✅ TIL
method (immutable): slice(), concat()
// 원본 배열을 변경하지 않는다.
mutator method (mutable): pop() , push(), shift(), unshift(), splice()
// 원본 배열을 변경한다.⚙️ 배열 속성
const word = "hello word";
word.length; // 속성⚙️ 배열 메서드
// 순서가 있는 자료(데이터)
const newArr = ["hi", "code"]
// "hi" -> newArr의 0번째 요소(element)
// "hi" -> 0 -> newArr의 'hi' 요소의 index는 0이다.// 빈 배열인지 아닌지 확인
arr.length === 0; -> 좋은 예시
let emptyArr = []; -> 좋지 않은 예시// 객체, object 중 배열인지 아닌지 확인
typeof words -> "object"
typeof [1, 2, 3] -> "object"
let obj = {a:1}
typeof obj -> "object"
Array.isArray("문자열") -> false
Array.isArray(123) -> false
Array.isArray(words) -> true
Array.isArray([1,2,3]) -> truelet words = ['Radagast', 'the', 'Brown'];
words.indexOf('the') -> 1
words.indexOf('Brown') -> 2
words.indexOf('Radagast') -> 0
words.indexOf('없는 단어') -> -1
// hasElement (배열, 찾으려는 엘리먼트)
function hasElement(arr, element) {
let isPresent = arr.indexOf(element) !== -1;
return isPresent;
}
hasElement(words, 'Brown') -> true
hasElement(words, '없는 것') -> false
words.includes('Brown') -> true
words.includes('없는 것') -> false⚙️ method (immutable)

Array.prototype.slice()
// 배열의 N번째 요소를 제외한 배열을 리턴
const animals = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'elephant'];
console.log(animals.slice(2));
// Expected output: Array ["camel", "duck", "elephant"]
console.log(animals.slice(2, 4));
// Expected output: Array ["camel", "duck"]Array.prototype.concat()
// 배열 merge
const array1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
const array2 = ['d', 'e', 'f'];
const array3 = array1.concat(array2);
console.log(array3);
// Expected output: Array ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"]
⚙️ mutator method (mutable)

Array.prototype.pop()
// 배열의 마지막 요소가 삭제된 배열을 리턴
const plants = ['broccoli', 'cauliflower', 'cabbage', 'kale', 'tomato'];
console.log(plants.pop());
// Expected output: "tomato"
console.log(plants);
// Expected output: Array ["broccoli", "cauliflower", "cabbage", "kale"]
plants.pop();
console.log(plants);
// Expected output: Array ["broccoli", "cauliflower", "cabbage"]
Array.prototype.push()
// 배열 끝에 추가
const animals = ['pigs', 'goats', 'sheep'];
const count = animals.push('cows');
console.log(count);
// Expected output: 4
console.log(animals);
// Expected output: Array ["pigs", "goats", "sheep", "cows"]
animals.push('chickens', 'cats', 'dogs');
console.log(animals);
// Expected output: Array ["pigs", "goats", "sheep", "cows", "chickens", "cats", "dogs"]
Array.prototype.shift()
// 배열의 첫번째 요소가 삭제된 배열을 리턴
