1. 액션
액션(Action)은 비동기식+동기식 양방향 메시지 송수신 방식으로 액션 목표(Goal)를 지정하는 액션 클라이언트(Action Client)와 액션 목표를 받아 특정 태스크를 수행하면서 중간 결괏값을 전송하는 액션 피드백(Action Feedback) 그리고 최종 결괏값에 해당되는 액션 결과(Action result)를 전송하는 액션 서버(Action Server)간의 통신이다.
액션에 대한 개념이 부족하다면
위 링크를 보고오자.
이번 장에서는 아래 그림과 같이 액션 목표를 지정하는 액션 클라이언트와 액션 목표를 받아 특정 태스크를 수행하면서 그 중간 결괏값을 전송하는 액션 피드백 그리고 최종 결괏값에 해당되는 액션 결과를 전송하는 액션 서브를 작성해 볼 것이다.
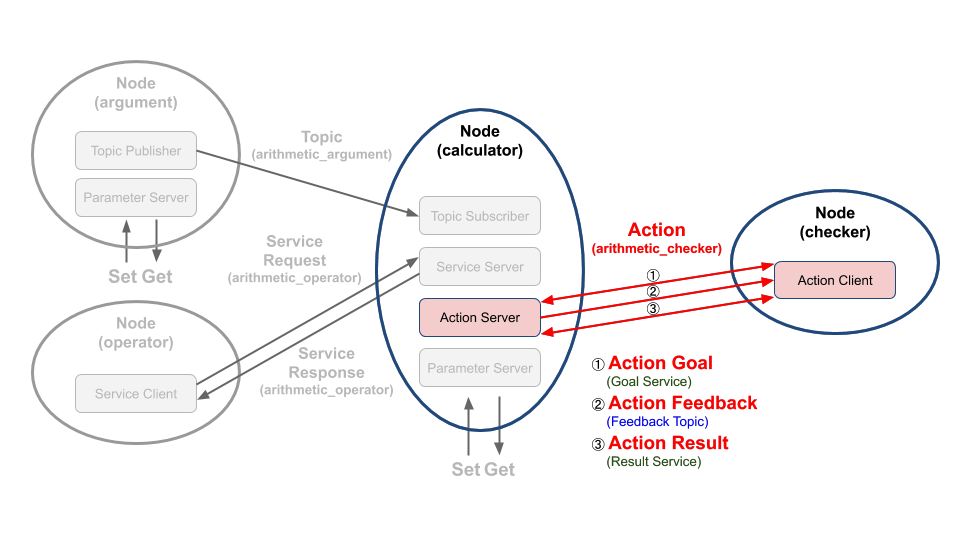
좀 더 세부 설명을 덧붙이자면 이 코드에서의 액션 목표로는 이전 강좌에서 설명하였던 매회 계산 값 합계의 최댓값이고 액션 피드백은 계산 공식의 문자열 값, 액션 결과는 매회 계산 값 합계가 지정된 액션 목표값에 도달하였을 때의 값이다.
예를 들어 액션 서버 클라이언트 역할을 하는 topic_service_action_rclpy_example 패키지의 checker 노드를 실행하면 하기와 같이 기본 액션 목표값으로 50으로 지정되고 매회 계산된 값이 10, 9, 6, 2, 36 일 때 지정된 50을 넘는 63이기에 63이 나오기 까지의 계산식을 피드백으로 받을 수 있고 최종 결괏값으로 모든 계산식을 받아 표시하고 있다.
$ ros2 run topic_service_action_rclpy_example checker
[INFO]: Action goal accepted.
[INFO]: Action feedback: ['7.0 + 3.0 = 10.0']
[INFO]: Action feedback: ['7.0 + 3.0 = 10.0', '8.0 + 1.0 = 9.0']
[INFO]: Action feedback: ['7.0 + 3.0 = 10.0', '8.0 + 1.0 = 9.0', '6.0 / 1.0 = 6.0']
[INFO]: Action feedback: ['7.0 + 3.0 = 10.0', '8.0 + 1.0 = 9.0', '6.0 / 1.0 = 6.0', '8.0 - 6.0 = 2.0']
[INFO]: Action feedback: ['7.0 + 3.0 = 10.0', '8.0 + 1.0 = 9.0', '6.0 / 1.0 = 6.0', '8.0 - 6.0 = 2.0', '6.0 * 6.0 = 36.0']
[INFO]: Action succeeded!
