PCAP : C언어의 PCAP(Packet Capture)은 네트워크 패킷을 캡처하고 분석하기 위한 라이브러리이다.
패킷(Packets) : 패킷은 네트워크 통신에서 데이터를 전송하는 기본 단위
캡처(Capture) : 캡처는 특정 정보를 가져오거나 기록하는 과정
패킷 캡처는 네트워크 통신에서 데이터를 전송하는 기본 단위를 잡아서 기록하는 것을 말합니다.
목표 : PCAP을 알고 작동시켜봄
- Ethernet 헤더에서 src mac / dst mac
- IP 헤더에서 src ip / dst ip
- TCP 헤더에서 src port / dst port
Ethernet 구조체

- DA : 목적지 MAC 주소
- SA : 출발지 MAC 주소
- TYPE : 이더넷 프레임 상단의 데이터 종류
- Data : 상위 레이어의 의해 사용되는 프로토콜의 정보
Ethernet Header
struct ethernet {
u_char ether_dhost[6];
u_char ether_shost[6];
u_short ether_type;
}
MAC Address 출력
Ethernet에서 mac주소의 정보를 얻어오기 위해 source mac 주소와 destination mac 주소를 파싱하여 출력
void mac_capture(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet) {
struct ethheader *eth = (struct ethheader *)packet;
printf("Source MAC = %s\n", ether_ntoa((struct ether_addr *)eth->ether_shost));
printf("Destination MAC = %s\n", ether_ntoa((struct ether_addr *)eth->ether_dhost));
printf("\n");
}
IP 구조체
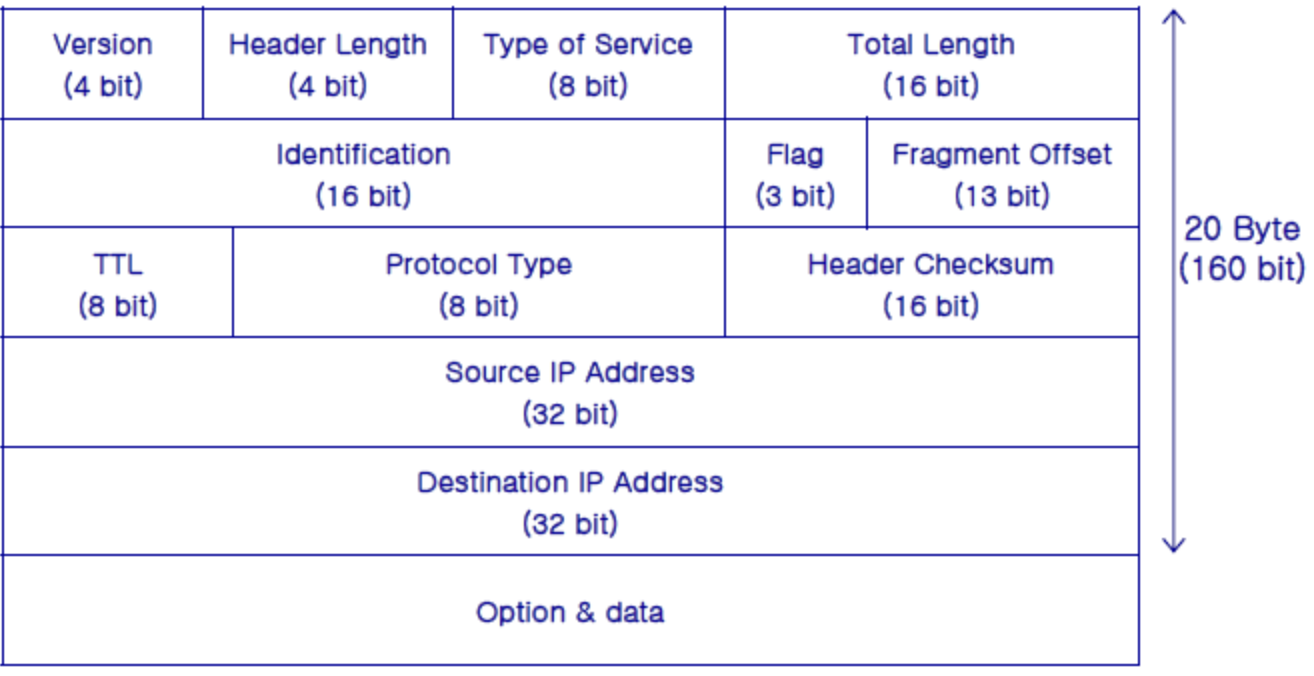
- Version : IP 버전
- Header Length : IP 헤더 길이
- TOS : 패킷 우선순위
- Length : 패킷의 총 길이
- Identification : 데이터가 크면 단편화가 일어남
- Flag : 단편화가 일어났는지 확인하기 위한 값
- Fragment Offset : 단편화 시 패킷이 몇 번째 패킷인지 나타내는 값
- TTL : 패킷의 생존 시간
- Protocol Type : TCP 등의 상위 전송 계층 타입
- Source IP : 출발지 IP 주소
- Destination IP : 목적지 IP 주소
IP Header
struct ipheader {
unsigned char iph_ihl:4, //IP header length
iph_ver:4; //IP version
unsigned char iph_tos; //Type of service
unsigned short int iph_len; //IP Packet length (data + header)
unsigned short int iph_ident; //Identification
unsigned short int iph_flag:3, //Fragmentation flags
iph_offset:13; //Flags offset
unsigned char iph_ttl; //Time to Live
unsigned char iph_protocol; //Protocol type
unsigned short int iph_chksum; //IP datagram checksum
