✔ Introduction
프로젝트에서 Fetch API를 활용하여 express 서버에 JSON 형식의 데이터를 보내고 서버에서 활용하기 위해 req.body를 확인해 보았으나 undefined라고 나왔다. Form 데이터를 POST 할 때는 express.urlencoded middleware가 form 데이터를 req.body에 parsing 해서 넣어주어서 req.body에서 확인할 수 있었는데 Fetch API를 통해 들어온 데이터는 어떻게 처리할 수 있는지 알아보는 과정에서 body parser에 대해 자세히 알아보았고 이에 대해 적어보고자 한다.
✔ What is BodyParser
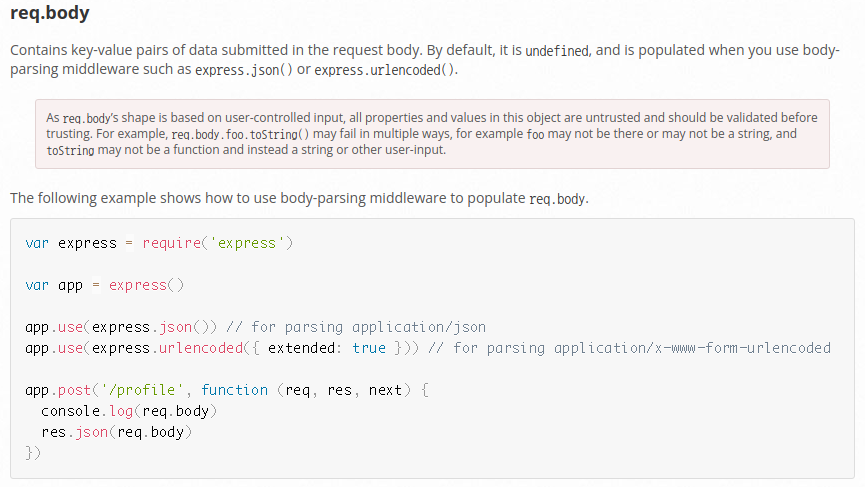
Contains key-value pairs of data submitted in the request body. By default, it is undefined, and is populated when you use body-parsing middleware such as express.json() or express.urlencoded().
Express 공식 문서에 따르면 req.body 안에 key-value pair는 기본적으로 undefined로 설정되어 있으므로 express.json(), express.urlencoded()와 같은 middleware를 사용하여 채워야 한다.
클라이언트 측에서 API를 post, put method로 요청 시 request.body에 있는 값을 서버 측에서 받는다고 그대로 사용할 수 있는 것이 아니고 서버 내에서 해석 가능한 형태로 변형해야 사용할 수 있게 된다.
이때 API 요청에서 받은 body 값을 파싱 하는 역할을 수행하는 것이 bodyParser middleware이다.(출처: https://velog.io/@yejinh/express-미들웨어-bodyParser-모듈)
✔ BodyParser
Parse incoming request bodies in a middleware before your handlers, available under the req.body property.
✔ bodyparser.text

Returns middleware that parses all bodies as a string and only looks at requests where the Content-Type header matches the type option. This parser supports automatic inflation of gzip and deflate encodings.
A new body string containing the parsed data is populated on the request object after the middleware (i.e. req.body). __This will be a "string of the body".
브라우저(front)에서 text 형식의 데이터를 보낸다면 bodyparser.text(express.text) middleware로 parsing 할 수 있다. 하지만 보통 text보다는 key-value 형식의 json 데이터를 많이 보낸다. 이 경우에는 이 middleware로 parsing 할 수 없고 뒤에 나오는 bodyparser.json middleware를 사용해야 한다.
✔ bodyparser.json

