SpringBoot 예외처리에 대한 지식이 없어 정리해보고자 한다.
스프링부트의 예외 처리 방식
@ControllerAdvice를 통한 모든 Controller에서 발생할 수 있는 예외 처리
@ExceptionHandler를 통한 특정 Controller 에서의 예외 처리가 있다.
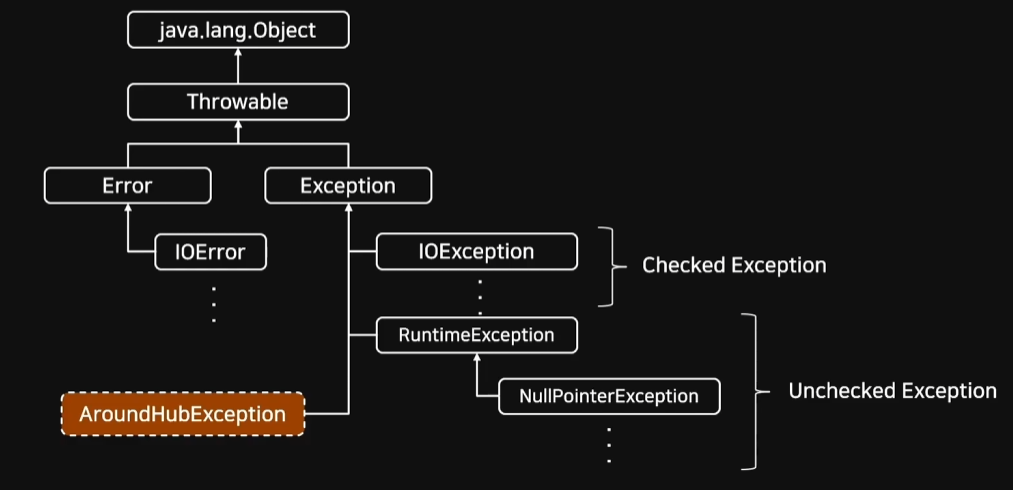
예외 처리하면 예외 클래스를 빼놓고 말할 수 없다.
AroundHubException은 새로운 Exception을 만들 수 있음을 의미한다.
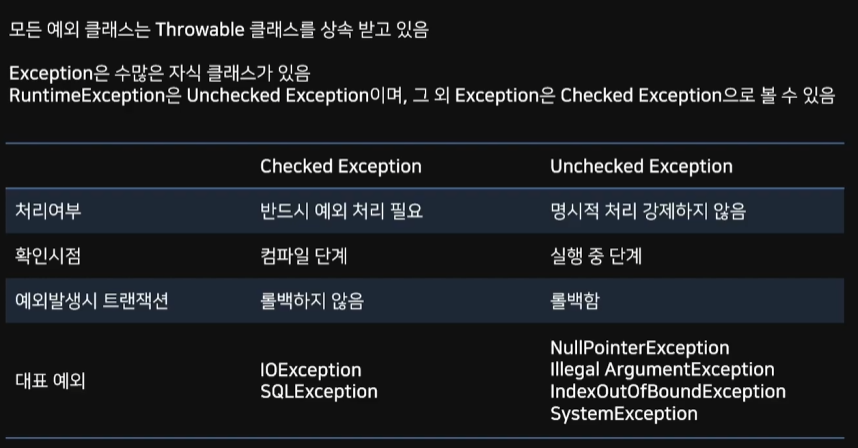
우리가 체크를 할 수 있는 것은 문법적으로 명백한 오류가 발생한 상황일 때를 의미한다.
즉 컴파일하면서 이미 오류가 있어서 처리하고 가야함을 의미 (Checked)
UnChecked는 가동중에 발생할 수 있는 에러를 의미한다.
예를들어 어떤 값들을 매개변수로 만들었을 때 제대로 값이 들어오지 않는다면?
이런 과정은 실행중에만 확인할 수 있어 명시적으로 처리를 강제할 수 없다.
@ControllerAdivce, @RestControllerAdvice
Spring에서 제공하는 어노테이션이다.
@Controller 나 @RestController 에서 발생하는 예외를 한곳에서 관리하고 처리할 수 있게
하는 어노테이션이다.
설정을 통해 범위 지정이 가능하며 Default 값으로 모든 컨트롤러에 대해 예외처리를 관리한다.