struct in_addr iph_sourceip; //Source IP address
struct in_addr iph_destip; //Destination IP address
}IP Address 출력
IP 헤더 구조체를 선언한 후 IP 헤더 내의 source IP 주소와 destination IP 주소를 파싱하여 출력
void ip_capture(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet) {
struct ethheader *eth = (struct ethheader *)packet;
struct ipheader *ip = (struct ipheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader));
printf("Source IP = %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip->iph_sourceip));
printf("Destination IP = %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip->iph_destip));
printf("\n");
TCP 구조체
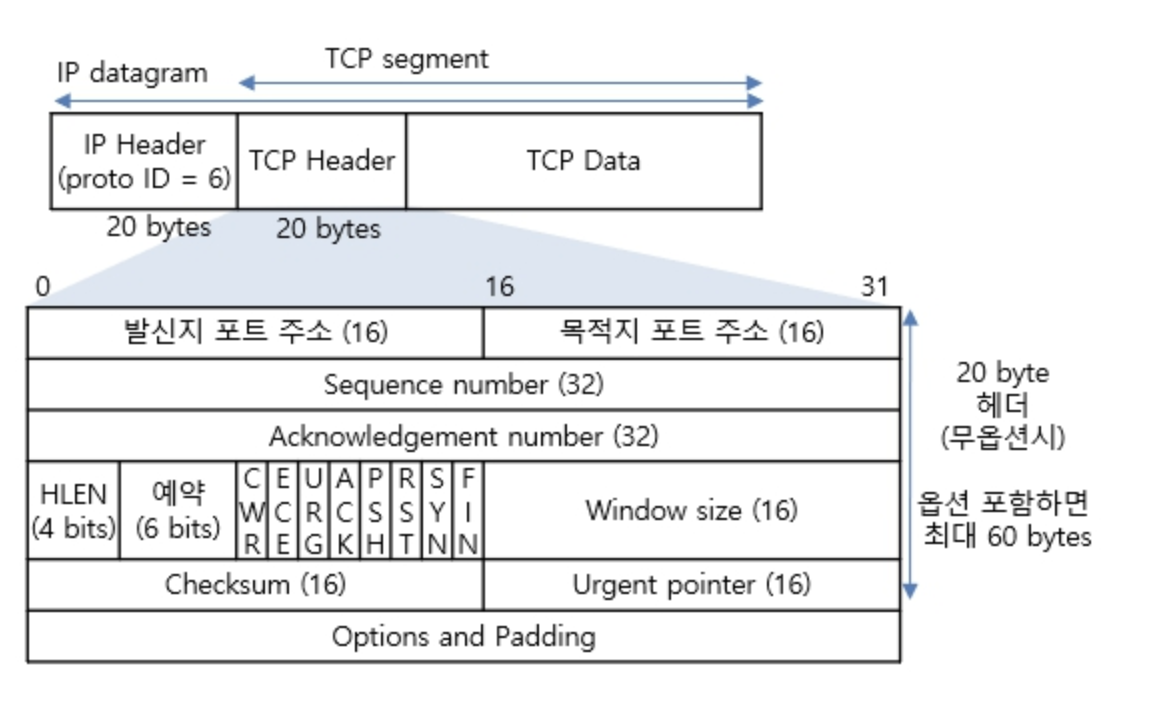
사진 출처 : http://www.ktword.co.kr/test/view/view.php?m_temp1=1889
- 발신지 포트 주소 (16bits - Source Port)
- 목적지 포트 주소 (16bits - Destination Port)
- Sequence number (32bits)
- Acknowledgement number (32bits)
- HLEN (4bits)
- 예약 (6bits)
- Flag (6bits)
TCP Header
struct tcpheader {
u_short tcp_sport; /* source port */
u_short tcp_dport; /* destination port */
u_int tcp_seq; /* sequence number */
u_int tcp_ack; /* acknowledgement number */
u_char tcp_offx2; /* data offset, rsvd */
#define TH_OFF(th) (((th)->tcp_offx2 & 0xf0) >> 4)
u_char tcp_flags;
#define TH_FIN 0x01
#define TH_SYN 0x02
#define TH_RST 0x04
#define TH_PUSH 0x08
#define TH_ACK 0x10
#define TH_URG 0x20
#define TH_ECE 0x40
#define TH_CWR 0x80
#define TH_FLAGS (TH_FIN|TH_SYN|TH_RST|TH_ACK|TH_URG|TH_ECE|TH_CWR)
u_short tcp_win; /* window */
u_short tcp_sum; /* checksum */
u_short tcp_urp; /* urgent pointer */
}
Port Number 출력
void tcp_capture(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet) {
struct ethheader *eth = (struct ethheader *)packet;
struct ipheader *ip = (struct ipheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader));
