12. 프림 알고리즘
최소 신장 트리
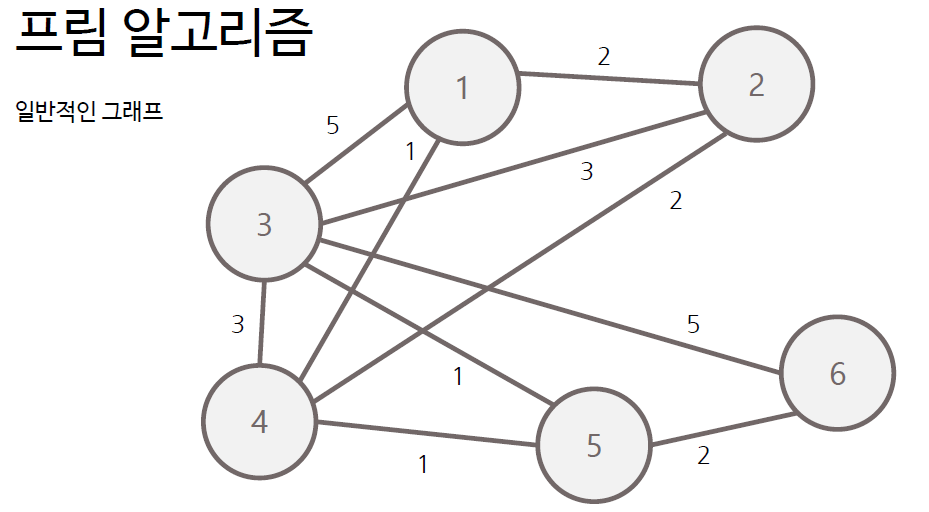
- 신장 트리란 특정한 그래프에서 모든 정점을 포함하는 그래프
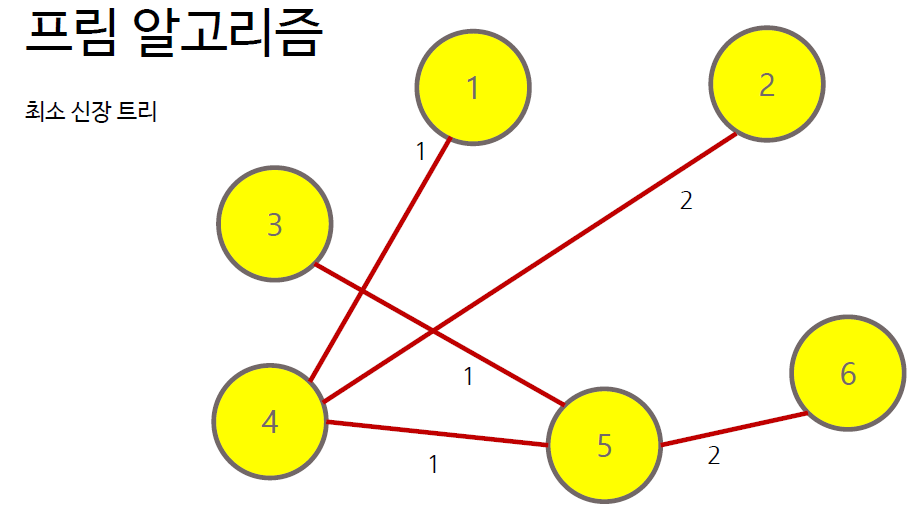
- 최소 신장 트리는 스패닝 트리 중에서 간선의 가중치 합이 가장 작은 트리
프림 알고리즘의 순서
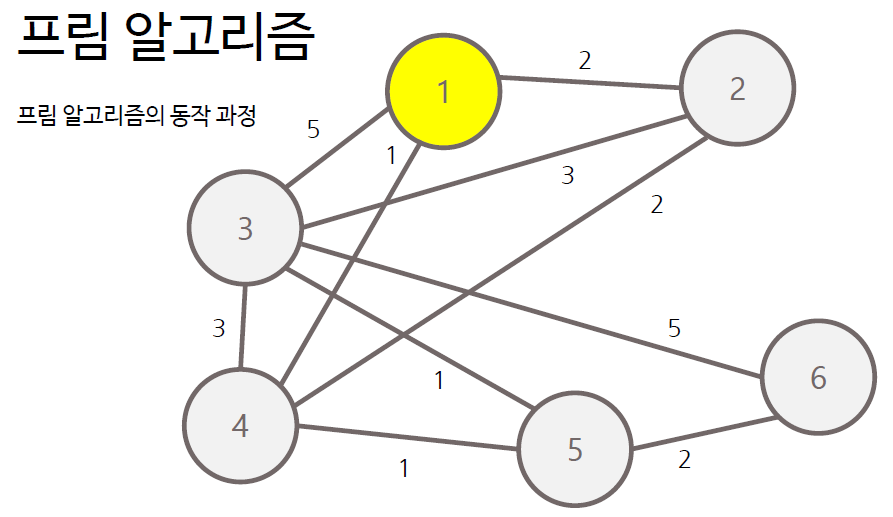
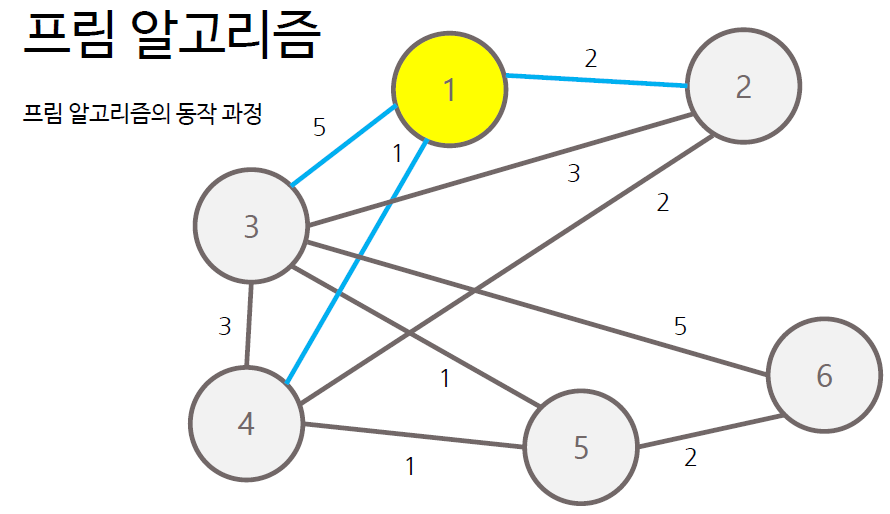
- 그래프에서 정점 하나를 선택하여 트리 T에 포함
- T에 포함된 노드와 T에 포함되지 않는 노드 사이의 간선 중 가중치가 가장 작은 간선 찾기
- 해당 간선에 연결된 T에 포함되지 않은 노드를 트리 T에 포함
- 모든 노드가 포함될 때까지 과정 반복
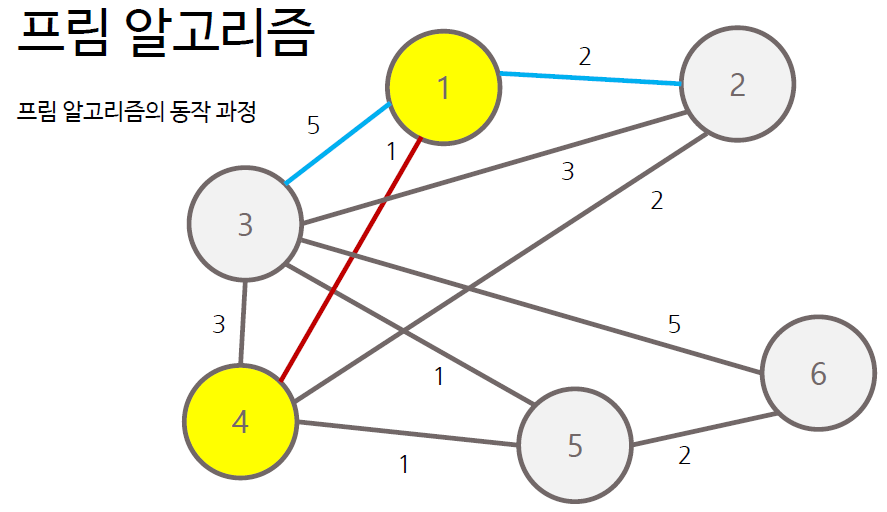
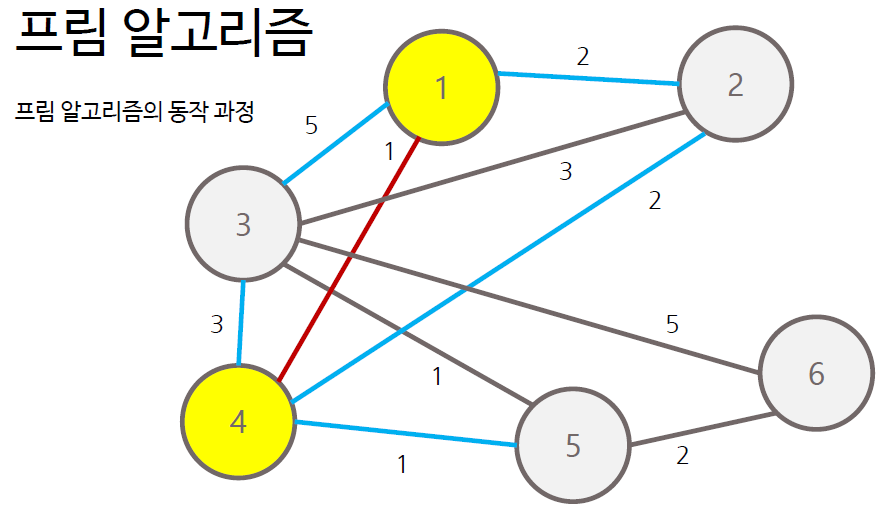
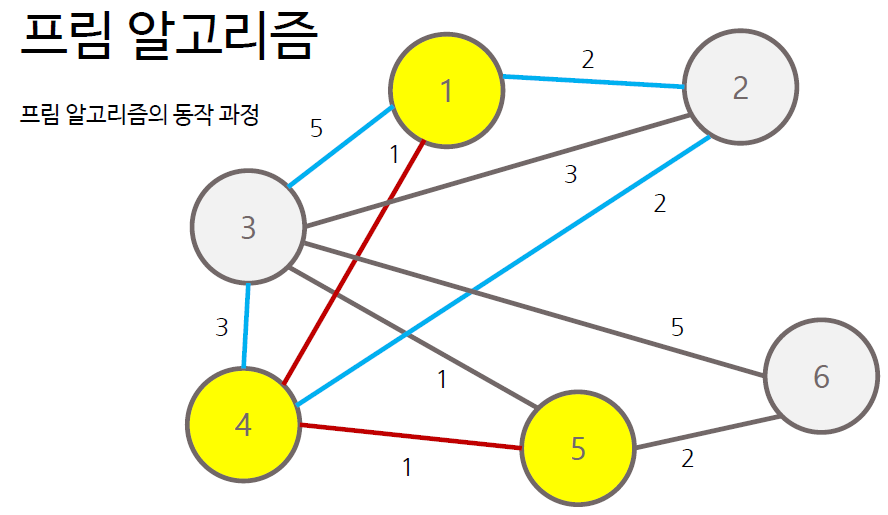
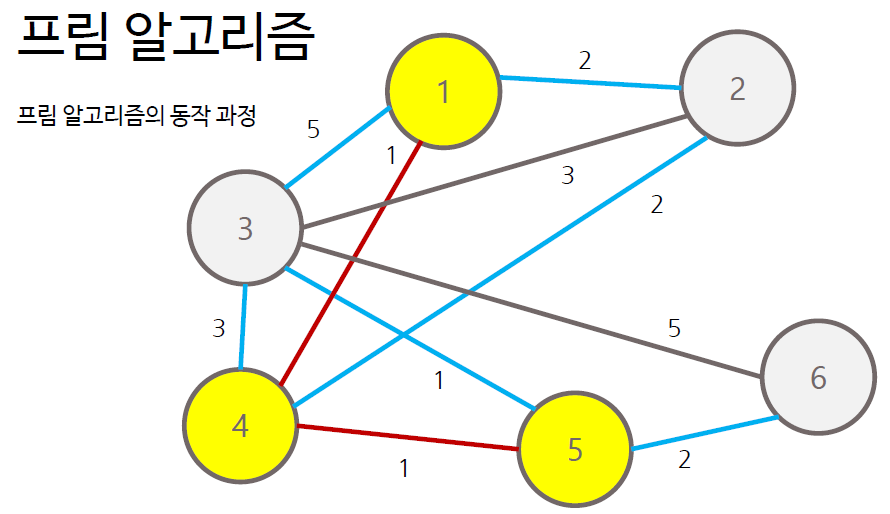
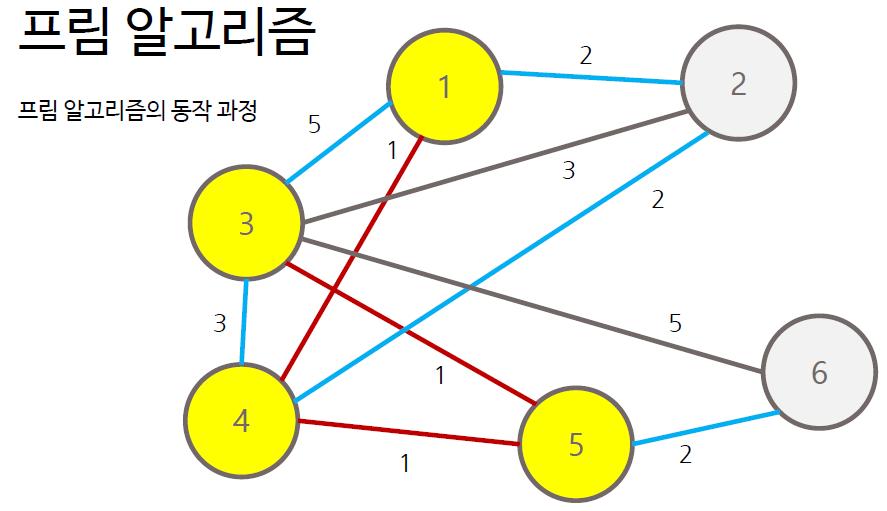
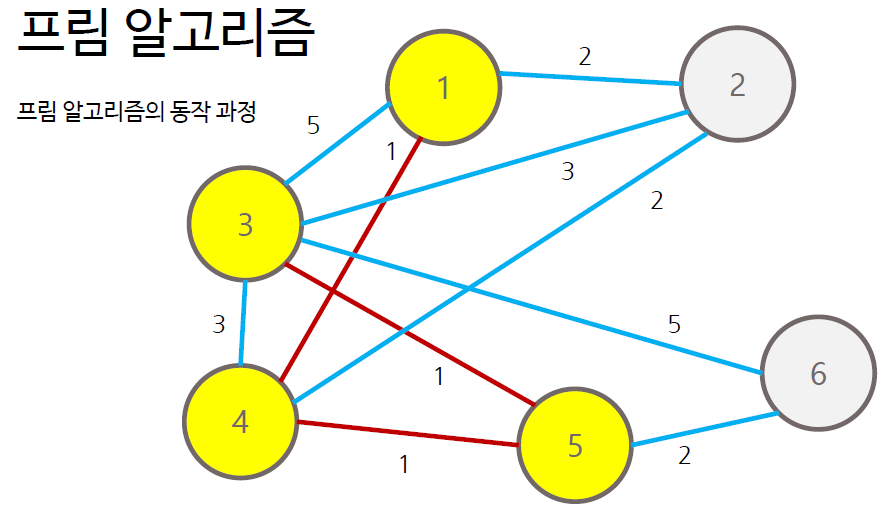