만약 예외 발생 시 json의 형태로 결과를 반환하고 싶다면 @RestControllerAdivce를 사용하면된다.
//패키지 범위를 설정한 예시
@RestControllerAdvice(basePackages = "arroundhub.thinkground.studio")@ExceptionHandler
예외처리 상황이 발생하면 해당 핸들러로 처리하겠다고 명시하는 어노테이션
괄호를 쳐서 어떤 ExceptionClass를 처리할지 설정하는게 좋다
@ExceptionHandler(00Exception.class)괄호를 사용하지 않는다면 특정 메서드에서 사용하고있는 매개변수에서 어떤 Exception을
처리하는지를 체크해서 핸들러 처리를하는데
다중의 익셉션 처리를 할때는 문제가 발생할 수 있어 괄호로 특정 익셉션을 설정해주는게 좋다.
Exception.class 는 최상위 클래스로 하위 세부 예외 처리 클래스로 설정한 핸들러가 존재하면
그 핸들러가 우선 처리되며 그 외에 처리되지 못하는 예외에 대해서는 ExceptionClass에서
핸들링한다.
@ControllerAdvice로 설정된 클래스 내에서 메서드로 정의할 수 있지만
각 Controller 안에도 설정이 가능하다.
전역설정 @ControllerAdvice 보다 지역설정 @Controller 안에 설정한 것이 우선순위를 가짐
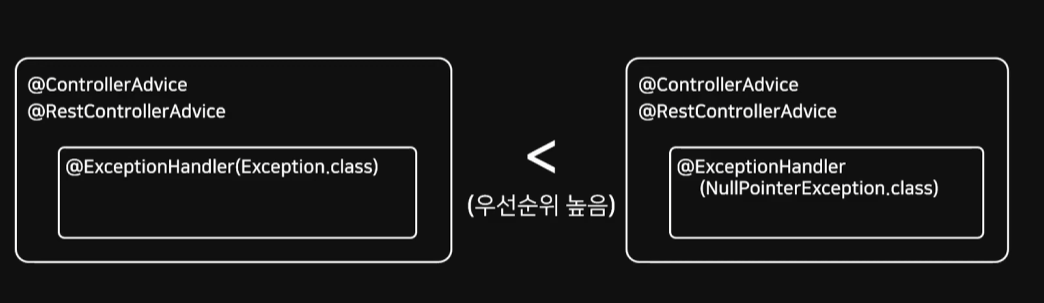
우선 순위를 도식화한 모습이다.
Exception.class 보다 하위 세부 예외 처리 클래스인 NPE 가 우선순위가 더 높다.
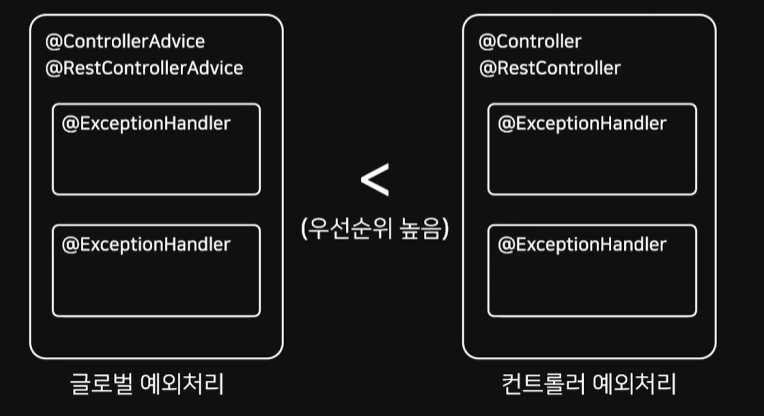
또한 아까 설명했듯이 @Controller 내부에 존재하는 ExceptionHandler가 우선순위가 더 높다.
예시
@RestController
@TypeAnnotation(name = "Hello?", value = "World")
public class HelloController {
@PostMapping("/exception")
public void exceptionTest() throws Exception {
throw new Exception();
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> ExceptionHandler(Exception e) {
HttpHeaders responseHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
// responseHeaders.add(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, "application/json");
HttpStatus httpStatus = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
LOGGER.info(e.getMessage());
LOGGER.info("Controller 내 ExceptionHandler 호출");
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("error type", httpStatus.getReasonPhrase());
map.put("code", "400");
map.put("message", "에러 발생");
return new ResponseEntity<>(map, responseHeaders, httpStatus);
}
}ExceptionHandler() 메서드가 정의되어있다.
value = Exception.class 이므로 당연히 POST 메서드로 /exception을 던지면
이 핸들러의 로직으로 처리한다는 의미를 갖는다.
