/복습/
Domain이란? 해결하고자 하는 관심영역
*DDD : Domain Driven Development
DTO란? Data Transfer Object로 데이터를 전달하기 위한 객체이다.
ex) rest api 응답시 잘 응답되도록 만들어 놓은 객체
Value Object란? 프로그래밍시 파라미터를 넣어야 할 때, 값을 전달해야 할 때, Getter/Setter/Constructor를 주로 사용한다
Entity란? Database의 테이블을 Java에서 사용할 수 있게 맵핑한 객체
ORM이란? Object-Relational Mapping
Java의 ORM : JPA
JPA 구현? Hybernate
Spring Data JPA -> Hybernate 기반으로 동작
Entity : JPA를 사용해 DB Table과 맵핑할 클래스
Entity Mapping : Entity 클래스에 DB 테이블과 컬럼, PK, FK 등을 설정하는 것
Entity Manager와 영속성 컨텍스트
- Entity Manager
* Entity의 저장, 수정, 삭제, 조회 등 Entity와 관련된 일을 처리하는 관리자 - 영속성 컨텍스트
* Entity를 영구 저장하는 환경- 1차 캐시 역할
*Static, Singleton 방법 세가지, data access 등 알아놓기
외래 키 맵핑: @JoinColumn
테이블 사이 관계 : @OneToOne, @OneToMany, @ManyToOne, (@ManyToMany)
fetch 전략: EAGER(ToOne), LAZY(ToMany)
cascade: Entity의 영속성 상태 변화를 연관된 Entity에도 함께 적용
방향성: 단방향, 양방향 (가능하면 단방향이 좋다)
Spring Data Repository - 기본 CRUD 제공
- data access layer 구현을 위해 반복해서 작성했던, 유사한 코드를 줄일 수 있는 추상화 제공
- interface 선언, JpaRepository 상속
JpaRepository
- 웬만한 CRUD, Paging, Sorting 메서드 제공
메서드 이름으로 쿼리 생성
- findBy, existsBy, countBy, deleteBy, Like, In, Between, And, Or ...
/복습 완/
Repository 고급
@Query : JPQL 쿼리나 Native 쿼리를 직접 수행
@Query("select i from Item i where i.price > ?1")
List<Item> getItemsHavingPriceAtLeast(long price);
@Query(value = "select * from Items where price > ?1", nativeQuery = true)
List<Item> getItemsHavingPriceAtLeast2(long price);하지만 일반적으로 JPQL을 쓰는게 좋다. 왜냐하면 native type은 DBMS에 종속적이라 DB가 바뀌면 에러가 나기 때문
Modifying : @Query 를 통해 insert, update, delete 쿼리를 수행할 경우 붙여줘야 함
@Modifying
@Query("update Item i set i.itemName = :itemName where i.itemId = :itemId")
int updateItemName(@Param("itemId") Long itemId, @Param("itemName")String itemName);DTO Projection : Repository 메서드가 Entity를 반환하는 것이 아니라 원하는 필드만 뽑아서 DTO(Data Transfer Object)로 반환하는 것 (필드 전부를 반환하는게 아니라 일부만 반환)
Dto Projection 방법
1) Interface 기반 Projection
2) Class 기반 (DTO) Projection
3) Dynamic Projection
//persistable interface도 기억하자!
