Chapter7 문제 [9/10]

다음은 단위를 변환하는 추상 클래스 Converter이다.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Converter {
protected:
double ratio;
virtual double convert(double src)=0; // src를 다른 단위로 변환한다.
virtual string getSourceString()=0; // src 단위 명칭
virtual string getDestString()=0; // dest 단위 명칭
public:
Converter(double ratio) { this->ratio = ratio; }
void run(){
double src;
cout << getSourceString() << "을 " << getDestString() << "로 바꿉니다. ";
cout << getSourceString() << "을 입력하세요>> ";
cin >> src;
cout << "변환 결과 : " << convert(src) << getDestString() << endl;
}
};9-1, 추상 클래스를 이용한 Won->Dollar
Converter 클래스를 상속받아 달러를 원화로 환산하는 WonToDollar 클래스를 작성하라. main() 함수와 실행 결과는 다음과 같다.
int main() {
WonToDollar wd(1010); // 1달러에 1010원
wd.run();
}원을 달러로 바꿉니다. 원을 입력하세요>> 10000
변환 결과 : 9.9099달러
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Converter
{
protected:
double radtio;
virtual double convert(double src) = 0; //src를 다른 단위로 변환한다.
virtual string getSourcesString() = 0; //src 단위 명칭
virtual string getDestString() = 0; //dest 단위 명칭
public:
Converter(double ratio) {
this->radtio = ratio;
};
void run() {
double src;
cout << getSourcesString() << "을 " << getDestString() << " 로 바꿉니다. ";
cout << getSourcesString() << "을 입력하세요 ";
cin >> src;
cout << "반환 결과 : " << convert(src) << getDestString() << endl;
}
};
class WonToDollar : public Converter
{
public:
WonToDollar(int radtio) : Converter(radtio) {
cout << "WonToDollar(int " << radtio << ") 생성자 실행" << endl;
}
virtual double convert(double src) {
return src / radtio * 10;
}
virtual string getSourcesString() {
return "원";
}
virtual string getDestString() {
return "달러";
}
};
int main()
{
WonToDollar wd(1010);
wd.run();
}9-2, 추상 클래스를 이용한 Km->Mile
Converter 클래스를 상속받아 km를 mile(마일)로 변환하는 KmToMile 클래스를 작성하라. main() 함수와 실행 결과는 다음과 같다.
int main() {
KmToMile toMile(1.609344); // 1마일은 1.609344 KM
toMile.run();
}Km을 Mile로 바꿉니다. Km을 입력하세요>> 25
변환 결과 : 15.534Mile
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Converter
{
protected:
double radtio;
virtual double convert(double src) = 0; //src를 다른 단위로 변환한다.
virtual string getSourcesString() = 0; //src 단위 명칭
virtual string getDestString() = 0; //dest 단위 명칭
public:
Converter(double ratio) {
this->radtio = ratio;
};
void run() {
double src;
cout << getSourcesString() << "을 " << getDestString() << " 로 바꿉니다. ";
cout << getSourcesString() << "을 입력하세요 ";
cin >> src;
cout << "반환 결과 : " << convert(src) << getDestString() << endl;
}
};
class KmToMile : public Converter
{
public:
KmToMile(double radtio) : Converter(radtio) {
cout << "WonToDollar(double " << radtio << ") 생성자 실행" << endl;
}
virtual double convert(double src) {
return src / radtio;
}
virtual string getSourcesString() {
return "Km";
}
virtual string getDestString() {
return "Mile";
}
};
int main()
{
KmToMile toMile(1.609344); //1 mile은 1.609344 Km
toMile.run();
}
다음 추상 클래스 LoopAdder가 있다.
class LoopAdder { // 추상 클래스
string name; // 루프의 이름
int x, y, sum; // x에서 y까지의 합은 sum
void read(); // x, y 값을 읽어 들이는 함수
void write(); // sum을 출력하는 함수
protected:
LoopAdder(string name="") { // 루프의 이름을 받는다. 초깃값은 ""
this->name = name;
}
int getX() { return x; }
int getY() { return y; }
virtual int calculate() = 0; // 순수 가상 함수. 루프를 돌며 합을 구하는 함수
public:
void run(); // 연산을 진행하는 함수
};
void LoopAdder::read() { // x, y 입력
cout << name << ":" << endl;
cout << "처음 수에서 두번째 수까지 더한다. 두 수를 입력하세요 >> ";
cin >> x >> y;
}
void LoopAdder::write() { // 결과 sum 출력
cout << x << "에서 " << y << "까지의 합 = " << sum << " 입니다" << endl;
}
void LoopAdder::run() {
read(); // x, y를 읽는다
sum = calculate(); // 루프를 돌면서 계산한다.
write(); // 결과 sum을 출력한다.
