label 태그
label의 for과 input의 name을 연결하면 된다!
label 태그는 두 가지 사용법이 있다.
- 텍스트의 설명과 input을 모두 포함하는 방식
<label
이름 :
<input type="text" name="이름">
</label>- input과 분리하여 label의 for와 input 의 name를 연결하는 방식
<label for="myName">이름 : </label>
<input type="text" name="이름" id="myName">동의하지 않음에 checked가 되어 있어서 동의합니다를 누르고 넘어갈 수 있도록 유도하는 센스!!
<label>
<input type="radio" name="terms1">
<span>약관에 동의합니다</span>
</label>
<label>
<input type="radio" name="terms1" checked>
<span>약관에 동의하지 않습니다.</span>
</label>table 태그
th : 테이블 헤딩(제일 윗 부분에 제목 들어가는 부분의 하나의 데이터)
td: 테이블 데이터(테이블 안에 들어가는 하나의 데이터)
tr: 테이블 row (테이블의 행)
colspan : rowspan 은 합치는 것
colspan : column의 경계선이 합쳐지는 것 → 옆으로 합치기
rowspan : row의 경계선이 합쳐지는 것 → 세로로 합치기
thead : 머리글
tbody : 본문
tfoot : 바닥
생략하지 말고 꼭 쓰기→ js로 다 컨트롤 함.
큰 기능이 있는 것은 아님. div 같은 애래.
- caption : 표의 제목, 설명
colgroup : 표의 열을 묶는 그룹을 정의합니다.
<예시1>
<!-- table>(tr>th*3)+(tr>td*3)*3 -->
<caption> <!--설명을 넣어도 되고 제목을 넣어도 됨-->
이 table은 영국에서 최초로 시작되어...
</caption>
<colgroup>
<col class="구분">
<col class="이름">
<col class="판매량">
</colgroup>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>구분</th>
<th>책이름</th>
<th>책가격</th>
<th>책 판매량</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>1</td>
<td>hello1</td>
<td>1,000</td>
<td>1</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2</td>
<td>hello2</td>
<td>2,000</td>
<td>2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>3</td>
<td>hello3</td>
<td>3,000</td>
<td>3</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td colspan="3">총 판매량</td>
<td>6</td>
</tr>
</tfoot>
</table>
| 구분 | 책이름 | 책가격 | 책 판매량 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hello1 | 1,000 | 1 |
| 2 | hello2 | 2,000 | 2 |
| 3 | hello3 | 3,000 | 3 |
| 총 판매량 | 6 |
<예시2>
<table>
<caption>Color names and values</caption>
<tbody>
<tr>
<th scope="col">Name</th>
<th scope="col">HEX</th>
<th scope="col">HSLa</th>
<th scope="col">RGBa</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">Teal</th>
<td><code>#51F6F6</code></td>
<td><code>hsla(180, 90%, 64%, 1)</code></td>
<td><code>rgba(81, 246, 246, 1)</code></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">Goldenrod</th>
<td><code>#F6BC57</code></td>
<td><code>hsla(38, 90%, 65%, 1)</code></td>
<td><code>rgba(246, 188, 87, 1)</code></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>| Name | HEX | HSLa | RGBa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Teal | #51F6F6 |
hsla(180, 90%, 64%, 1) |
rgba(81, 246, 246, 1) |
| Goldenrod | #F6BC57 |
hsla(38, 90%, 65%, 1) |
rgba(246, 188, 87, 1) |
fieldset, legend 태그
the fieldset element provides a grouping for a part of an HTML form
form 태그 안에서 연관된 것들끼리 묶어주는 역할.
legend 태그는 fieldset 의 설명 혹은 제목 역할을 한다.
<form>
<fieldset>
<legend>Choose your favorite monster</legend>
<input type="radio" id="kraken" name="monster">
<label for="kraken">Kraken</label><br/>
<input type="radio" id="sasquatch" name="monster">
<label for="sasquatch">Sasquatch</label><br/>
<input type="radio" id="mothman" name="monster">
<label for="mothman">Mothman</label>
</fieldset>
</form> <form>
<fieldset oninput="볼륨.value=parseInt(볼륨바.value)"> <!--여기는 js-->
<legend>볼륨바</legend>
<input id="볼륨바" name="bar" type="range" title="범위선택">
<output name="볼륨" title="볼륨표시">0</output>
</fieldset>
</form> <form>
<fieldset>
<legend>Programming Skill</legend>
<label for="html">HTML</label>
<progress id="html" value="0.85" max="1">85%</progress><br>
<label for="css">CSS</label>
<progress id="css" value="0.85" max="1">85%</progress><br>
<label for="javascript">Javascript</label>
<progress id="javascript" value="0.35" max="1">35%</progress><br>
</fieldset>
</form>progress 태그는 어느 작업의 진행정도를 나타낸다.
shadow DOM
DOM
html 문서의 구조화된 표현이다. 브라우저가 페이지에 무엇을 렌더링 할지 결정하기 위해, 혹은 자바스크립트 프로그램이 페이지의 콘텐츠 및 구조, 스타일을 수정하기 위해 사용된다.