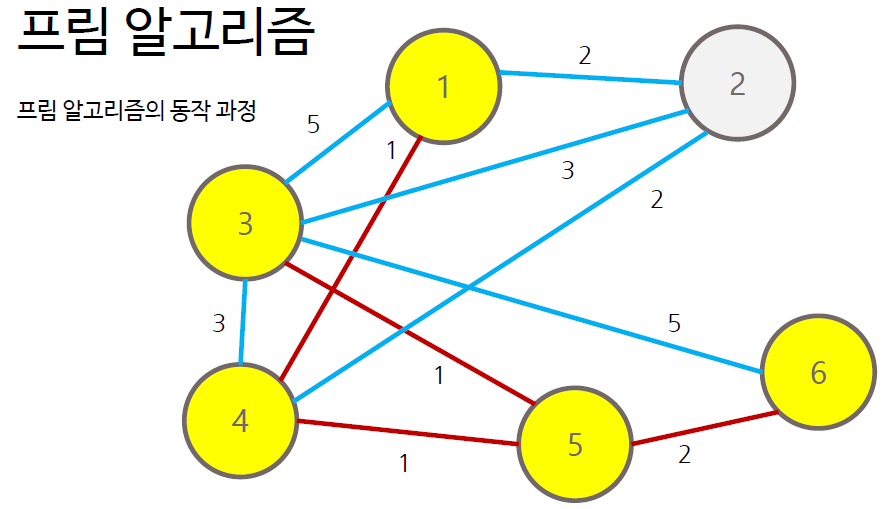
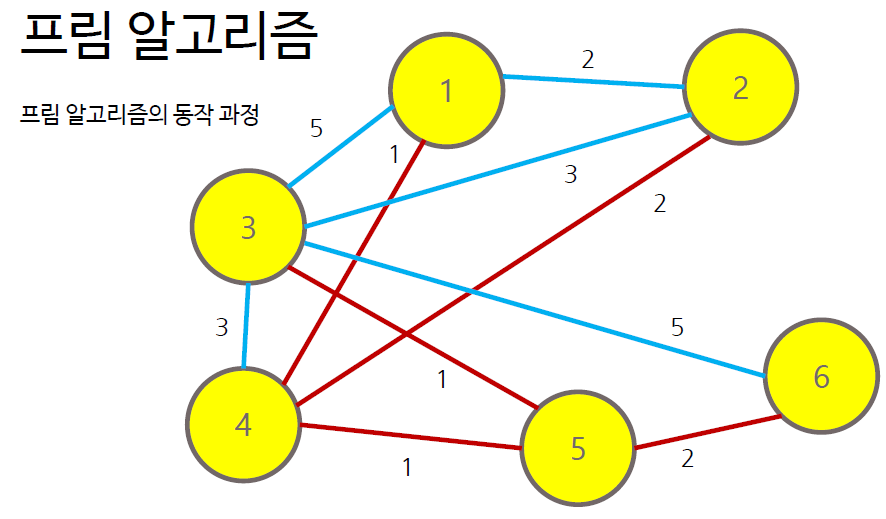
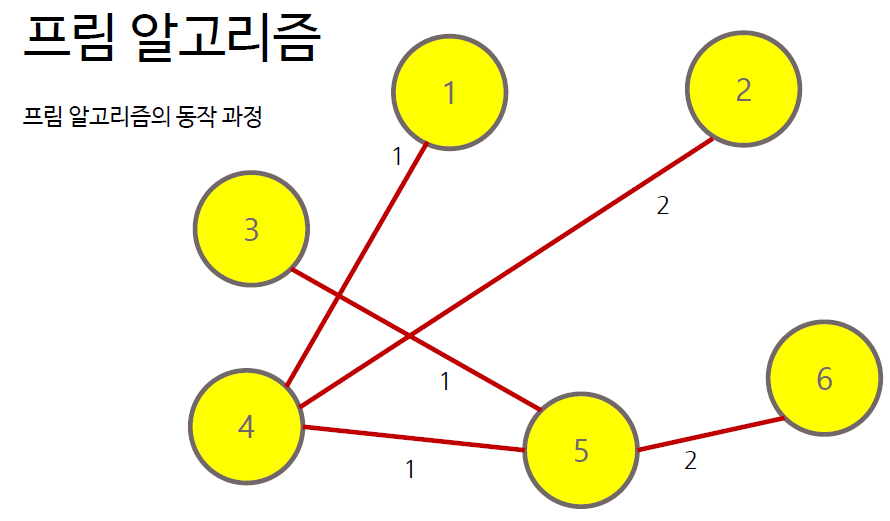
프림 알고리즘은 각 간선에 대한 정보를 우선순위 큐에 담아 처리하는 방식으로 구현
프림 알고리즘의 구현
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
#define NODE_MAX 1001
#define EDGE_MAX 200001 // 양방향 간선이므로 100,000 개 * 2
// 간선구조체 정의
typedef struct {
int cost;
int node;
} Edge;
// 교환 함수
void swap(Edge* a, Edge* b) {
Edge temp;
temp.cost = a->cost;
temp.node = a->node;
a->cost = b->cost;
a->node = b->node;
b->cost = temp.cost;
b->node = temp.node;
}
// 우선 순위 큐
typedef struct {
int heap[EDGE_MAX];
int count;
} priorityQueue;
// 삽입 함수
void push(priorityQueue* pq, Edge *edge) {
if (pq->count >= EDGE_MAX) return;