}9-3
LoopAdder 클래스를 상속받아 다음 main() 함수와 실행 결과처럼 되도록 ForLoopAdder 클래스를 작성하라. ForLoopAdder 클래스의 calculate() 함수는 for 문을 이용하여 합을 구한다.
int main() {
ForLoopAdder forLoop("For Loop");
forLoop.run();
}For Loop:
처음 수에서 두번째 수까지 더합니다. 두 수를 입력하세요>> 3 10
3에서 10까지의 합 = 52입니다.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class LoopAdder //추상클래스
{
string name;
int x, y, sum;
void read(); //x, y 값을 읽어 들이는 함수
void write(); //sum을 출력하는 함수
protected:
LoopAdder(string name = "") {
this->name = name;
x = 0;
y = 0;
sum = 0;
}
int getX() { return x; }
int getY() { return y; }
virtual int calculate() = 0;
public:
void run(); //연산을 진행하는 함수
};
void LoopAdder::read() {
cout << name << ":" << endl;
cout << "처음 수에서 두번째 수까지 더합니다. 두 수를 입력하세요>> ";
cin >> x >> y;
}
void LoopAdder::write() { //결과 sum 출력
cout << x << "에서 " << y << "까지의 합 = " << sum << " 입니다." << endl;
}
void LoopAdder::run() {
read(); //x, y를 읽는다.
sum = calculate();
write();
}
class ForLoopAdder : public LoopAdder
{
public:
ForLoopAdder(string name) : LoopAdder(name) {
};
virtual int calculate() {
int sum = 0;
int i = getX();
for (i; i <= getY(); i++)
{
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
};
int main()
{
ForLoopAdder forLoop("For Loop");
forLoop.run();
}9-4
LoopAdder 클래스를 상속받아 다음 main() 함수와 실행 결과처럼 되도록 WhileLoopAdder, DoWhileLoopAdder 클래스를 작성하라. while 문, do-while 문을 이용하여 합을 구하도록 calculate() 함수를 각각 작성하면 된다.
int main() {
WhileLoopAdder whileLoop("While Loop");
DoWhileLoopAdder doWhileLoop("Do While Loop");
whileLoop.run();
doWhileLoop.run();
}
While Loop:
처음 두수에서 두번째 수까지 더합니다. 두 수를 입력하세요>> 3 5
3에서 5까지의 합 = 12입니다.
Do While Loop
처음 수에서 두번째 수까지 더합니다. 두 수를 입력하세요 >> 10 20
10에서 20까지의 합 = 165입니다.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class LoopAdder //추상클래스
{
string name;
int x, y, sum;
void read(); //x, y 값을 읽어 들이는 함수
void write(); //sum을 출력하는 함수
protected:
LoopAdder(string name = "") {
this->name = name;
x = 0;
y = 0;
sum = 0;
}
int getX() { return x; }
int getY() { return y; }
virtual int calculate() = 0;
public:
void run(); //연산을 진행하는 함수
};
void LoopAdder::read() {
cout << name << ":" << endl;
cout << "처음 수에서 두번째 수까지 더합니다. 두 수를 입력하세요>> ";
cin >> x >> y;
}
void LoopAdder::write() { //결과 sum 출력
cout << x << "에서 " << y << "까지의 합 = " << sum << " 입니다." << endl;
}
void LoopAdder::run() {
read(); //x, y를 읽는다.
sum = calculate();
write();
}
class WhileLoopAdder : public LoopAdder
{
public:
WhileLoopAdder(string name) : LoopAdder(name) {
};
virtual int calculate() {
int sum = 0;
int bigNum = 0;
int smallNum = 0;
if (getX() > getY())
{
bigNum = getX();
smallNum = getY();
}
else
{
bigNum = getY();
smallNum = getX();
}
while (bigNum >= smallNum)
{
sum += smallNum;
smallNum++;
}
return sum;
}
};
class DoWhileLoopAdder : public LoopAdder
{
public:
DoWhileLoopAdder(string name) : LoopAdder(name) {
};
virtual int calculate() {
int sum = 0;
int bigNum = 0;
int smallNum = 0;
if (getX() > getY())
{
bigNum = getX();
smallNum = getY();
}
else
{
bigNum = getY();
smallNum = getX();
}
do
{
sum += smallNum;
smallNum++;
} while (bigNum >= smallNum);
return sum;
}
};
int main()
{
WhileLoopAdder whileLoop("While Loop");
DoWhileLoopAdder doWhileLoop("Do while Loop");
whileLoop.run();
doWhileLoop.run();
}9-5, 추상클래스를 이용한 OR & AND & XOR
디지털 회로에서 기본적인 게이트로 OR 게이트, AND 게이트, XOR 게이트 등이 있다. 이들은 각각 두 입력 신호를 받아 OR 연산, AND 연산, XOR 연산을 수행한 결과를 출력한다. 이 게이트들을 각각 ORGate, XORGate, ANDGate 클래스로 작성하고자 한다. ORGate, XORGate, ANDGate 클래스가 AbstractGatef를 상속받도록 작성하라.