다음은 DOM 트리이다.
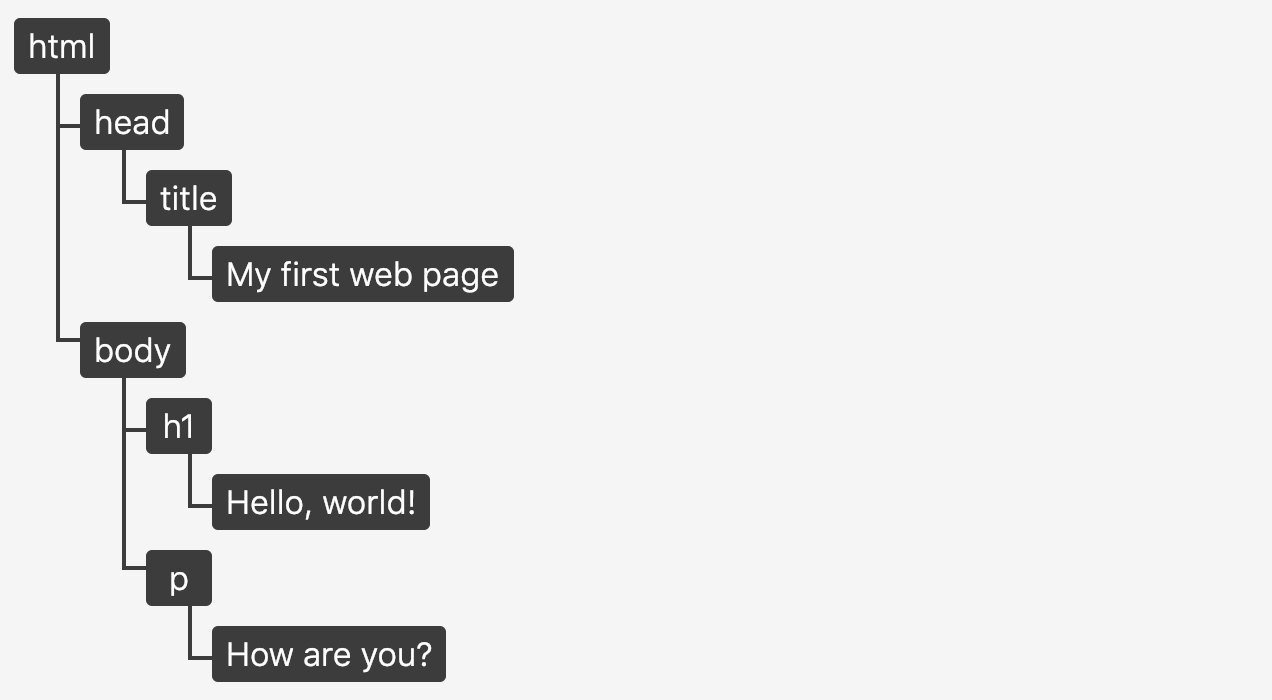
shadow DOM 과 virtual DOM 이라는 용어가 있는데, DOM과 관련이 있지만 매우 다른 개념을 가리킨다.
Shadow DOM
DOM도 이해를 못했는데 shadow DOM을 언급하셔서.. 찾아봤지만 이해하진 못했다.. https://wit.nts-corp.com/2019/03/27/5552
추후에 다시 공부하는 걸로
Entity code
https://www.toptal.com/designers/htmlarrows/symbols/snowman/
https://dev.w3.org/html5/html-author/charref
html 마크업
내가 과제로 했던 마크업
https://github.com/vnfdusdl/html/blob/main/assignment_1.html
한 분이 공유해주신 마크업
https://dreamfulbud.notion.site/Korea-Startup-Forum-fd449e924ad44582ab3df082233b5f69
오늘 강사님과 함께 해본 마크업
https://github.com/vnfdusdl/html/blob/main/assignment_1_feedback.html
배운 점 정리
- h1은 body 전체에 하나 쓴다고 생각하면 된다.
- li 안에도 ul이 얼마든지 올 수 있다. 예를들어, nav bar 만들 때
- 버튼을 만드는 경우 a태그로만 만들기도 하고 이를 button으로 감싸주기도 한다.
- br 태그가 문장 안에 있으면 스크린리더기가 제대로 읽지를 못한다. 그리고 반응형 웹사이트에서도 문제가 되는 경우가 있다. 그래서 문장 안에서는 br 태그를 잘 사용하지 않는다. 대신 다른 태그를 넣고 css로 처리한다.
