activity에서 flow를 수집하는방법을 알아보자.
1. launchWhenXXX
첫번째 유형은 launchWhenXXX이다.

launchWhenXXX는 XXX가 콜백으로 시작될때, 주어진 블록을 실행하며, 해당 Activity가 Destoryed 될때 파기된다.
XXX에는 launchWhenStarted , launchWhenResumed, launchWhenCreated가 들어간다.
override fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View? {
//해당 프래그먼트가 started될때 시작하고, destroy될때 저절로 해제된다.
viewLifecycleOwner.lifecycleScope.launchWhenStarted {
println("started될때 시작")
}하지만 애석하게도 문제점이 있으니, BackGround시에 suspend된다는 문제이다.
Activity가 Stopped되었을때, 해당 블록은 suspend에 빠지는데, emit(producer)녀석은 계속 emit를 시도하기 때문에 리소스 낭비가 빠질수 있다.
대안법은?
override fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View? { job1 = viewLifecycleOwner.lifecycleScope.launchWhenStarted { println("started될때 시작") } override fun onStop(){ job1?.cancel() super.onStop() }해당 job()을 Stop()일때 cancel()시키면 되지만 bolierplate 하다.
추가) 메모리에 상주되는 상태를 유지하고 싶다면, 리소스 낭비가 아니기때문에 잘 구분해서 선택하자.
2. repeatOnLifeCycle
두번째로 나온 repeatOnLifecycle은 launchWhenXXX을 보안한 녀석이다.
repeatOnLifecycle 은 호출하는 coroutine 을 suspend 시키며, lifecycle 이 target state 에서 벗어나면 re-launch(자동 생성 및 시작) 를 시킨다.
그리고 Lifecycle 이 destroyed 되면 호출하는 coroutine 을 resume 시킨다.
일반적으로 Lifecycle.State.STARTED를 넣는다.
class exampleFragment: Fragment() {
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
// ...
viewLifecycleOwner.lifecycleScope.launch {
//Started에라는 State에 콜백으로 들어올때마다 re-launch된다.
viewLifecycleOwner.repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
exampleFlow().collect {
}
}
}
}
}
statein
stateIn()함수를 사용하면 Flow()를 StateFlow로 쉽게 변환할수있다.

stateIn은 세가지 변수를 갖는다.
- scope: StateFlow가 데이터를 구독받을 CoroutineScope를 명시해준다.
- stated: Flow로 부터 언제 구독을 할지 명시할수 있다.
- intialValue : StateFlow에 저장될 초기값을 설정할 수 있다.
SharedFlow와 다른점중 가장 중요한것은 초기값을 설정할수 있는것인데, 해당 초기값을 세팅함으로서, 중복된 값을 방지할 수 있다.
sharedIn
sharedIn()함수는 Flow()를 SharedFlow로 변환할수 있다.
sharedFlow 는 다음 값들을 customize 할 수 있다.
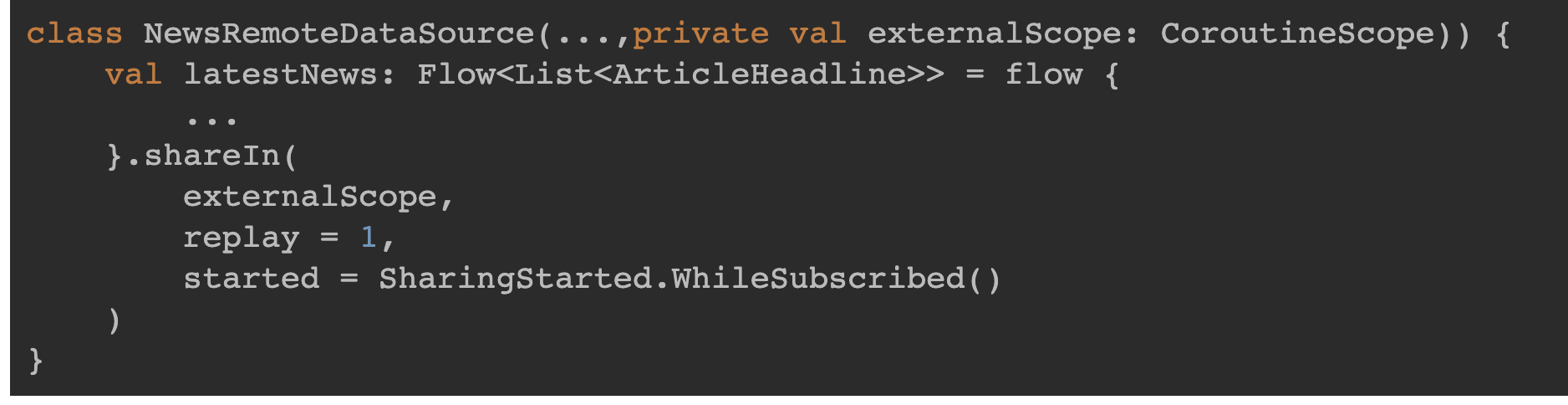
- replay : 새로운 subscribe 에게 몇 개의 기존 value 를 emit 할 것인지
- onBufferOverflow : buffer 가 full 일 때 어떻게 할 것인가.
기본값은 BufferOverflow.SUSPEND 이며 caller 를 suspend 시킨다. 다른 옵션은 DROP_LATEST, DROP_OLEST 가 있다.stateIn()과 차이점은 이전값을 Slot에 담아놓을수 있다는점이다.
stateFlow()는 기본적으로 replayCache를 1로 갖고있어 최신값만을 호출하지만,
SharedFlow는 모든 구독자들에게 최신값 + 이전값을 보낼수 있다.