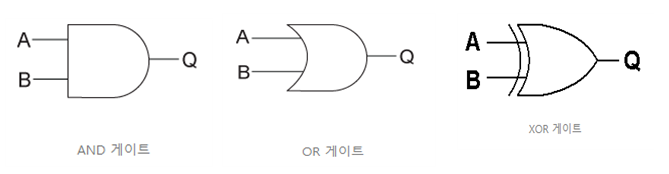
class AbstractGate { // 추상 클래스
protected:
bool x, y;
public:
void set(bool x, bool y) { this->x = x; this->y = y; }
virtual bool operation()=0;
};ANDGate, ORGate, XORGate를 활용하는 사례와 결과는 다음과 같다.
ANDGate andGate;
ORGate orGate;
XORGate xorGate;
andGate.set(true, false);
orGate.set(true, false);
xorGate.set(true, false);
cout.setf(ios::boolalpha); // 불린 값을 "true", "false" 문자열로 출력할 것을 지시
cout << andGate.operation() << endl; // AND 결과는 false
cout << orGate.operation() << endl; // OR 결과는 true
cout << xorGate.operation() << endl; // XOR 결과는 true false
true
true
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class AbstractGate
{
protected:
bool x, y;
public:
AbstractGate()
{
x = false;
y = false;
}
void set(bool x, bool y) {
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
bool getX() { return x; }
bool getY() { return y; }
virtual bool operation() = 0;
};
class ANDGate : public AbstractGate
{
public:
virtual bool operation()
{
if (getX() && getY())
return true;
else
return false;
}
};
class ORGate : public AbstractGate
{
public:
virtual bool operation()
{
if (getX() || getY())
return true;
else
return false;
}
};
class XORGate : public AbstractGate
{
public:
virtual bool operation()
{
if (getX() != getY())
return true;
else
return false;
}
};
int main()
{
ANDGate andGate;
ORGate orGate;
XORGate xorGate;
andGate.set(true, false);
orGate.set(true, false);
xorGate.set(true, false);
cout.setf(ios::boolalpha);
cout << andGate.operation() << endl;
cout << orGate.operation() << endl;
cout << xorGate.operation() << endl;
}9-6, 추상클래스를 이용한 Instack 구현
다음 AbstractStack은 정수 스택 클래스로서 추상 클래스이다.
class AbstrackStack {
public:
virtual bool push(int n) = 0; // 스택에 n을 푸시한다. 스택이 full이면 false 리턴
virtual bool pop(int& n) = 0; // 스택에서 팝한 정수를 n에 저장하고 스택이 empty이면 false 리턴
virtual int size() = 0;
};이를 상속받아 정수를 푸시, 팝하는 IntStack 클래스를 만들고 사용 사례를 보여라.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class AbstractStack {
public:
virtual bool push(int n) = 0;
virtual bool pop(int& n) = 0;
virtual int size() = 0;
};
class IntStack : AbstractStack {
int* stack;
int top, capacity;
public:
IntStack(int capacity = 100) {
this->capacity = capacity;
stack = new int[capacity];
top = -1;
}
~IntStack() { if (stack) delete[]stack; }
virtual bool push(int n)
{
if (top == capacity - 1) {
cout << "Stack is Full" << endl;
return false;
}
else {
stack[++top] = n;
return true;
}
}
virtual bool pop(int& n) {
if (top == -1) {
cout << "Stack is Empty" << endl;
return false;
}
else {
n = stack[top--];
return true;
}
}
virtual int size() { return top + 1; }
};
int main() {
IntStack IS(100);
int n;
cout << "스택에 삽입할 5개의 정수를 입력하라>> ";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cin >> n;
IS.push(n);
}
cout << "스택의 크기 : " << IS.size() << endl;
cout << "스택의 원소를 순서대로 제거하여 출력한다 >> ";
while (IS.size() != 0) {
IS.pop(n);
cout << n << ' ';
}
cout << endl << "스택의 현재 크기 : " << IS.size() << endl;
}풀지 못한 이유
virtual int size() = 0; 을 생각못하고 변수에 size을 써서 애러 메시지를 해결못하였다. 또한 계속 실수하는 부분이 순수 가상 함수로 구현하였지만 파생 클래스에서 이를 구현 안해 애러 메이지를 발생하는 경우다. stack 구현 자체는 여러 번 풀어서 알고리즘 자체는 쉬웠다.
