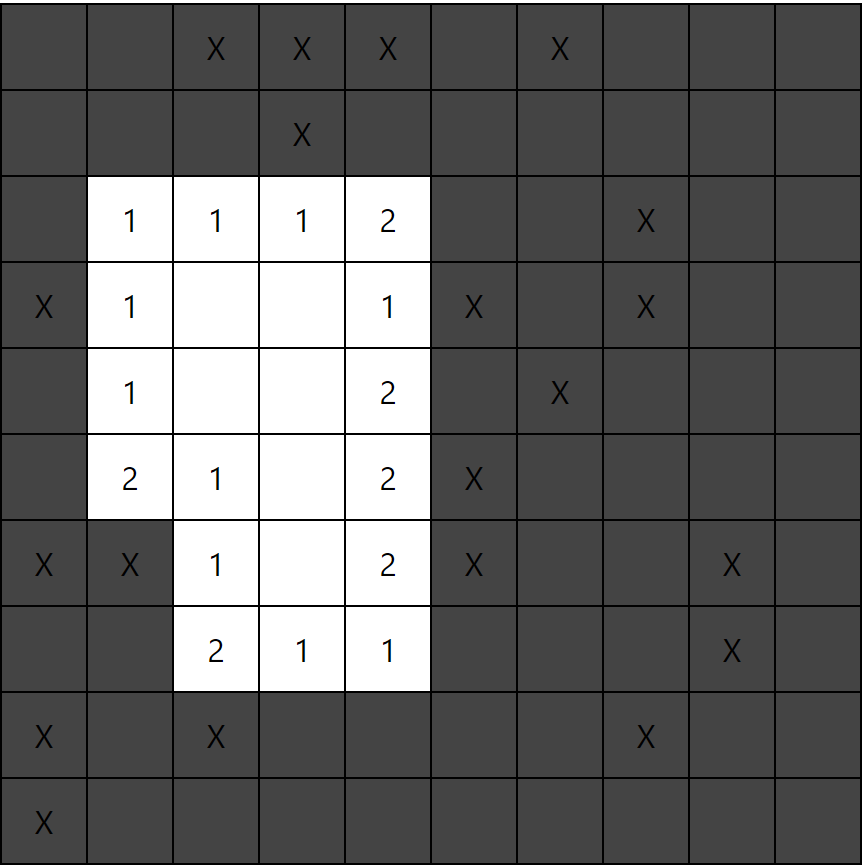
Step 4
지뢰 개수 표시하기
MineSearch.jsx 의 OPEN_CELL 액션을 건드려 줘야한다.
case OPEN_CELL: {
const tableData = [...state.tableData];
tableData[action.row] = [...state.tableData[action.row]];
let around = [] // 주변의 상태 값을 담는다
if (tableData[action.row - 1]) { // 양 옆이 없을 때는 undefined를 배열에 담는다
around = around.concat(
[tableData[action.row - 1][action.cell - 1],
tableData[action.row - 1][action.cell],
tableData[action.row - 1][action.cell + 1],]
);
}
around = around.concat(
[tableData[action.row][action.cell - 1],
tableData[action.row][action.cell + 1],]
);
if (tableData[action.row + 1]) {
around = around.concat(
[tableData[action.row + 1][action.cell - 1],
tableData[action.row + 1][action.cell],
tableData[action.row + 1][action.cell + 1],]
);
}
const count = around.filter((v) => [CODE.FLAG_MINE,CODE.MINE,CODE.QUESTION_MINE].includes(v)).length;
tableData[action.row][action.cell] = count;
return {
...state,
tableData,
}
}around라는 배열을 두고
주변 8개의 상태값을 다 담아준다. concat은 파이썬의 extend와 같다
편의상 위아래만 있는지 검사하고 양옆은 검사 안하는것 같은데 양옆이 없으면 undefined가 들어간다. → 자바스크립트의 특성상 위아래는 검사를 안해주면 속성에 접근할 수 없어서 위아래 체크는 필수라고 한다.
그 다음 fillter로 지뢰코드인지 확인한 다음 맞으면 새로운 배열에 넣어서 그 배열의 개수를 count에 담고 tableData[action.row][action.cell] 을 count로 갱신해준다.
Td.jsx
const getTdText = (code) => {
switch (code) {
case CODE.NORMAL:
return '';
case CODE.MINE:
return 'X';
case CODE.CLICKED_MINE:
return '펑';
case CODE.FLAG_MINE:
case CODE.FLAG:
return '!';
case CODE.QUESTION_MINE:
case CODE.QUESTION:
return '?';
default:
return code;
}
};그 다음 Td의 getTdText 함수의 디폴트 값을 들어오는 그대로의 code로 변경해주면 화면에 count값이 나타난다!
여기서 0인경우에는 숫자를 안 표시하기 위해
default:
return code || '';이렇게 해준다.
그러면 이렇게 된다.
