|
onBlur | 입력 폼 양식을 다른 곳으로 이동하는 이벤트 |
onChange | 입력 폼 양식을 변경해주는 이벤트 |
onClick | 입력 폼 양식을 마우스로 클릭해주는 ㅣ |
onKeyUp | 사용자가 키를 눌렀다가 떼었을 때 발생하는 이벤트 |
onLoad | 이미지나 문서 프레임 등을 로드 시키는 이벤트 |
onMouseOut | 링크나 클라이언트 측에서 마우스를 옮기는 이벤트 |
onMouseOver | 마우스를 링크나 클라이언트 측으로 옮기는 이벤트 |
onSubmit | 폼을 보내는 이벤트 |
onFocus | 문서나 윈도우, 폼 요소 등에 입력 포커스를 설정하는 이벤트 |
이벤트와 이벤트 핸들러 연결 [이벤트 모델]
이벤트 모델의 핵심은 이벤트와 이벤트 핸들러이다.
HTML의 어떤 요소에서 발생하는 이벤트에 대해서 어떤 이벤트 핸들러를 사용할지를 정해서 구현한다.
- js에서 이벤트와 이벤트 핸들러를 연결하기 위한 방법
- DOM Level 0
인라인 이벤트 모델, 고전 이벤트 모델
- DOM Level 2
표준 이벤트 모델 방법이다.
- DOM Level 0
😮위의 방법 말고 시작은 <button>, <input="text"> 태그 등에서 바로 접근할 수 있다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function init(){
console.log("모든 html이 모두 DOM으로 생성된후 실행");
}
function xxx(){
console.log("onclick");
}
function yyy(){
console.log("onmouseover");
}
function zzz(){
console.log("onmouseout");
}
function kkk(x){
console.log(x);
}
function xyz(e){
console.log(e);
console.log(e.screenX, e.screenY);
console.log(event);
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="init()">
<button onclick = "xxx()" onmouseover="yyy()" onmouseout="zzz()">클릭</button>
<input type="text" name = "userid" onkeyup = "kkk(this.value)">
<button onclick="xyz(event)">이벤트 정보</button>
</body>
</html>--> body부분에 <onload="init()"> 옵션을 넣어 연결하고, 이벤트를 사용할 태그에 핸들러를 추가한다.
Dom Level 0
👍Dom Level 0 에서 제공하는 이벤트 핸들러의 이름은 주요 이벤트명 앞에 on접두사를 지정하여 사용된다.
ex) onload, onclick, onfocus, onblur, onchange, onkeyup, onmouseover 등
- 고전 이벤트 모델
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
//고전 이벤트
window.onload = init; //함수 등록
//window.onload = init();은 안됨
function init(){
console.log("모든 html이 모두 DOM으로 생성된 후 실행");
//xxx에 클릭이벤트 핸들러 붙인 후 처리할 익명 함수 구현
document.getElementById("xxx").onclick = function(){
console.log("clicked");
};
//xxx onmouseover핸들러 -> console.log("mouseover");
document.getElementById("xxx").onmouseover=function(){
console.log("onmouseover");
};
// xxx onmouseover핸들러 -> console.log("mouseover");
document.getElementById("xxx").onmouseout=function(){
console.log("onmouseout");
};
document.getElementById("userid").onkeyup=function(){
console.log(this.value);
}
document.getElementById("xyz").onclick=function(){
console.log(event.screenX, event.screenY); //매개변수 없이 사용가능
}
} //end init
</script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 이벤트 처리 코드가 없음 -->
<button id="xxx">클릭</button>
<input type="text" name="userid" id="userid">
<button id="xyz">이벤트 정보</button>
</body>
</html>--> <body>에서 직접 접근한 것과 달리 <script> 태그에서 <body>의 태그에 이벤트를 지정하여 사용한다.
- 특징 (인라인 이벤트, 고전 이벤트 모델에 공통 적용)
- 각 요소에 이벤트 타입별로 하나의 이벤트 핸들러만 연결할 수 있다.
- 이벤트 핸들러 내에서 이벤트 발생 객체를 사용하려면
this를 사용한다.
- 이벤트 핸들러 내에서 발생된 이벤트의 정보를 담고 있는 이벤트 객체를 사용하려면 핸들러 함수의 파라미터로 전달받는다. (IE 8 이하는
window.event사용)
- 요소에 등록되어 있는 기본 이벤트 핸들러를 해제하려면 이벤트 핸들러 함수에서 마지막에
false를 되돌린다.
- 고전 이벤트 모델은 요소에 연결된 이벤트 핸들러를 해제할 수 있지만 인라인 이벤트 모델은 해제할 수 없다.
- 각 요소에 이벤트 타입별로 하나의 이벤트 핸들러만 연결할 수 있다.
DOM Level 2
2000년 11월 W3C에서 이벤트 처리 표준안으로 발표했다.
IE에서는 9버전부터 지원된다.
함수의 파라미터로 이벤트 정보가 전달된다.