ResponseEntity를 사용하기 때문에 Header, Status 같은 값을 채워주는게 좋다.
Map 에 error type , 에러 코드, 메시지를 담아 클라이언트에 리턴해주는 작업이다.
@RestControllerAdvice
public class AroundHubExceptionHandler {
private final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AroundHubExceptionHandler.class);
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> ExceptionHandler(Exception e) {
HttpHeaders responseHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
// responseHeaders.add(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, "application/json");
HttpStatus httpStatus = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
LOGGER.error("Advice 내 ExceptionHandler 호출, {}, {}", e.getCause(), e.getMessage());
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("error type", httpStatus.getReasonPhrase());
map.put("code", "400");
map.put("message", "에러 발생");
return new ResponseEntity<>(map, responseHeaders, httpStatus);
}
}이제 @RestControllerAdvice 로 어노테이션이 설정된 핸들러를 살펴보자.
Controller 단에서 발생하는 모든 에러는 다 이 클래스 핸들러가 처리한다는 의미이다.
하지만 위에서 Controller 내부에 존재하는 핸들러가
@RestControllerAdivce클래스 핸들러보다 우선순위가 높다고 했으므로
우선은 HelloController 내의 ExceptionHandler로 에러가 처리될 것임을 알 수 있다.
만약 Controller 내부의 ExceptionHandler를 주석처리하면 AroundHub~ 에서 처리된다.
둘의 동작은 동일하지만 우선순위의 차이가 있다는 사실을 알 수 있다.
어떻게 에러를 통합적으로 처리하는지 알아보는 과정이었다.
Custom Exception 사용
{
"error code": "400",
"error type": "Bad Request",
"message": "Product Exception. 의도한 에러가 발생했습니다."
}위의 예시와 같이 에러 타입, 코드, 메시지를 응답함으로써 Client에게 정확히 어떤 에러가 발생했는지 공유하도록 하기위해 Custom Exception을 사용해 볼 것이다.
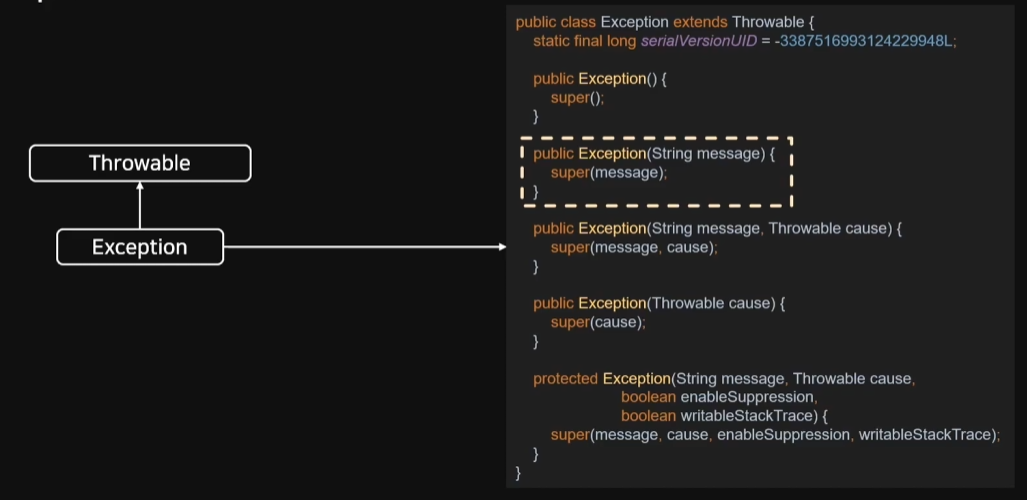
Excpetion의 구조이다.
코드는 Exception 클래스의 전체 내용이다. 생각보다 Exception 내부 내용은 많지 않다.
대부분은 Throwable에 구현되어있음을 알 수 있다.
생성자를 잘 보면 String 값을 받고 이것이 메시지가 된다는 것을 알아야하고
Throwable 쪽에서 메시지를 처리하는 기능이 있구나 라고 예측할 수 있다.