[INFO]: Action result(all formula): ['7.0 + 3.0 = 10.0', '8.0 + 1.0 = 9.0', '6.0 / 1.0 = 6.0', '8.0 - 6.0 = 2.0', '6.0 * 6.0 = 36.0']
[INFO]: Action result(total sum): 63.02. 액션 서버 코드
액션 서버 역할을 하는 노드는 calculator 노드로 앞에서 설명한것처럼 토픽 서브스크라이브, 서비스 서버, 액션 서버 모두 포함하는 노드라 소스코드가 매우 길어 전체 소스코드 중 액션 서버 부분만 분석해 보겠다.
import time
from msg_srv_action_interface_example.action import ArithmeticChecker
from msg_srv_action_interface_example.msg import ArithmeticArgument
from msg_srv_action_interface_example.srv import ArithmeticOperator
from rclpy.action import ActionServer
from rclpy.callback_groups import ReentrantCallbackGroup
from rclpy.node import Node
from rclpy.qos import QoSDurabilityPolicy
from rclpy.qos import QoSHistoryPolicy
from rclpy.qos import QoSProfile
from rclpy.qos import QoSReliabilityPolicy
class Calculator(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('calculator')
self.argument_a = 0.0
self.argument_b = 0.0
self.argument_operator = 0
self.argument_result = 0.0
self.argument_formula = ''
self.operator = ['+', '-', '*', '/']
self.callback_group = ReentrantCallbackGroup()
self.declare_parameter('qos_depth', 10)
qos_depth = self.get_parameter('qos_depth').value
QOS_RKL10V = QoSProfile(
reliability=QoSReliabilityPolicy.RELIABLE,
history=QoSHistoryPolicy.KEEP_LAST,
depth=qos_depth,
durability=QoSDurabilityPolicy.VOLATILE)
self.arithmetic_argument_subscriber = self.create_subscription(
ArithmeticArgument,
'arithmetic_argument',
self.get_arithmetic_argument,
QOS_RKL10V,
callback_group=self.callback_group)
self.arithmetic_service_server = self.create_service(
ArithmeticOperator,
'arithmetic_operator',
self.get_arithmetic_operator,
callback_group=self.callback_group)
self.arithmetic_action_server = ActionServer(
self,
ArithmeticChecker,
'arithmetic_checker',
self.execute_checker,
callback_group=self.callback_group)
def get_arithmetic_argument(self, msg):
self.argument_a = msg.argument_a
self.argument_b = msg.argument_b
self.get_logger().info('Timestamp of the message: {0}'.format(msg.stamp))
self.get_logger().info('Subscribed argument a: {0}'.format(self.argument_a))
self.get_logger().info('Subscribed argument b: {0}'.format(self.argument_b))
def get_arithmetic_operator(self, request, response):
self.argument_operator = request.arithmetic_operator
self.argument_result = self.calculate_given_formula(
self.argument_a,
self.argument_b,
self.argument_operator)
response.arithmetic_result = self.argument_result
self.argument_formula = '{0} {1} {2} = {3}'.format(
self.argument_a,
self.operator[self.argument_operator-1],
self.argument_b,
self.argument_result)
self.get_logger().info(self.argument_formula)
return response
def calculate_given_formula(self, a, b, operator):
if operator == ArithmeticOperator.Request.PLUS:
self.argument_result = a + b
elif operator == ArithmeticOperator.Request.MINUS:
self.argument_result = a - b
elif operator == ArithmeticOperator.Request.MULTIPLY:
self.argument_result = a * b
elif operator == ArithmeticOperator.Request.DIVISION:
try:
self.argument_result = a / b
except ZeroDivisionError:
self.get_logger().error('ZeroDivisionError!')
self.argument_result = 0.0
return self.argument_result
else:
self.get_logger().error(
'Please make sure arithmetic operator(plus, minus, multiply, division).')
self.argument_result = 0.0
return self.argument_result
def execute_checker(self, goal_handle):
self.get_logger().info('Execute arithmetic_checker action!')
feedback_msg = ArithmeticChecker.Feedback()
feedback_msg.formula = []
total_sum = 0.0
goal_sum = goal_handle.request.goal_sum
while total_sum < goal_sum:
total_sum += self.argument_result
feedback_msg.formula.append(self.argument_formula)
self.get_logger().info('Feedback: {0}'.format(feedback_msg.formula))
goal_handle.publish_feedback(feedback_msg)
time.sleep(1)
goal_handle.succeed()
result = ArithmeticChecker.Result()
result.all_formula = feedback_msg.formula
result.total_sum = total_sum
return resultcalculator 노드는 서브스크라이브한 변수 a,b 와 operator 노드로부터 요청값으로 받은 연산자를 저장한다. 그리고 이를 이용하여 연산하고 operator 노드에게 연산의 결괏값을 서비스 응답값으로 보낸다는것을 이전에 설명했다.
액션 서버와 관련된 코드는 다음과 같다. 액션 서버 코드는 액션 서버로 선언하는 부분과 콜백 함수를 지정하는 것이다.