DTO 예제
@JsonPropertyOrder({"itemName", "orderItems"})
public interface ItemDto {
String getItemName();
List<OrderItemDto> getOrderItems();
@JsonPropertyOrder({"order", "quantity"})
interface OrderItemDto {
OrderDto getOrder();
Integer getQuantity();
}
interface OrderDto {
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyyMMdd")
Date getOrderDate();
}
}
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@WebAppConfiguration
@Transactional
@ContextHierarchy({
@ContextConfiguration(classes = RootConfig.class),
@ContextConfiguration(classes = WebConfig.class)
})
public class ItemRepositoryTest3 {
@Autowired
private ItemRepository itemRepository;
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@BeforeEach
public void setUp() {
objectMapper.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS);
}
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
assertThat(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(itemRepository.findAllBy()))
.isEqualTo("[{\"itemName\":\"apple\",\"orderItems\":[{\"order\":{\"orderDate\":\"20180823\"},\"quantity\":3}]},"
+ "{\"itemName\":\"grape\",\"orderItems\":[{\"order\":{\"orderDate\":\"20180823\"},\"quantity\":1}]},"
+ "{\"itemName\":\"banana\",\"orderItems\":[{\"order\":{\"orderDate\":\"20180823\"},\"quantity\":2}]},"
+ "{\"itemName\":\"cherry\",\"orderItems\":[{\"order\":{\"orderDate\":\"20180824\"},\"quantity\":1}]},"
+ "{\"itemName\":\"kiwi\",\"orderItems\":[{\"order\":{\"orderDate\":\"20180824\"},\"quantity\":1}]},"
+ "{\"itemName\":\"lemon\",\"orderItems\":[{\"order\":{\"orderDate\":\"20180824\"},\"quantity\":2}]},"
+ "{\"itemName\":\"lime\",\"orderItems\":[{\"order\":{\"orderDate\":\"20180824\"},\"quantity\":1}]},"
+ "{\"itemName\":\"mango\",\"orderItems\":[{\"order\":{\"orderDate\":\"20180824\"},\"quantity\":5}]},"
+ "{\"itemName\":\"orange\",\"orderItems\":[{\"order\":{\"orderDate\":\"20180824\"},\"quantity\":1}]},"
+ "{\"itemName\":\"peach\",\"orderItems\":[]},"
+ "{\"itemName\":\"melon\",\"orderItems\":[]}]");
}
}
// JsonPropertyOrder가 없으면 작성되는 순서가 변경될 수 있음
// OjbectMapper가 Serializable시 내가 적은 순서 기반으로 작성해줌Web Support : Spring Data에서 제공하는 Web 확장 기능
@EnableSpringDataWebSupport
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@EnableSpringDataWebSupport
public class WebConfig {
// ...
}Basic Web Support
-
DomainClassConverter : MVC request parameter나 path variable로부터 Spring Data Repository가 관리하는 도메인 클래스로의 conversion을 제공
ex) /users/{user_id} -> @PathVarible({user_id}) User user // 원래는 Long userId를 썼는데, DomainClassConverter가 엔티티 객체로 변환해줌
ModelAttribute와 비슷하다?
//closedProjection : @Value("#{target.foo}")
target->entity이다. 따라서 target.itemName -> Entity.properties.
Spel이라고 한다(Spring EL) -
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver : MVC request parameter를 Pageable, Sort 인스턴스로 resolver할 수 있도록 해줌
-
Spring Data가 page, size 파라미터 값을 Controller의 Pageable 파라미터로 변환해서 전달해줌
Pageable : Pagenation 정보를 추상화 한 인터페이스
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/items")
public class ItemController {
@Autowired
private ItemService itemService;
@GetMapping
public List<ItemDto> getItems(Pageable pageable) { // GET /items?page=0&size=30
return itemService.getItems(pageable);
}
}
Pageable
public interface Pageable {
int getPageNumber();
int getPageSize();
int getOffset();
Sort getSort();
Pageable next();
Pageable previousOrFirst();
Pageable first();
boolean hasPrevious();
}Pageable Interface의 대표적 구현 : PageImpl Class
// ?page=0&size=30
PageRequest.of(0, 30);Pageable을 이용한 Pagenation 구현
- JpaRepository.findAll(Pageable pageable) 메서드로 Controller에서 전달받은 Pageable 객체를 그대로 전달
@Service
public class ItemServiceImpl implement ItemService {
public List<ItemDto> getItems(Pageable pageable) {
Page<Item> itemPage = itemRepository.findAll(pageable);
// ...
}
}
sort를 하고 싶으면(Rest API), Get 요청시 sort를 같이 달아주면 된다.