- section과 article에는 heading 태그를 넣어주는 게 좋다. 웹 페이지에서는 안 보이도록 css 처리를 하더라도! 스크린리더가 읽을 수 있도록
- href안에 mailto: 나 telto:를 붙여주면 클릭했을 때 메일을 보내거나 전화를 걸 수 있다.
<a href="mailto:hi@kstartupforum.org">hi@kstartupforum.org</a>
<a href="tel:02-6211-9400">02-6211-9400</a>- small 태그는 덧붙이는 글이나, 저작권과 법률 표기 등의 작은 텍스트를 나타낸다.
<small>
Copyright 2021. Korea Startup Forum. all rights reserved.
</small>CSS
- 내부 css : head에
<style>를 사용 - 외부 css :
<link rel="stylesheet" href="">으로 외부 css파일 연결 혹은<style>@import url ("016.css");</style> - 인라인 css :
<h1 style="color:red;">hello world</h1>
우선 순위: 인라인 > 내부 > 외부
선택자
1. 하위 선택자
하위 선택자는 선택자 사이를 공백을 사용하여 나타낸다. 앞 요소의 자손인 뒤 요소를 선택한다.
예를 들어 이 태그는 section 아래 있는 모든 ul태그를 가리키기 때문에 바로 아래 자식을 선택할 때에는 자식선택자를 사용한다.
section ul {
text-shadow: none;
}2. 자식 선택자
하위 선택자는 선택자 사이를 > 를 사용하여 나타낸다. 앞 요소의 자식 인 뒤 요소를 선택한다.
section > ul {
text-shadow: none;
}자손은 자식 을 포괄하는 의미이다. 자손은 모든 하위 요소를 의미하고 자식은 바로 아래의 하위 요소만을 뜻한다.
3. 인접 형제 선택자
인접 형제 선택자는 선택자 사이를 + 를 사용하여 나타낸다. + 를 기준으로 앞 요소 직후에 나오는 뒷 요소를 선택한다.
h1 + ul {
color: red;
}h1과 ul 둘 다를 선택하는 게 아니라 ul만을 선택하는 것.
둘 다 선택하려면 h1, ul {} 이렇게 쓰겠징
4. 일반 형제 선택자
일반 형제 선택자는 선택자 사이에 ~ 를 사용하여 나타낸다. ~ 을 기준으로 앞 요소 이후에 나오는 모든 뒤 요소를 선택한다.
h1 ~ ul {
color: red;
}h1태그 뒤에 나오는 모든 ul태그를 선택하는 거.
형제 선택자는 같은 부모를 가지는 요소들을 말한다.
5. 속성 선택자
a[title] { }
a[href="https://example.com"] { }
<a href="http://www.paullab.co.kr">이동햇!</a>input[type="text"] : input 엘리먼트 중 type 속성의 값이 text인 엘리먼트를 선택.
태그의 이름, 클래스 이름, ID 이름 외에도 속성으로 접근할 수 있다. 이를 속성 선택자 라고 한다.
5.1 태그[속성이름]
속성이름 에 해당되는 속성을 가진 태그를 모두 선택한다.
a[href] {
font-size: 10px;
}a 태그 중 href를 가진 모든 태그를 선택
5.2 태그[속성이름="변수"]
속성이름 의 속성값이 변수와 일치하는 태그를 선택한다.
a[href="http://www.paullab.co.kr"] {
font-size: 32px;
}5.3 태그[속성이름~="변수"]
속성이름 의 속성값이 변수 를 포함하는 태그를 선택한다. (단어)
속성값이 정확히 '변수'인 요소를 선택한다.
a[href~="paullab"] {
color: black;
}5.4 태그[속성^="변수"]
속성 의 속성값이 변수 로 시작하는 태그를 선택합니다.
a[href^="http"] {
color: black;
}5.5 태그[속성$="변수"]
속성 의 속성값이 변수 로 끝나는 요소를 선택합니다.
a[href$="kr"]{
color: black;
}
a[href$=".pdf"]{
color: black;
}확장자 별로 선택하기에 좋음
5.6 태그[속성*="변수"]
속성 의 속성값이 변수 를 포함하는 태그를 선택합니다. (문자열)
a[href*="paul"] {
color: black;
}- (참고) 태그[속성이름~=""변수]와 태그[속성이름*="변수"] 차이
~= 는 단어를 기준으로 *= 는 문자열을 기준으로 판단을 한다. 예를 들어서 ~= 은 단어를 기준으로 naver 와 navers 를 다르다고 인식하고 *= 은 문자열을 기준으로 navers 안에 naver가 포함되기 때문에 선택을 한다. 즉, 문자열은 어떤 문자를 넣어도 잡아낸다. 그러나 단어는 그 단어 그대로를 적어야 됨.