액션 서버는 rclpy.action 모듈의 ActionServer 클래스를 이용하여 arithmetic_action_server 로 선언한다. 액션의 타입으로 ArithmeticChecker를 선언하였고, 액션 이름은 arithmetic_checker, 액션 클라이언트로부터 액션 목표를 받으면 실행되는 콜백 함수는 execute_checker 로 지정했다. 멀티 스레드 병렬 콜백 함수의 실행을 위해 callback_group 설정을 하였다. 이러한 설정들은 액션 서버를 위한 기본 설정이고 실제 액션 목표를 받은 후 실행되는 콜백 함수는 execute_checker 함수이다.
self.arithmetic_action_server = ActionServer(
self,
ArithmeticChecker,
'arithmetic_checker',
self.execute_checker,
callback_group=self.callback_group)그러면 execute_checker 함수의 내용을 보자. 우선 rclpy.action 모듈의 ServerGoalHandle 클래스로 생성된 액션 상태 처리를 위한 goal_handle 매개변수는 execute, succeed, abort, canceled 등과 같이 액션 상태에 따른 관련 함수 호출이 가능하며 publish_feedback 함수를 통해 피드백 메시지를 퍼블리시하는 기능을 가진다.
함수의 내용을 자세히 살펴보면, 첫 줄에서는 get_logger().info 함수를 이용해 터미널 창에 액션 서버가 시작됨을 표시하고, 다음 줄에서는 ArithmeticChecker.Feedback 클래스로 액션 피드백을 보낼 feedback_msg 변수를 선언하였다. 이어서 연산식을 담을 feedback_msg.formula 와 연산 누적값을 담을 total_sum 변수를 초기화하였다. 그 뒤 앞서 설명한 goal_handle를 이용하여 goal_handle.request.goal_sum 변수를 통해 액션 목푯값을 불러왔다.
def execute_checker(self, goal_handle):
self.get_logger().info('Execute arithmetic_checker action!')
feedback_msg = ArithmeticChecker.Feedback()
feedback_msg.formula = []
total_sum = 0.0
goal_sum = goal_handle.request.goal_sum
while total_sum < goal_sum:
total_sum += self.argument_result
feedback_msg.formula.append(self.argument_formula)
self.get_logger().info('Feedback: {0}'.format(feedback_msg.formula))
goal_handle.publish_feedback(feedback_msg)
time.sleep(1)
goal_handle.succeed()
result = ArithmeticChecker.Result()
result.all_formula = feedback_msg.formula
result.total_sum = total_sum
return result다음 while 반복 구문은 액션 목푯값(goal_sum)과 get_arithmetic_operator 함수를 통해 매번 계산되는 연산 결괏값인 argument_result의 누적(total_sum) 값을 비교한다. 그리고 누적 값이 액션 목푯값보다 커질 때까지의 연산식(argument_formula)을 액션 피드백 메시지(feedback_msg.formula)에 저장하는 구문을 볼 수 있다. 이 피드백 값은 디버깅을 위해 get_logger().info()을 통해 터미널창에 출력하고 goal_handle.publish_feedback() 함수를 통해 액션 클라이언트에서 전송하게 된다.
while total_sum < goal_sum:
total_sum += self.argument_result
feedback_msg.formula.append(self.argument_formula)
self.get_logger().info('Feedback: {0}'.format(feedback_msg.formula))
goal_handle.publish_feedback(feedback_msg)
time.sleep(1)마지막으로 다음 구문들을 통해 액션 목표를 달성했다는 상태 전환 함수인 상태 전환 함수인 goal_handle.succeed() 함수를 실행시켜 액션 클라이언트에게 현재의 액션 상태를 알린다. 그리고 ArithmeticChecker.Result 클래스로 액션 결괏값을 보낼 result 변수를 선언하였다. 액션 결괏값인 result.all_formula 변수에 피드백 메시지에 담긴 계산식 전체를 저장하고 result.total_sum 변수에는 연산 누적값을 저장하여 이를 반환하는 것으로 액션 서버의 역할을 마치게 된다.
goal_handle.succeed()
result = ArithmeticChecker.Result()
result.all_formula = feedback_msg.formula
result.total_sum = total_sum
return result3. 액션 클라이언트 코드
액션 클라이언트 역할을 하는 노드는 checker 노드로 전체 소스코드는 다음과 같다.
from action_msgs.msg import GoalStatus
from msg_srv_action_interface_example.action import ArithmeticChecker
from rclpy.action import ActionClient
from rclpy.node import Node
class Checker(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('checker')
self.arithmetic_action_client = ActionClient(
self,
ArithmeticChecker,
'arithmetic_checker')
def send_goal_total_sum(self, goal_sum):
wait_count = 1
while not self.arithmetic_action_client.wait_for_server(timeout_sec=0.1):
if wait_count > 3:
self.get_logger().warning('Arithmetic action server is not available.')