asc,desc는 sort=id,desc(asc) 이런식으로 하면 됨
sort가 2개면 &sort=userId,asc&sort=userName,desc 이렇게
GET /members?page=1&size=3&sort=id
Content-Type: application/json
Host: localhost:8080HiberNate 영속성 컨텍스트 : Session
영속성 컨텍스트 벗어나서 Lazy Loading 시도시 LazyInitialization Exception이 발생함
- OSIV(Open Session(HiberNate:Session, JPA: EntityManager) In View, Open EntityManager In View) 적용해서 해결
참고)
- org.springframework.orm.jpa.support.OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor
- org.springframework.orm.jpa.support.OpenEntityManagerInViewFilter
Querydsl : 정적 타입을 이용해 JPQL을 코드로 작성할 수 있게 해주는 프레임워크
- Criteria API에 비해 편하고 실용적
- Type-safe
Querydsl 쿼리 스타일
from(entity)
.where(/*조건*/)
.list();예시)
QPost post = QPost.post;
QPostUser postUser = QPostUser.postUser;
QProjectMember projectMember = QProjectMember.projectMember;
QMember member = QMember.member;
List<Post> posts = from(post)
.innerJoin(post.postUsers, postUser)
.innerJoin(postUser.projectMember, projectMember)
.innerJoin(projectMember.member, member)
.where(member.name.eq("dongmyo"))
.distinct()
.select(post)
.fetch();
-------------------------------------------------------
List<Post> posts = from(post).fetch();Spring Data JPA + Querydsl
- QuerydslPredicateExecutor
- QuerydslRepositorySupport
QuerydslPredicateExecutor 적용
도메인 repository interface가 QuerydslPredicateExecutor interface를 상속받으면 됨
그런데 조인을 받을 수 없어서 잘 안씀
public interface ItemRepository extends QuerydslPredicateExecutor<Item>, JpaRepository<Item, Long> {
// ...
}QuerydslRepositorySupport : Querydsl의 모든 기능을 사용함, Join도 사용 가능함
- QuerydslRepositorySupport를 상속받는 Custom Repository 구현 필요
@Repository
public abstract class QuerydslRepositorySupport {
protected JPQLQuery from(EntityPath<?>... paths) { /* ... */ }
protected DeleteClause<JPADeleteClause> delete(EntityPath<?> path) { /* ... */ }
protected UpdateClause<JPAUpdateClause> update(EntityPath<?> path) { /* ... */ }
// ...
}
public interface JPQLQuery<T> {
JPQLQuery<T> from(EntityPath<?>... sources);
<P> JPQLQuery<T> from(CollectionExpression<?,P> target, Path<P> alias);
<P> JPQLQuery<T> innerJoin(EntityPath<P> target);
<P> JPQLQuery<T> innerJoin(EntityPath<P> target, Path<P> alias);
<P> JPQLQuery<T> join(EntityPath<P> target);
<P> JPQLQuery<T> leftJoin(EntityPath<P> target);
<P> JPQLQuery<T> rightJoin(EntityPath<P> target);
// ...
}CustomRepository 구현
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface MyCustom{
//querydsl로 복잡한 쿼리 수행할 메소드
List<Custom> complexQuery();
}
public class MyCustomImpl extends QuerydslRepositorySupport implements MyCustom{
public MyCustomImpl(){
super(Custom.class // 엔티티의 클래스 타입);
}
@Override
public List<Custom> complexQuery() {
QCustom custom = QCustom.custom;
JPQLQuery query = from(custom).where(/* ... */);
// ...
}
}CustomRepository 사용 : 기본 Repository Interface를 통해 Custom 메소드 호출
@Autowired CustomRepository c;
List<Custom> customs = c.complexQuery();N+1 문제 : 쿼리 한 번으로 N 건의 레코드를 가져왔을 때, 연관관계 Entity를 가져오기 위해 쿼리를 N번 추가 수행하는 문제
- 부가적인 쿼리가 발생하는 문제
단일 Entity 조회 시 :
itemRepository.findById(1l);을 하면... 실제 수행되는 쿼리는
select
item0_."item_id" as item_id1_4_0_,
item0_."item_name" as item_nam2_4_0_,
item0_."price" as price3_4_0_
from
"Items" item0_
where
item0_."item_id"=1여러개의 Entity 조회시
itemRepository.findAll();
->
select
item0_."item_id" as item_id1_4_,
item0_."item_name" as item_nam2_4_,
item0_."price" as price3_4_
from
"Items" item0_여기서 여러 엔티티 조회에 객체 그래프 탐색을 적용한다면?
itemRepository.findAll()
.stream()
.map(Item::getOrderItems)
.flatMap(Collection::stream)
.collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(OrderItem::getQuantity));
-> 결과가 너무 많아진다!