Returns middleware that only parses json and only looks at requests where the Content-Type header matches the type option. This parser accepts any Unicode encoding of the body and supports automatic inflation of gzip and deflate encodings.
A new body object containing the parsed data is populated on the request object after the middleware (i.e. req.body).
이 글을 적게 된 계기에 해당하는 문제에 대한 답이다. body-parser를 기반으로 request payload로 전달한 JSON을 파싱 한다. String을 받아서 json으로 바꿔준다. 주의할 점은 express.json()은 header에 Content-Type이 express.json()의 기본 값인 "application/json"과 일치하는 request만 보는 미들웨어를 반환한다는 것이다. 즉, headers: { "Content-type": "application/json" }인 request만 express.json()을 실행한다.
✔ request.ContentType: JSON vs x-www-form-urlencoded
그렇다면 form에서 post 한 데이터를 parsing 하기 위한 express.urlencoded middleware와 fetch api에서 request payload를 통해 보낸 json을 parsing 하기 위한 express.json middleware의 차이는 뭘까? 이는 request.ContentType에 따른 것이다. 즉, contentType이 x-www-form-urlencoded 이면 전자, JSON 이면 후자를 이용하여 parsing 할 수 있다.
아래는 두 request.ContentType에 대한 설명이다. 둘의 큰 차이점은 json type의 경우 원본 데이터의 형태를 보존하나 urlencoded type의 경우 모든 property를 string으로 변환한다는 것이다.
If you send HTTP GET request, you can use query parameters as follows:
http://example.com/path/to/page?name=ferret&color=purple
The content of the fields is encoded as a query string. The application/x-www-form-urlencoded's name come from the previous url query parameter but the query parameters is in where the body of request instead of url.
The whole form data is sent as a long query string.The query string contains name- value pairs separated by & character.
e.g. field1=value1&field2=value2
One of the biggest differences between the two is that JSON-encoding the post usually preserves the data types of the values that are sent in (as long as they are valid JSON datatypes), whereas application/x-www-form-urlencoded will usually have all properties converted to strings.
✔ Comment
이 글 작성하면서 공식문서 보는 것에 좀 익숙해진 것 같다. mdn, stack overflow가 친절하다는 것을 새삼 느낀다
✔ [22.02.26 update] Why should frontend send string to backend?
생각해 보니 왜 front에서 서버로 자바스크립트 object 형태 그대로 전송하면 안 되고 string으로 보내서 parser로 parsing 하는 번거로운 과정을 거쳐야 하는지 의문이 들었다.
이에 대한 답은 서버가 자바스크립트로 구성되어 있지 않을 수도 있다는 것이다. 예를 들어 자바로 서버를 구성하였을 경우 서버에 자바스크립트 object를 보내는 것은 좋은 방법이 아니다. 따라서 string 형태로 전송한 후 서버에서 parsing 한 후 가공하는 것이 적절할 것이다.
✔ [22.04.11 update] HTTP Request Data
HTTP 요청 메시지를 통해 클라이언트에서 서버로 데이터를 전달할 때에는 주로 다음 3가지 방법을 사용한다.
GET - 쿼리 파라미터
- /url?username=hello&age=20
- message body 없이, URL의 쿼리 파라미터에 데이터를 포함해서 전달
- 예) 검색, 필터, 페이징등에서 많이 사용하는 방식
GET URL 쿼리 파라미터 형식으로 클라이언트에서 서버로 데이터를 전달할 때는 HTTP 메시지 바디를
사용하지 않기 때문에 content-type이 없다.
POST - HTML Form
- content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- 메시지 바디에 쿼리 파리미터 형식으로 전달 username=hello&age=20
- 예) 회원 가입, 상품 주문, HTML Form 사용
POST HTML Form 형식으로 데이터를 전달하면 HTTP 메시지 바디에 해당 데이터를 포함해서 보내기
때문에 바디에 포함된 데이터가 어떤 형식인지 content-type을 꼭 지정해야 한다. 이렇게 폼으로 데이터를
전송하는 형식을 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 라 한다.
HTTP message body에 데이터를 직접 담아서 요청
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용, JSON, XML, TEXT
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON 사용
- POST, PUT, PATCH
(출처: 인프런 김영한님 스프링 MVC 1편 강의자료 https://www.inflearn.com/course/%EC%8A%A4%ED%94%84%EB%A7%81-mvc-1)
✔ Conclusion
express에서는 http request message의 본문을 parsing 할 때 본문의 content-type에 따라 다른 bodyparser가 parsing을 해준다. 그리고 스프링에서는 servlet이 해준다. 이 모든 것은 http message parsing 하는 데 힘 빼지 말고 비즈니스 로직 구현하는데 집중하기 위해 존재
✔ 참고자료
https://expressjs.com/ko/api.html#req
http://expressjs.com/en/resources/middleware/body-parser.html
https://velog.io/@yejinh/express-미들웨어-bodyParser-모듈)
https://gomakethings.com/how-to-send-data-to-an-api-with-the-vanilla-js-fetch-method/#sending-data-as-a-json-object
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9870523/what-are-the-differences-between-application-json-and-application-x-www-form-url

일단 개추