사각형에 내접하는 도형을 표한하기 위한 Shape 클래스가 있다.
class Shape {
protected:
string name; // 도형의 이름
int width, height; // 도형이 내접하는 사각형의 너비와 높이
public:
Shape(string n="", int w=0, int h=0) { name = n; width = w; height = h; }
virtual double getArea() { return 0; } // dummy 값 리턴
string getName() { return name; } // 이름 리턴
};
9-7
Shape 클래스를 상속받아 타원을 표현하는 Oval, 사각형을 표현하는 Rect, 삼각형을 표현하는 Triangular 클래스를 작성하라. main()을 작성하고 실행하면 다음과 같다.
int main() {
Shape *p[3];
p[0] = new Oval("빈대떡", 10, 20);
p[1] = new Rect("찰떡", 30, 40);
p[2] = new Triangular("토스트", 30, 40);
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
cout << p[i]->getName() << " 넓이는 " << p[i]->getArea() << endl;
for(int i=0; i<3; i++) delete p[i];
} 빈대떡 넓이는 628
찰떡 넓이는 1200
토스트 넓이는 600
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Shape
{
protected:
string name;
int w, h;
public:
Shape(string n = "", int w = 0, int h = 0)
{
name = n;
this->w = w;
this->h = h;
}
virtual double getArea() { return 0; }
string getName() { return name; }
};
class Oval : public Shape
{
public:
Oval(string name, int w, int h) : Shape()
{
this->name = name;
this->w = w;
this->h = h;
}
virtual double getArea()
{
return 3.14 * w * h;
}
};
class Rect : public Shape
{
public:
Rect(string name, int w, int h) : Shape()
{
this->name = name;
this->w = w;
this->h = h;
}
virtual double getArea()
{
return w * h;
}
};
class Triangular : public Shape
{
public:
Triangular(string name, int w, int h) : Shape()
{
this->name = name;
this->w = w;
this->h = h;
}
virtual double getArea()
{
return (w * h) / 2;
}
};
int main()
{
Shape* p[3];
p[0] = new Oval("빈대떡", 10, 20);
p[1] = new Rect("찰떡", 30, 40);
p[2] = new Triangular("토스트", 30, 40);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
cout << p[i]->getName() << " 넓이는 " << p[i]->getArea() << endl;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
delete p[i];
}
}9-8
Shape을 추상 클래스로 만들려면 getArea() 함수를 순수 가상 함수로 만들면 된다.
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Shape
{
protected:
string name;
int w, h;
public:
Shape(string n = "", int w = 0, int h = 0)
{
this->name = n;
this->w = w;
this->h = h;
}
virtual double getArea() = 0;
string getName() { return name; }
};
class Oval : public Shape
{
public:
Oval(string name, int w, int h) : Shape()
{
this->name = name;
this->w = w;
this->h = h;
}
virtual double getArea()
{
return 3.14 * w * h;
}
};
class Rect : public Shape
{
public:
Rect(string name, int w, int h) : Shape()
{
this->name = name;
this->w = w;
this->h = h;
}
virtual double getArea()
{
return w * h;
}
};
class Triangular : public Shape
{
public:
Triangular(string name, int w, int h) : Shape()
{
this->name = name;
this->w = w;
this->h = h;
}
virtual double getArea()
{
return (w * h) / 2;
}
};
int main()
{
Shape* p[3];
p[0] = new Oval("빈대떡", 10, 20);
p[1] = new Rect("찰떡", 30, 40);
p[2] = new Triangular("토스트", 30, 40);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
cout << p[i]->getName() << " 넓이는 " << p[i]->getArea() << endl;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
delete p[i];
}
}
9-9, 가상 함수를 이용한 프린터
다음 그림과 같은 상속 구조를 갖는 클래스를 설계한다.