select
item0_."item_id" as item_id1_4_,
item0_."item_name" as item_nam2_4_,
item0_."price" as price3_4_
from
"Items" item0_
select
orderitems0_."item_id" as item_id4_8_0_,
orderitems0_."line_number" as line_num1_8_0_,
orderitems0_."order_id" as order_id2_8_0_,
orderitems0_."line_number" as line_num1_8_1_,
orderitems0_."order_id" as order_id2_8_1_,
orderitems0_."item_id" as item_id4_8_1_,
orderitems0_."quantity" as quantity3_8_1_,
order1_."order_id" as order_id1_9_2_,
order1_."order_date" as order_da2_9_2_
from
"OrderItems" orderitems0_
inner join
"Orders" order1_
on orderitems0_."order_id"=order1_."order_id"
where
orderitems0_."item_id"=1
select
orderitems0_."item_id" as item_id4_8_0_,
orderitems0_."line_number" as line_num1_8_0_,
orderitems0_."order_id" as order_id2_8_0_,
orderitems0_."line_number" as line_num1_8_1_,
orderitems0_."order_id" as order_id2_8_1_,
orderitems0_."item_id" as item_id4_8_1_,
orderitems0_."quantity" as quantity3_8_1_,
order1_."order_id" as order_id1_9_2_,
order1_."order_date" as order_da2_9_2_
from
"OrderItems" orderitems0_
inner join
"Orders" order1_
on orderitems0_."order_id"=order1_."order_id"
where
orderitems0_."item_id"=2
....등해결방안?
1) Fetch Join
JPQL join fetch
Querydsl .fetchJoin()
2) Entity Graph
이중 fetchJoin이나 EntityGraph를 쓰는게 좋다
*fetchJoin 예시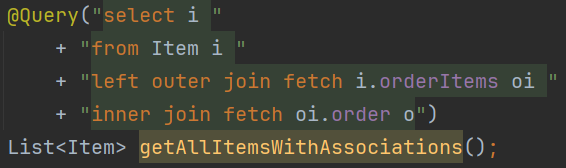
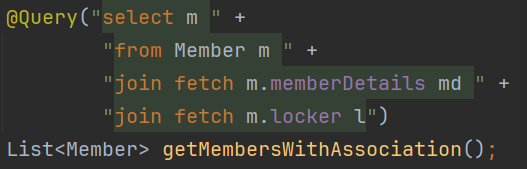
*inner join을 쓰든, outer join을 쓰든, fetch만 뒤에 붙여주면 된다. 안쓰면 default innerjoin
Fetch Join 유의사항
- Pagination 쿼리에 Fetch JOIN을 적용하면 "모든" 레코드를 가져오는 쿼리가 실행됨
- 절대 절대 절대 절대 쓰면 안됨
*둘 이상의 컬렉션을 Fetch Join시 MultipleBagFetchException 발생
- Java의 java.util.List 타입은 기본적으로 Hibernate의 Bag 타입으로 맵핑됨
- Bag은 Hibernate에서 중복 요소를 허용하는 비순차(unordered) 컬렉션
- 둘 이상의 컬렉션(Bag)을 Fetch Join하는 경우
- 그 결과로 만들어지는 카테시안 곱(Cartesian Product)에서
- 어느 행이 유효한 중복을 포함하고 있고
- 어느 행이 그렇지 않은 지 판단할 수 없어
- MultipleBagFetchException 발생
해결 방법 : List를 Set으로 변경
Entity Graph : Entity를 조회하는 시점에 연관 Entity들을 함께 조회할 수 있도록 해주는 기능
1) 정적 선언 : @NamedEntityGraph
2) 동적 선언 : EntityManager.createEntityGraph()
ex)
@NamedEntityGraphs({
@NamedEntityGraph(name = "itemWithOrderItems", attributeNodes = {
@NamedAttributeNode("orderItems")
}),
@NamedEntityGraph(name = "itemWithOrderItemsAndOrder", attributeNodes = {
@NamedAttributeNode(value = "orderItems", subgraph = "orderItems")
}, subgraphs = @NamedSubgraph(name = "orderItems", attributeNodes = {
@NamedAttributeNode("order")
}))
})
@Entity
public class Item {
// ...
}적용시 JPA에서 제공하는 메소드 위에 @NamedEntityGraph("name")으로 달면 된다
@EntityGraph("itemWithOrderItems")
List<Item> readAllBy();