pq->heap[pq->count] = edge;
int now = pq->count;
int parent = (pq->count - 1) / 2;
// 새 원소 삽입 후 상향식으로 힙 구성
while (now > 0 && pq->heap[now]->cost < pq->heap[parent]->cost) {
swap(pq->heap[now], pq->heap[parent]);
now = parent;
parent = (parent - 1) / 2;
}
pq->count++;
}
// 추출 함수
int pop(priorityQueue* pq) {
if (pq->count <= 0)return NULL; // 더 이상 추출할 것이 없을 경우
Edge* res = pq->heap[0]; // 루트 노드 값을 담아 둠
pq->count--;
pq->heap[0] = pq->heap[pq->count]; // 마지막 원소를 루트 노드로 넣음
int now = 0, leftChild = 1, rightChild = 2;
int target = now;
// 새 원소 추출 후 하향식으로 힙 구성
while (leftChild < pq->count) {
if (pq->heap[target]->cost > pq->heap[leftChild]->cost)target = leftChild;
if (pq->heap[target]->cost > pq->heap[rightChild]->cost && rightChild < pq->count) target = rightChild;
if (target == now) break; // 더 이상 내려가지 않아도 될 때 종료
else {
swap(pq->heap[now], pq->heap[target]);
now = target;
leftChild = now * 2 + 1;
rightChild = now * 2 + 2;
}
}
return res;
}
// 간선 연결 리스트 구현
typedef struct Node {
Edge* data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
Node** adj;
int d[NODE_MAX];
void addNode(Node** target, int index, Edge* edge) {
if (target[index] == NULL) {
target[index] = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
target[index]->data = edge;
target[index]->next = NULL;
}
else {
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = edge;