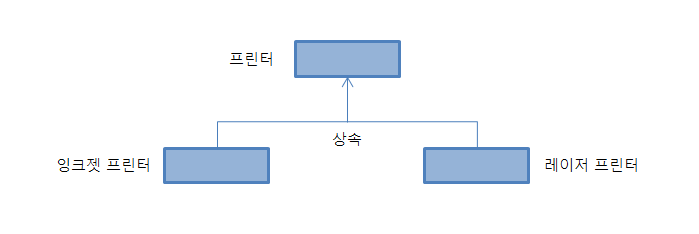
모든 프린터는 모델명(model), 제조사(manufacturer), 인쇄 매수(printedCount), 인쇄 종이 잔량(availableCount)을 나타내는 정보를 가진다. print(int pages) 함수와 show() 함수는 가상 함수로 구현하라. print(int pages)는 pages 만큼 프린트하는 함수이고, show() 함수는 현재 프린트의 모델, 제조사, 인쇄 매수, 인쇄 종이 잔량 등을 출력하는 함수이다.
잉크젯 프린터는 잉크 잔량(availableInk) 정보를 추가적으로 가지며, 레이저 프린터는 토너 잔량(availableToner) 정보를 추가적으로 가진다. 이들의 print(int pages) 멤버 함수는 프린터 타입에 맞게 구현하라. 각 클래스를 설계 구현하고 다음과 같이 실행되도록 전체 프로그램을 완성하라. InkJetPrinter 객체와 LaserPrinter 객체를 각각 하나만 동적으로 생성하여 시작한다.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Printer
{
protected:
string model; //모델명
string manufacturer; //제조사
int printedCount; //인쇄 매수
int availableCount; //인쇄 종이 잔량
public:
Printer(string model = "", string manufacturer = "", int printedCount = 0,int availableCount = 0) {
this->model = model;
this->manufacturer = manufacturer;
this->printedCount = printedCount;
this->availableCount = availableCount;
}
virtual void print(int pages) = 0;
virtual void show() = 0;
};
class InkJetPrinter : public Printer
{
int availableInk; //잉크 잔량
public:
InkJetPrinter(string model, string manufacturer, int availableCount, int availableInk) : Printer()
{
this->model = model;
this->manufacturer = manufacturer;
this->availableCount = availableCount;
this->availableInk = availableInk;
}
virtual void print(int pages)
{
//남은 인쇄 종이가 pages보다 클 때, 인쇄 가능
if (availableCount > pages)
{
cout << "프린트하였습니다" << endl;
availableCount -= pages;
availableInk -= pages;
}
else //인쇄 불가능
{
cout << "용지가 부족하여 프린트할 수 없습니다" << endl;
}
}
virtual void show()
{
cout << model << " ," << manufacturer << " ,남은 종이" << availableCount << "장 ," << "남은 토너" << availableInk << endl;
}
};
class LaserPrinter : public Printer
{
int availableToner; //토너 잔량
public:
LaserPrinter(string model, string manufacturer, int availableCount, int availableToner) : Printer()
{
this->model = model;
this->manufacturer = manufacturer;
this->availableCount = availableCount;
this->availableToner = availableToner;
}
virtual void print(int pages)
{
//남은 인쇄 종이가 pages보다 클 때, 인쇄 가능
if (availableCount > pages)
{
cout << "프린트하였습니다" << endl;
availableCount -= pages;
availableToner -= pages;
}
else //인쇄 불가능
{
cout << "용지가 부족하여 프린트할 수 없습니다" << endl;
}
}
virtual void show()
{
cout << model << " ," << manufacturer << " ,남은 종이" << availableCount << "장 ," << "남은 토너" << availableToner << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
InkJetPrinter inkJetPrinter("Officejet V40", "HP", 5, 10);
LaserPrinter laserPrinter("SCX-6x45", "삼성전자", 3, 20);
int num, pages; //번호와 매수
string printString;
cout << "현재 작동중인 2 대의 프린터는 아래와 같다." << endl;
cout << "잉크젯 : ";
inkJetPrinter.show();
cout << "레이저 : ";
laserPrinter.show();
cout << endl;
while (true)
{
cout << "프린터(1:잉크젯, 2:레이저)와 매수 입력>>";
cin >> num >> pages;
switch (num)
{
case 1: //잉크젯
inkJetPrinter.print(pages);
break;
case 2: //레이저
laserPrinter.print(pages);
break;
}
inkJetPrinter.show();
laserPrinter.show();
cout << "계속 프린트 하시겠습니까(y/n)>>";
cin >> printString;
if (printString == "n")
break;
cout << endl << endl;
}
}