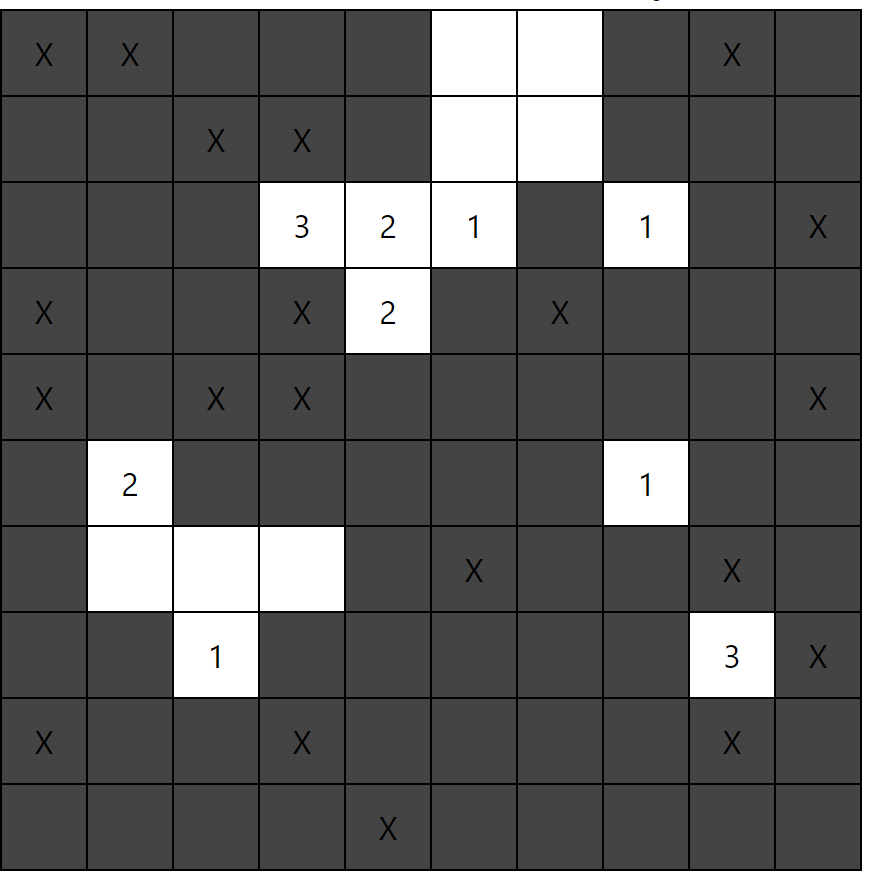
빈 칸 재귀를 이용해 자동으로 열기
마찬가지로
MineSearch.jsx 의 OPEN_CELL 액션을 건드려 줘야한다.
case OPEN_CELL: {
const tableData = [...state.tableData];
//tableData[action.row] = [...state.tableData[action.row]];
tableData.forEach((row,i) => {
tableData[i] = [...state.tableData[i]];
}) // 모든 칸을 새로운 객체로 만들어 준다.
...불변성 유지를 위해
tableData[action.row] = [...state.tableData[action.row]]; 해줬던 것을
전부다 새로운 객체로 만들어준다. → 재귀가 일어나면 어떤 것이 불변을 유지해야할지 모르기 때문
case OPEN_CELL: {
const tableData = [...state.tableData];
//tableData[action.row] = [...state.tableData[action.row]];
tableData.forEach((row,i) => {
tableData[i] = [...row];
}) // 모든 칸을 새로운 객체로 만들어 준다.
const checked = []
const checkAround = (row, cell) => {
// 상하 좌우 필터링
if (row < 0 || row >= tableData.length || cell < 0 || cell >= tableData[0].length) {
return;
}
// 못여는 칸 필터링
if ([CODE.FLAG,CODE.FLAG_MINE,CODE.OPENED,CODE.QUESTION,CODE.QUESTION_MINE].includes(tableData[row][cell])) {
return;
}
// 중복 체크
if (checked.includes(row + ',' + cell)) {
return;
} else {
checked.push(row + ',' + cell);
}
let around = [] // 주변의 상태 값을 담는다
if (tableData[row - 1]) { // 양 옆이 없을 때는 undefined를 배열에 담는다
around = around.concat(
[tableData[row - 1][cell - 1],
tableData[row - 1][cell],
tableData[row - 1][cell + 1],]
);
}
around = around.concat(
[tableData[row][cell - 1],
tableData[row][cell + 1],]
);
if (tableData[row + 1]) {
around = around.concat(
[tableData[row + 1][cell - 1],
tableData[row + 1][cell],
tableData[row + 1][cell + 1],]
);
}
const count = around.filter((v) => [CODE.FLAG_MINE,CODE.MINE,CODE.QUESTION_MINE].includes(v)).length;
if (count === 0) {
if (row > -1) {
const near = [];
if (row - 1 > -1) {
near.push([row-1,cell-1]);
near.push([row-1,cell]);
near.push([row-1,cell+1]);
}
near.push([row,cell-1]);
near.push([row,cell+1]);
if (row + 1 < tableData.length) {
near.push([row+1,cell-1]);
near.push([row+1,cell]);
near.push([row+1,cell+1]);
}
near.forEach((n) => {
if(tableData[n[0]][n[1]] !== CODE.OPENED) {
checkAround(n[0],n[1]);
}
})
}
}
tableData[row][cell] = count;
};
checkAround(action.row, action.cell);
return {
...state,
tableData,
}
}checkAround로 count를 세는 과정을 묶어주고 (action.row와 action.cell을 row, cell로 바꿔줘야함)
count가 0일시 주변 것들을 near라는 배열에 넣어
checkAround 재귀를 해준다.
상하좌우 필터링과 닫힌칸 필터링을 하고 → undefined 방지
checked배열을 만들어서 중복체크해줘야한다. → 무한재귀 방지
이제 칸들이 자동으로 열린다!