node->next = target[index];
target[index] = node;
}
}
// main
int main(void) {
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
adj = (Node**)malloc(sizeof(Node*) * (n + 1));
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
adj[i] = NULL;
}
priorityQueue* pq;
pq = (priorityQueue*)malloc(sizeof(priorityQueue));
pq->count = 0;
for (int i = 0;i < m;i++) {
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
Edge* edge1 = (Edge*)malloc(sizeof(Edge));
edge1->node = b;
edge1->cost = c;
addNode(adj, a, edge1);
Edge* edge2 = (Edge*)malloc(sizeof(Edge));
edge2->node = a;
edge2->cost = c;
addNode(adj, b, edge2);
}
// 프림 알고리즘 시작
long long res = 0;
Edge* start = (Edge*)malloc(sizeof(Edge));
start->cost = 0;
start->node = 1;
push(pq, start);
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++) {
int nextNode = -1, nextCost = INT_MAX;
while (1) {
Edge* now = pop(pq);
if (now == NULL) break;
nextNode = now->node;
if (!d[nextNode]) {
nextCost = now->cost;
break;
}
}
if (nextCost == INT_MAX) printf("연결 그래프가 아닙니다.\n");
res += nextCost;
d[nextCost] = 1;
Node* cur = adj[nextCost];
while (cur != NULL) {
push(pq, cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
system("pause");
return 0;
}프림 알고리즘은 최소 스패닝 트리를 구하는 과정에서 O(E log V)의 시간 복잡도를 가짐
E : 모든 간선의 정보를 큐에 넣어서 처리하는 데 필요한 시간 복잡도
log V : 큐에서 원소를 꺼낼 때 필요한 시간 복잡도