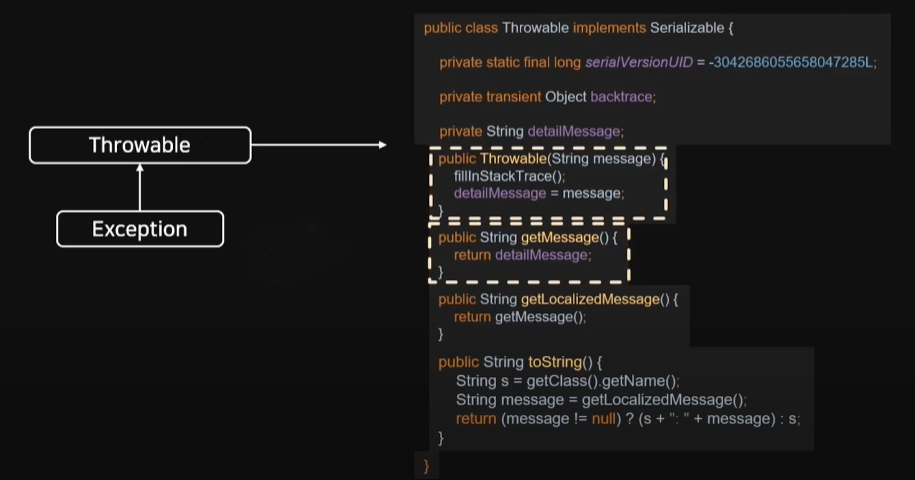
이번엔 Throwable 의 구조이다.
우리가 주요 봐야할 것들을 뽑아왔다.
private String detailMessage 가 아까 봤던 message이다.
생성자를 보면 아까 받았던 message를 detailMessage로 값을 넣는 것을 볼 수 있다.
getMessage(), getLocalizedMessage() 로 값을 가져올 수 있다.
이 쯤 알아보고
우리는 HttpStatus를 사용해서 이제 Exception을 상속받는 Custom Exception을 만들 것이다.
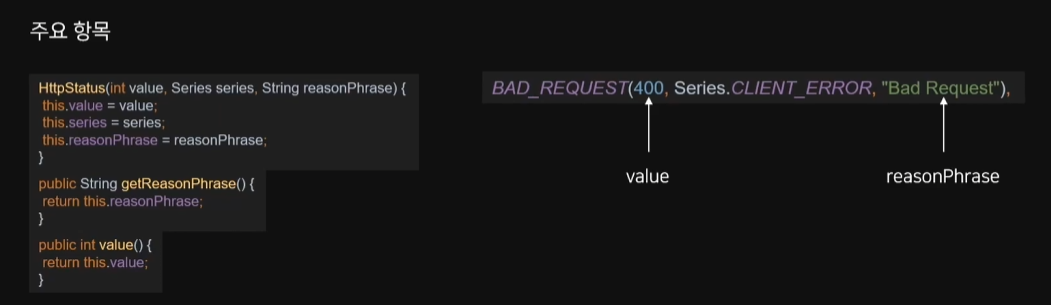
HttpStatus는 Enum 클래스이다.
코드, 어떤 시리즈의 에러인지, String 값 이 들어있다.
getReasonPhrase() 는 400 에러코드가 의미하는 String 값
value() 는 코드값을 가져올 수 있다.
따라서 위에서 봤던 json 형태로 값을 보내주기 위해서는
error type : HttpStatus의 reasonPhrase
error code : HttpStatus의 value
message : 상황별 detail Message의 내용이 필요하다.
우리가 만드려는 커스텀 익셉션 클래스 에서는 HttpStatus값과 message값을 가지고있어야한다.
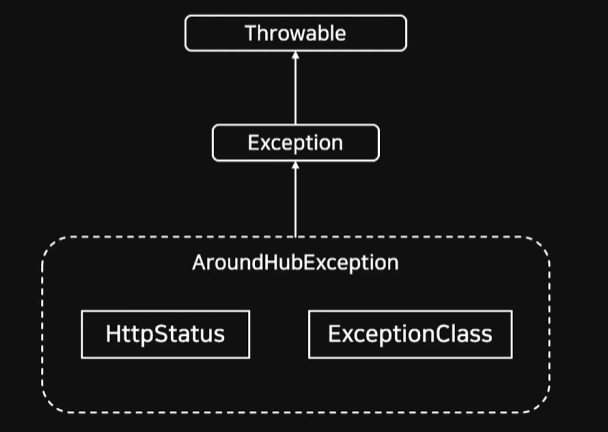
이런 식으로 구성될 것이다.
