09. 너비 우선 탐색
너비 우선 탐색의 정의
- Breadth First Search는 너비를 우선으로 하여 탐색하는 알고리즘
- 맹목적으로 전체 노드를 탐색할 때 사용
- 큐 자료구조에 기초
고급 그래프 탐색 알고리즘에 자주 활용
너비 우선 탐색의 과정
- 탐색 시작 노드를 큐에 삽입하고 방문 처리
- 큐에서 노드를 꺼내 해당 인접 노드 중 방문하지 않은 노드들을 모두 큐에 삽입 후 방문 처리
- 위 과정을 수행 할 수 없을 때까지 반복
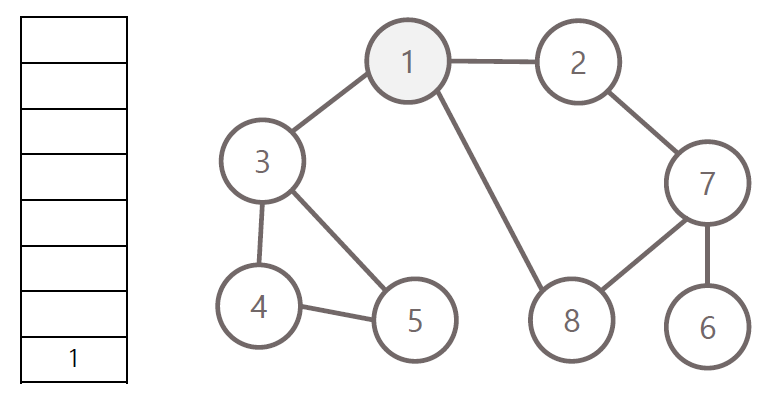
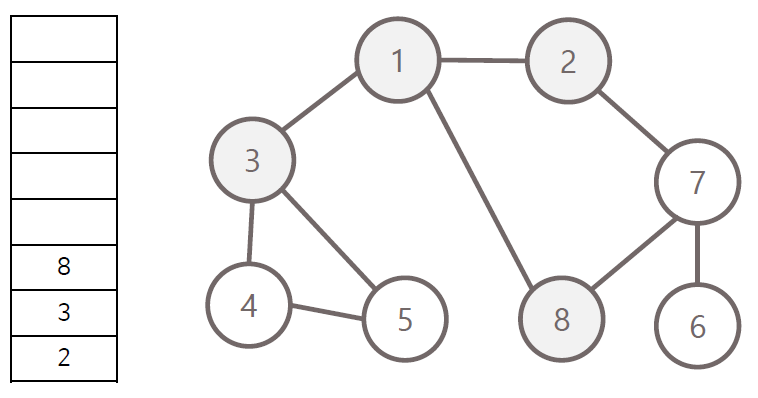
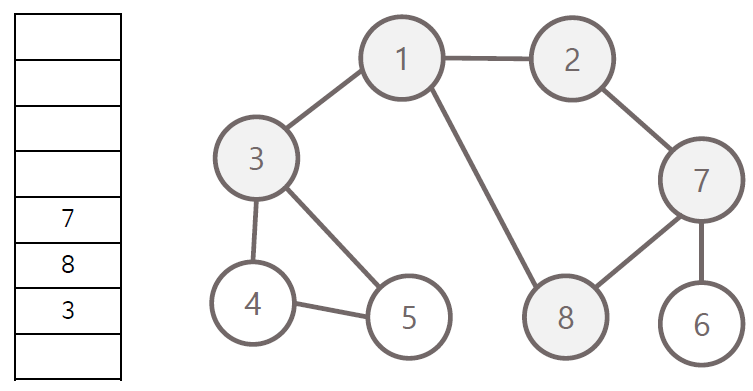
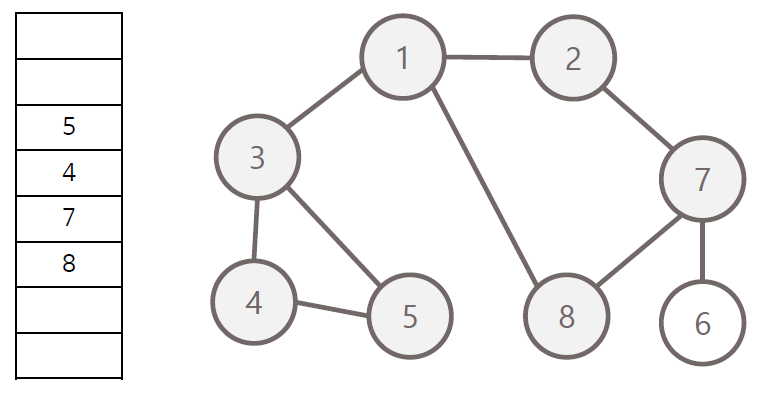
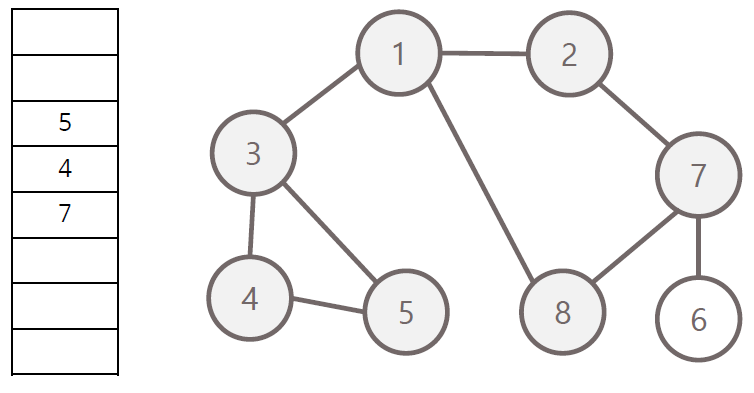
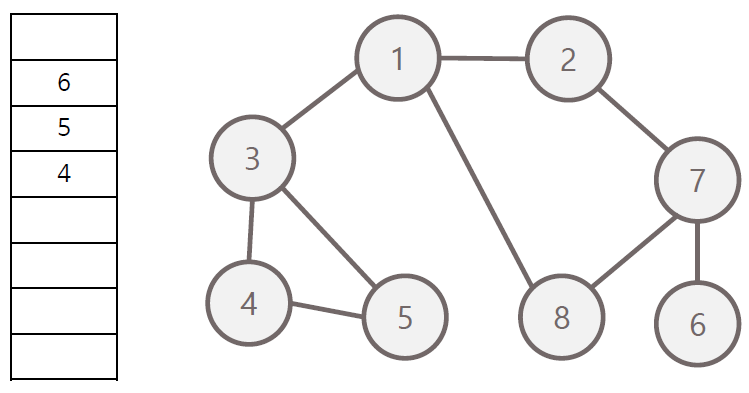
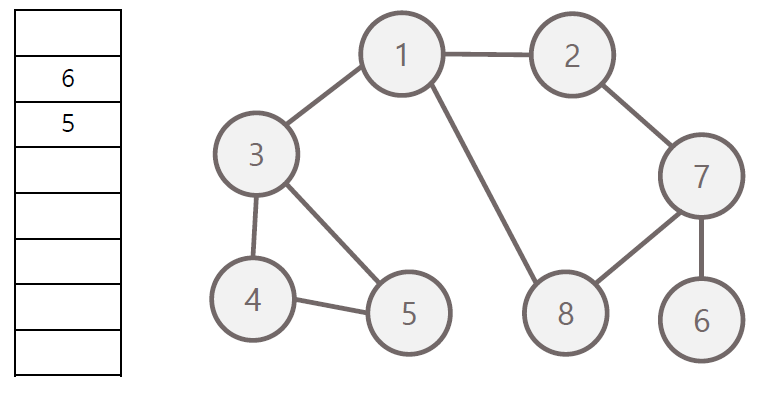
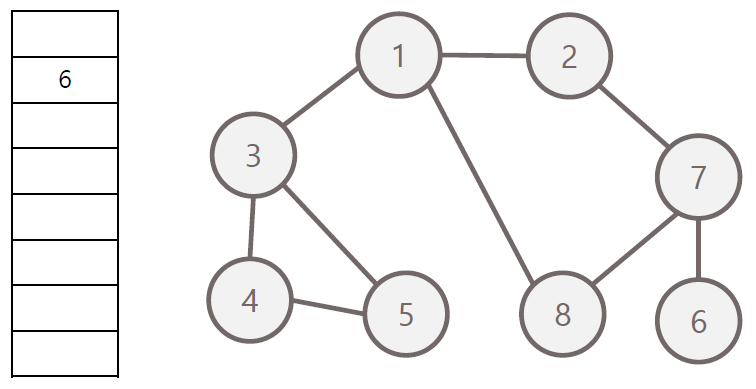
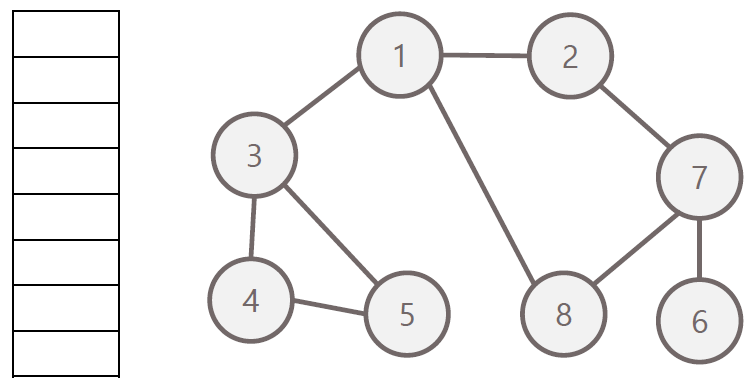
방문 순서 : 1 - 2 - 3 - 8 - 7 - 4 - 5 - 6
너비 우선 탐색의 구현
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define INF 99999999
#define MAX_SIZE 1001
// 노드 구현
typedef struct {
int index;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
// 큐 구현
typedef struct {
Node* front;