const array1 = [1, 2, 3];
const firstElement = array1.shift();
console.log(array1);
// Expected output: Array [2, 3]
console.log(firstElement);
// Expected output: 1Array.prototype.splice()
const months = ['Jan', 'March', 'April', 'June'];
months.splice(1, 0, 'Feb');
// Inserts at index 1
console.log(months);
// Expected output: Array ["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April", "June"]
months.splice(4, 1, 'May');
// Replaces 1 element at index 4
console.log(months);
// Expected output: Array ["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April", "May"]Array.prototype.join()
const elements = ['Fire', 'Air', 'Water'];
console.log(elements.join());
// Expected output: "Fire,Air,Water"
console.log(elements.join(''));
// Expected output: "FireAirWater"
console.log(elements.join('-'));
// Expected output: "Fire-Air-Water"String.prototype.split()
const str = 'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.';
const words = str.split(' ');
console.log(words[3]);
// Expected output: "fox"
const chars = str.split('');
console.log(chars[8]);
// Expected output: "k"
const strCopy = str.split();
console.log(strCopy);
// Expected output: Array ["The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."]✅ 문제 복습
📝 getAllWords
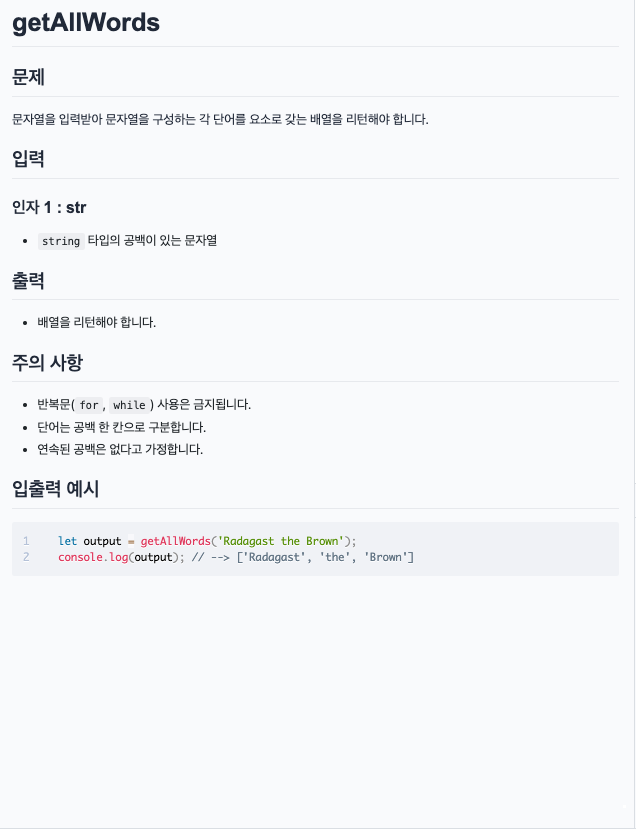
내가 적은 답
function getAllWords(str) {
if(str.length === 0){
return [];
}
return str.split(' ');
}정답 & 풀이
function getAllWords(str) {
if (str === '') {
return [];
}
return str.split(' ');
}나는 개인적으로 배열이 빈 칸인지 확인하는 방법은, 내가 적은 str.length === 0 가 최고라고 생각한다.
split()은 안에 ' ' 한 칸 뛴 공백을 넣으면 문자열의 공백을 모두 없애고 배열에 넣어준다.
📝 getAllLetters
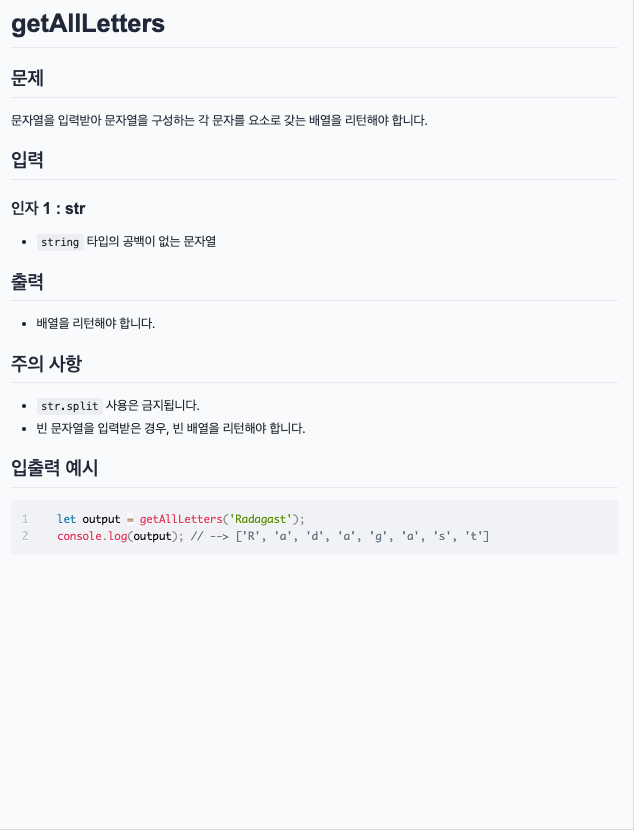
내가 적은 답
function getAllLetters(str) {
let arr = [];
for(let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
arr.push(str[i]);
}
return arr;
}
정답 & 풀이
function getAllLetters(str) {
let result = [];
for (let el of str) {
result.push(el);
}
return result;
}arr.push() 를 제대로 아는지 물어보는 문제였다.
✨ [] 안에 str[i]인 string 타입을 push 해주면, 한 글자씩 묶여 배열이 완성된다.
정답은 내가 쓴 것과 같은 반복문 문법이다.
덕분에 'mdn for of' 서칭해서 이런 것도 있구나.. 했다.
그리고 ( ) 안에 str[i]와 같은 매개변수를 넣는 형태가 자꾸 손이 안 간다.
때문에 까먹지 말자는 의미로 리마인드한다.
📝 getEvenNumbers
내가 적은 답
function getEvenNumbers(arr) {
let result = [];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] % 2 === 0) {
result.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return result;
}정답 & 풀이
function getAllLetters(str) {
let result = [];
for (let el of str) {
result.push(el);
}
return result;
}arr.push() 를 제대로 아는지 물어보는 문제였다.