- 표준 이벤트 모델
--> 연결
addEventListener( eventName, handler, useCapture )
--> 해제
removeEventListener( eventName, handler )
- useCapture
- false : 기본값, 이벤트 버블링으로 이벤트 전파
- true : 이벤트 캡쳐링으로 이벤트 전파
DOM Level 0에서 사용한 on접두사를 빼고 addEventListener( eventName, handler, useCapture ) 형식으로만 바꾸면 로직은 같다.
- 특징 (표준 이벤트 모델에 적용)
- 각 요소에 이벤트 타입별로 여러 개의 이벤트 핸들러를 연결할 수 있다.
- 이벤트 핸들러 내에서 이벤트 발생 객체를 사용하려면
this를 사용한다. ( IE 8 이하에서는window.srcElement를 사용한다.
- 이벤트 핸들러 내에서 발생된 이벤트의 정보를 담고 있는 이벤트 객체를 사용하여면 핸들러 함수의 파라미터로 전달받는다. ( IE 8 이하는
window.event사용)
- 요소에 등록되어 있는 기본 핸들러를 해제하려면 이벤트 객체의
preventDefault()를 호출한다. ( IE 8 이하는windowevent.returnValue = false;를 사용한다.
- 각 요소에 이벤트 타입별로 여러 개의 이벤트 핸들러를 연결할 수 있다.
폼을 전송할 수 있는 이벤트 (submit)의 다양한 전송 방법
폼을 이용하여 데이터를 전송하는 작업을 onsubmit을 사용하여 다양한 방법으로 할 수 있다.
- 단순 인라인 방식 처리
<form action="target.html" onsubmit="xxx()">- return을 이용한 방식
<form action="target.html" onsubmit="return xxx2()"> function xxx2(){ //return false 이용 제출 금지
var id = document.getElementById("userid2").value;
var passwd = document.getElementById("passwd2").value;
var result = false; //호출곳으로 리턴시킬 boolean 값
if(id.length >= 3 && passwd.length != 0){
result = true; //계속 진행 제출
}else{
result = false; //진행 금지
alert("xxx2 에러");
}
return result; // true, false 선택 리턴
//return false
}--> boolean형태의 리턴값으로 action을 할 것인지 아닌지 가능
- ❗
event.preventDefault();를 이용한 방식
(❗해당 방법을 가장 권장❗)
<form action="target.html" onsubmit="xxx3()"> --> 인라인 방식과 똑같이 호출하되, xxx3() 함수에서 처리한다.
function xxx3(){ //event를 매개변수로 받음
var id = document.getElementById("userid3").value;
var passwd = document.getElementById("passwd3").value;
console.log(id, "\t", passwd);
if(id.length != 0 && passwd.length != 0){
alert("xxx3제출");
}else{
alert("xxx3에러");
event.preventDefault();
}
}event.preventDefault(); 는 기능의 사용을 원치 않는 경우(조건문 작성)에 그 이벤트 기능을 삭제하는 기능을 한다.
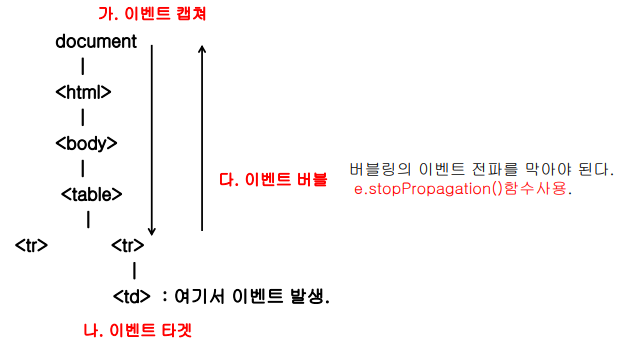
✨이벤트 전파 개념
이벤트가 처음 발생되면 DOM의 최상위 객체인 document객체로 이벤트가 전달된다.
js에서는 발생된 이벤트를 다음 과정을 거쳐 전파시킨다.
- 이벤트 캡쳐(캡쳐링)
document부터 아래로 내려가서 이벤트 발생 요소의 부모객체까지 전달되는 것을 의미
- 이벤트 타겟
이벤트 발생요소까지 전달
- 이벤트 버블(버블링): JavaScript의 기본 처리 방식
이벤트 발생요소의 부모로부터 위로 document까지 거슬러 올라가는 것을 의미한다.
- 코드로 증명해보기
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload = function(){
var a = document.getElementById("a");
var b = document.getElementById("b");
a.addEventListener("click", function(){
console.log("a click");
}, false);
b.addEventListener("click", function(){
console.log("b click");
}, false);
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id = "a" style = "background-color : #ff0000">
a
<div id = "b" style = "background-color: #00ff00">
b
<!-- window.onload, b addEventListener 사용 -->
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>b를 클릭하면 콘솔창에 b click 후 a click이 출력된다.
b부분의 핸들러 함수에 event.stopPropagation(); 메서드를 넣으면 b click만 출력되고 a click이 출력되지 않는다.