Node* rear;
int count;
} Queue;
// 연결 리스트
Node** a;
// 정점과 간선, 방문여부
int n, m, c[MAX_SIZE];
// 연결 리스트 삽입 함수
void addFront(Node* root, int index) {
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->index = index;
node->next = root->next;
root->next = node;
}
// 큐 삽입 함수
void queuePush(Queue* queue, int index) {
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->index = index;
node->next = NULL;
if (queue->count == 0) queue->front = node;
else queue->rear->next = node;
queue->rear = node;
queue->count++;
}
// 큐 추출 함수
int queuePop(Queue* queue) {
// 큐 비어있을 경우
if (queue->count == 0) {
printf("Queue underflow");
return -INF;
}
Node* node = queue->front;
int index = node->index;
queue->front = node->next;
free(node);
queue->count--;
return index;
}
// 너비 우선 탐색
void bfs(int start) {
// 큐 초기화
Queue q;
q.front = q.rear = NULL;
q.count = 0;
// 해당 정점 시작
queuePush(&q, start);
c[start] = 1;
while (q.count != 0) {
int x = queuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", x);
Node* cur = a[x]->next;
while (cur != NULL) {
int next = cur->index;
// 방문 처리 안된 인접 노드 큐 삽입 및 방문 처리
if (!c[next]) {
queuePush(&q, next);
c[next] = 1;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
}
}
// 방문 순서에 대해서는 기준 정립 x
int main(void) {
// 정점과 간선 입력
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
a = (Node**)malloc(sizeof(Node*) * (MAX_SIZE));
// 초기화
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
a[i] = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
a[i]->next = NULL;
}
// 정점들을 연결하는 간선 입력
for (int i = 0;i < m;i++) {
int x, y;
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
addFront(a[x], y);
addFront(a[y], x);
}
bfs(1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}BFS는 큐 자료구조에 기초해 구현이 간단 탐색을 수행함에 O(N)의 시간 소요
cf. 일반적으로 실제 수행 시간은 DFS보다 좋음