struct tcpheader *tcp = (struct tcpheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader) + ip -> i
printf("Source Port = %d\n", ntohs(tcp->tcp_sport));
printf("Destination Port = %d\n", ntohs(tcp->tcp_dport));
printf("\n");
}
Header Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pcap.h>
#include <netinet/ether.h>
struct ethernet {
u_char ether_dhost[6];
u_char ether_shost[6];
u_short ether_type;
}
struct ipheader {
unsigned char iph_ihl:4, //IP header length
iph_ver:4; //IP version
unsigned char iph_tos; //Type of service
unsigned short int iph_len; //IP Packet length (data + header)
unsigned short int iph_ident; //Identification
unsigned short int iph_flag:3, //Fragmentation flags
iph_offset:13; //Flags offset
unsigned char iph_ttl; //Time to Live
unsigned char iph_protocol; //Protocol type
unsigned short int iph_chksum; //IP datagram checksum
struct in_addr iph_sourceip; //Source IP address
struct in_addr iph_destip; //Destination IP address
}
struct tcpheader {
u_short tcp_sport; /* source port */
u_short tcp_dport; /* destination port */
u_int tcp_seq; /* sequence number */
u_int tcp_ack; /* acknowledgement number */
u_char tcp_offx2; /* data offset, rsvd */
#define TH_OFF(th) (((th)->tcp_offx2 & 0xf0) >> 4)
u_char tcp_flags;
#define TH_FIN 0x01
#define TH_SYN 0x02
#define TH_RST 0x04
#define TH_PUSH 0x08
#define TH_ACK 0x10
#define TH_URG 0x20
#define TH_ECE 0x40
#define TH_CWR 0x80
#define TH_FLAGS (TH_FIN|TH_SYN|TH_RST|TH_ACK|TH_URG|TH_ECE|TH_CWR)
u_short tcp_win; /* window */
u_short tcp_sum; /* checksum */
u_short tcp_urp; /* urgent pointer */
}
Main Code
void packet_capture(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet){