5.7 태그[속성|="변수"]
속성 의 속성값이 변수 이거나 변수 로 시작하는 태그를 선택한다.
a[href|="http"]{
color: black;
}6. 가상 클래스 선택자(Pseudo class selector)
nth-child, active, focus, hover, focus-within 등
7. 가상 요소 선택자(Pseudo element selector)
실제로 존재하는 element는 아니지만, styling을 도와준다.
즉, 마크업 없는 요소를 삽입할 수 있다.
가장 많이 사용하는 가상 요소 선택자는 after와 before.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>가상요소선택자</title>
<style>
p::after {
content: 'cm'
}
p::before {
content: '!!'
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>10</p>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width">
<title>JS Bin</title>
<style>
p::after{
content:'';
display:inline-block;
width:15px;
height:15px;
background-image:url(https://e1.pngegg.com/pngimages/635/155/png-clipart-emoji-sticker-three-yellow-stars-illustration-thumbnail.png);
background-size:cover;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>안녕하세요 찡긋~ </p>
</body>
</html>-> 이때, pseudo element selector로 삽입한 거는 드래그가 안됨 (신기)
단위
고정 크기 단위(absolute)
px, ptm in, cm, mm
pxdms css에서 많이 쓰이는 단위.
초기 기본 px의 크기는 16px.
가변 크기 단위(relative)
%, em, rem, vw, vh, vmin, vmax
- em
parent element related.
em은 부모의 배수 단위이다. 즉, 부모의 font-size에 따라 기준점을 세우며, 부모의 font-size에 따라 크기가 달라진다.
-
rem
root element related.
rem은 parent element의 font-size와는 상관없이 html을 기준점으로 한다. -
%
부모 설정값의 %크기로 보인다. 초기 설정 크기는 100%. -
vw
viewport width, 브라우저 너비의 %크기로 보임 -
vh
viewport height, 브라우저 높이의 %크기로 보임
-
parent에 따라 크기가 변경되어야 하는 경우 : %, em
-
browser에 따라 크기가 변경되어야 하는 경우 : v*,rem
-
요소의 너비와 높이에 따라 변경되어야 하는 경우 : %, v*
-
font size에 따라 변경 되어야 하는 경우 : em, rem
-
component가 어디서 사용되든 크기가 유지 : rem
-
component가 어디에 사용되는지에 따라 크기가 변동 : em
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>가변크기단위</title>
<style>
html, body {
font-size: 10px;
}
p {
font-size: 2em ;
}
/* em은 부모의 배수 단위
단위가 다 px로 되어있다면 나중에 크기 수정하고 싶을 때 다 수정해야하는데
em단위로 해두면 body의 font-size만 바꿔주면 되니까 편하다
*/
div {
font-size: 2em;
}
.one {
font-size: 2rem;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello World</p>
<div>
<!--10px*2 = 20px -->
<div>
<!-- 20px*2=40px -->
<div>
<!-- 40px*2=80px -->
Hello world
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<div>
<div class="one">
<!-- html font-size에 2배인 20px -->
Hello world
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>가변크기단위</title>
<style>
.one {
/* 자기 부모가 가진 width의 절반. 즉, body의 절반 */
width: 50%;
height: 200px;
background-color: darkblue;
}
.two {
width: 50%;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
.three {
width: 50vw; /*보이는 화면의 절반*/
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="one">
<div class="two"></div>
</div>
<br>
<div class="one">
<div class="three"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>📢 오늘의 회고
어제 html 마크업을 하면서 어떤 태그들을 써야할까 긴가민가 했던 것들이 있었는데, 어제 디스코드에서 어떤 분이 본인 마크업을 공유해주신 거 보고도 많이 배웠고, 오늘 함께 마크업 해보면서도 많은 걸 얻었다. 대표적으로, 시각장애인들이 사용하는 스크린리더기 사용도 고려해야한다는 점, 그리고 키보드 접근성(포커스) 등도 고려해야한다는 걸 알았다. 강의 듣고 가장 배운 게 많았던 ㅎㅎ.
DOM 얘기는 많이 들었는데... DOM이 뭔지도 모르는 채 shadow DOM을 먼저 들어버렸다.. 넌 대체 누구니...?
fieldset이랑 table도 처음 알았다! 빈곳들이 채워지는 느낌이 든다~
자바스크립트 공부해야하는데 평일엔 9to6로 수업을 하니.. 복습만 해도 잘 시간이 된다..ㅠㅠ 그래도 시간을 내서 해야지..!! 안 그러면 나중에 따라가기 힘들 거 같아😂