코드로 보기
public class Constants {
public enum ExceptionClass {
//예시에 불과, 자신의 클래스 이름으로 구성할 수 있음
PRODUCT("Product"),
SIGN("Sign");
private String exceptionClass;
ExceptionClass(String exceptionClass) {
this.exceptionClass = exceptionClass;
}
public String getExceptionClass() {
return exceptionClass;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return getExceptionClass() + " Exception. ";
}
}
}
public class AroundHubException extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4663380430591151694L;
private Constants.ExceptionClass exceptionClass;
private HttpStatus httpStatus;
public AroundHubException(
Constants.ExceptionClass exceptionClass, HttpStatus httpStatus, String message) {
super(exceptionClass.toString() + message);
this.exceptionClass = exceptionClass;
this.httpStatus = httpStatus;
}
public Constants.ExceptionClass getExceptionClass() {
return exceptionClass;
}
public int getHttpStatusCode() {
return httpStatus.value();
}
public String getHttpStatusType() {
return httpStatus.getReasonPhrase();
}
public HttpStatus getHttpStatus() {
return httpStatus;
}
}Constants는 어느 클래스에서 Exception이 발생했는지 보기 좋게 해주는 enum 클래스이다.
Exception을 상속받았고 직렬화를 위해 serialVersionID 가 존재한다.
Constants의 ExceptionClass 값, HttpStatus, message를 받아 생성자가 구현되는
모습을 볼 수 있다.
super를 이용해 전체 message 값을 정의하고 있다.
ExceptionClass 의 toString() 은 exceptionClass의 이름 + Exception. 의 String을 반환한다.
즉 최종 메시지는
ProductException. 디테일한 에러 알림 메시지 이런 식으로 구성될 것이다.
그외에 코드값을 불러오는 getHttpStatusCode,
HttpStatus의 message를 가져오는 getHttpStatusType이 존재하는 모습을 볼 수 있다.
이건 예시일 뿐이고 Custom Exception을 구현하는 방식은 상이하다.
사용해보는 예시
@RestControllerAdvice
public class AroundHubExceptionHandler {
private final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AroundHubExceptionHandler.class);
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> ExceptionHandler(Exception e) {
HttpHeaders responseHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
// responseHeaders.add(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, "application/json");
HttpStatus httpStatus = HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
LOGGER.error("Advice 내 ExceptionHandler 호출, {}, {}", e.getCause(), e.getMessage());
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("error type", httpStatus.getReasonPhrase());
map.put("code", "400");
map.put("message", "에러 발생");
return new ResponseEntity<>(map, responseHeaders, httpStatus);
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = AroundHubException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> ExceptionHandler(AroundHubException e) {
HttpHeaders responseHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("error type", e.getHttpStatusType());
map.put(
"error code",
Integer.toString(e.getHttpStatusCode())); // Map<String, Object>로 설정하면 toString 불필요
map.put("message", e.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(map, responseHeaders, e.getHttpStatus());
}
}아까 처음 @RestControllerAdvice를 구성했을 때에서 하나가 더 추가되었다.
value = AroundHubException 인 ExceptionHandler() 가 추가된 모습을 볼 수 있다.
map에 e(에러값)를 사용해서 타입, 코드, 메시지를 넣고 아까처럼 반환해주고있다.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/product-api")
public class ProductController {
@PostMapping(value = "/product/exception")
public void exceptionTest() throws AroundHubException {
throw new AroundHubException(
Constants.ExceptionClass.PRODUCT, HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN, "접근이 금지되었습니다.");
}
}그 후 ProductController 에서 우리가 만든 AroundHubException 을 던지고 있다.
이 때 매개변수 값이 아까 생성자에 넣어주던 타입들과 동일하다.
{
"error code": "403",
"error type": "Forbidden",
"message": "Product Exception. 접근이 금지되었습니다."
}만약 클라이언트에서 exceptionTest() 를 호출하면 이렇게 json 형태로 반환되게된다.
전체적인 흐름을 알게되었으니 이제 이걸 실제로 예외처리할 때 적용하기만 하면 된다.