struct ethheader *eth = (struct ethheader *)packet;
struct ipheader *ip = (struct ipheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader));
struct tcpheader *tcp = (struct tcpheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader) + ip->iph_ihl * 4);
// Ethernet 정보 출력
printf("Source MAC = %s\n", ether_ntoa((struct ether_addr *)eth->ether_shost));
printf("Destination MAC = %s\n", ether_ntoa((struct ether_addr *)eth->ether_dhost));
// IP 정보 출력
printf("Source IP = %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip->iph_sourceip));
printf("Destination IP = %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip->iph_destip));
// TCP 포트 정보 출력
printf("Source Port = %d\n", ntohs(tcp->tcp_sport));
printf("Destination Port = %d\n", ntohs(tcp->tcp_dport));
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
pcap_t *handle;
char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
handle = pcap_open_live("eth0", BUFSIZ, 1, 1000, errbuf);
pcap_loop(handle, 0, packet_capture, NULL);
pcap_close(handle);
return 0;
}pcap_open_live(device, snaplen, promisc, to_ms, ebuf)
- device: 캡처할 네트워크 인터페이스의 이름을 나타내는 문자열입니다. 예를 들어, "eth0" 또는 "wlan0"과 같은 형식
- snaplen: 캡처할 패킷의 최대 길이를 지정하는 정수이며, 이 값은 일반적으로 패킷의 크기보다 크거나 같아야 함
- promisc: 프로미스큐어스 모드를 사용할지 여부를 나타내는 정수
- to_ms: 읽을 수 있는 데이터가 없을 때 대기하는 시간을 나타내는 정수
pcap_loop(p, cnt, callback, user)
- p: 패킷 캡처 핸들(pcap_t)
- cnt: 읽을 패킷의 최대 개수를 나타내는 정수
- callback: 각 패킷을 처리하기 위해 호출되는 콜백 함수이며, 패킷 데이터와 사용자가 정의한 데이터(user)를 인자로 받음
- user: 사용자가 정의한 데이터
내용 기반 : https://velog.io/@p5tat5/PCAP-Programming
Ubuntu 환경에서는 이 파일을 실행하기 위해
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install libpcap-dev
gcc example.c -o example -lpcap
이런 형식으로 컴파일 되어야 합니다.
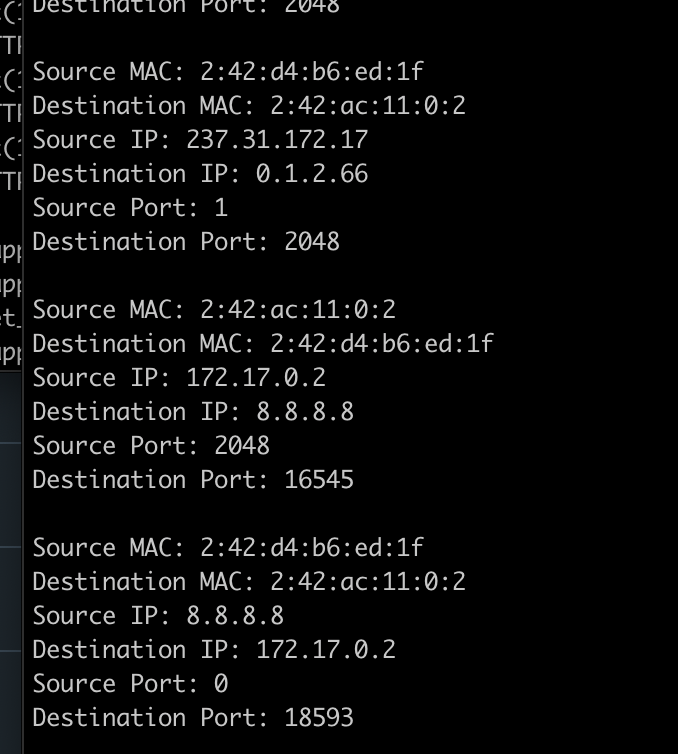
이렇게 잘 동작하였습니다.