✨ [] 안에 str[i]인 string 타입을 push 해주면, 한 글자씩 묶여 배열이 완성된다.
정답과 똑같이 썼지만, ( ) 안에 str[i]와 같은 매개변수를 넣는 형태가 어색하다.
때문에 까먹지 말자는 의미로 리마인드한다.
📝 removeFromBackofNew
내가 적은 답
function removeFromBackOfNew(arr) {
// TODO: 여기에 코드를 작성합니다.
let result = arr.slice(); // 주소 값 건드리지 않고 전체 복사
result.pop();
return result;
// result = result.pop(); // 하게되면 결과 값이 3이 리턴 됌
// 바로 return arr.slice(0,arr.length-1); 은 가능
}정답 & 풀이
function removeFromBackOfNew(arr) {
return arr.slice(0, arr.length - 1);
}이 문제에서 뭔가 🍯 팁을 많이 느꼈다.
- ✨ let result = arr.slice() 로 arr의 주소 값을 Save 할 수 있다. -> 원본을 건들지 않는 개념
- ✨ result.pop 후, return 하면 result 이므로 주소 값이 바뀐 것이다.
- arr.pop(); return arr; 시, 입력받은 배열을 수정한다. -> 2번과 같은 개념
- 바로 slice를 return하면 입력받은 배열은 수정이 되지 않지만, 새로운 배열(주소 값 다름)을 갖는다.
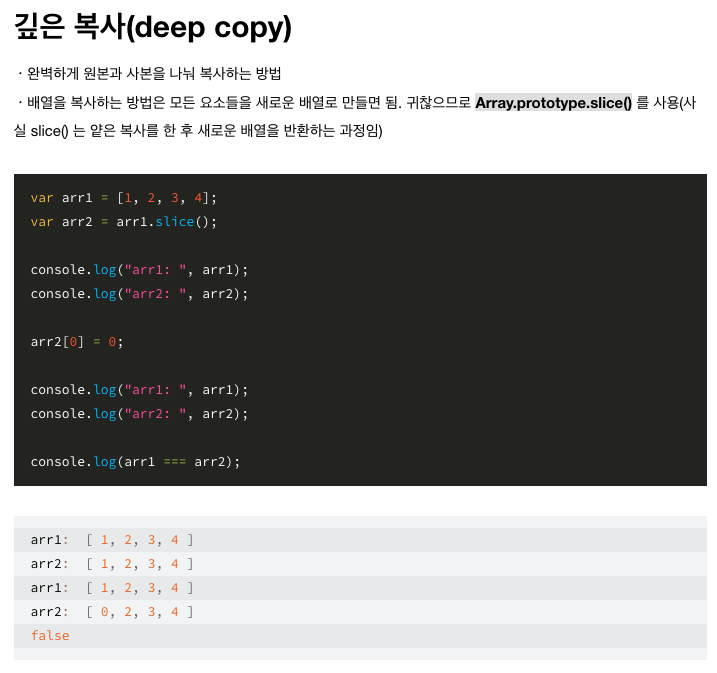
즉, slice() 메서드는 어떤 배열의 begin 부터 end 까지(end 미포함)에 대한 얕은 복사본을 새로운 배열 객체로 반환한다. 원본 배열은 바뀌지 않는다
-> ✨ slice는 method (immutable)
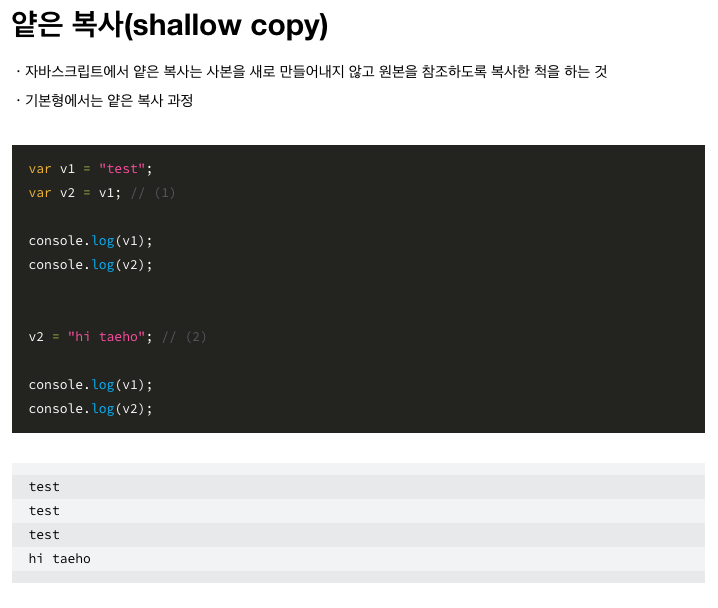
🔥 얕은 복사와 깊은 복사