return False
wait_count += 1
goal_msg = ArithmeticChecker.Goal()
goal_msg.goal_sum = (float)(goal_sum)
self.send_goal_future = self.arithmetic_action_client.send_goal_async(
goal_msg,
feedback_callback=self.get_arithmetic_action_feedback)
self.send_goal_future.add_done_callback(self.get_arithmetic_action_goal)
return True
def get_arithmetic_action_goal(self, future):
goal_handle = future.result()
if not goal_handle.accepted:
self.get_logger().warning('Action goal rejected.')
return
self.get_logger().info('Action goal accepted.')
self.action_result_future = goal_handle.get_result_async()
self.action_result_future.add_done_callback(self.get_arithmetic_action_result)
def get_arithmetic_action_feedback(self, feedback_msg):
action_feedback = feedback_msg.feedback.formula
self.get_logger().info('Action feedback: {0}'.format(action_feedback))
def get_arithmetic_action_result(self, future):
action_status = future.result().status
action_result = future.result().result
if action_status == GoalStatus.STATUS_SUCCEEDED:
self.get_logger().info('Action succeeded!')
self.get_logger().info(
'Action result(all formula): {0}'.format(action_result.all_formula))
self.get_logger().info(
'Action result(total sum): {0}'.format(action_result.total_sum))
else:
self.get_logger().warning(
'Action failed with status: {0}'.format(action_status))우선 Checker 클래스인데 rclpy.node 모듈의 Node 클래스를 상속하고 있으며 생성자에서 'checker' 이라는 노드 이름으로 초기화되었다. 그 뒤 arithmetic_action_client 이라는 이름으로 액션 클라이언트를 선언해주는데 이는 rclpy.action모듈의 ActionClient 클래스 이용하여 액션 클라이언트로 선언하는 부분으로 액션의 타입으로 액션 서버와 동일하게 ArithmeticChecker으로 선언하였고, 액션 이름으로는 'arithmetic_checker'으로 선언하였다.
class Checker(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('checker')
self.arithmetic_action_client = ActionClient(
self,
ArithmeticChecker,
'arithmetic_checker')send_goal_total_sum 함수는 액션 목표를 액션 서버에게 전송하고, 액션 피드백 및 결괏값을 받기 위한 콜백 함수를 지정하는 함수로 사용하고 있다.
def send_goal_total_sum(self, goal_sum):
wait_count = 1
while not self.arithmetic_action_client.wait_for_server(timeout_sec=0.1):
if wait_count > 3:
self.get_logger().warning('Arithmetic action server is not available.')
return False
wait_count += 1
goal_msg = ArithmeticChecker.Goal()
goal_msg.goal_sum = (float)(goal_sum)
self.send_goal_future = self.arithmetic_action_client.send_goal_async(
goal_msg,
feedback_callback=self.get_arithmetic_action_feedback)
self.send_goal_future.add_done_callback(self.get_arithmetic_action_goal)
return True먼저 액션 클라이언트가 액션 서버와 연결을 시도한다. 만약 연결에 문제가 있다면 이를 세 번 반복하게된다. 문제 없이 연결되었을때는 다음 구문으로 넘어간다.
wait_count = 1
while not self.arithmetic_action_client.wait_for_server(timeout_sec=0.1):
if wait_count > 3:
self.get_logger().warning('Arithmetic action server is not available.')
return False
wait_count += 1그 다음 ArithmeticChecker.Goal 클래스로 액션 메시지 goal_msg 를 선언하고, goal_msg.goal_sum 변수를 통해 액션 목푯값을 설정하게 된다. 그리고 ActionClient 클래스의 send_goal_async 함수를 이용하여 미리 설정해둔 액션 메시지를 매개변수로 넣고 피드백을 전달 받기 위한 콜백함수로 get_arithmetic_action_feedback 함수를 지정하였다. 마지막으로 send_goal_async를 통해 선언된 비동기 future task로 선언된 send_goal_future의 add_done_callback 함수를 통해 액션 결괏값을 받을 때 사용할 콜백함수로 get_arithmetic_action_goal를 선언하였다.
goal_msg = ArithmeticChecker.Goal()
goal_msg.goal_sum = (float)(goal_sum)
self.send_goal_future = self.arithmetic_action_client.send_goal_async(
goal_msg,
feedback_callback=self.get_arithmetic_action_feedback)
self.send_goal_future.add_done_callback(self.get_arithmetic_action_goal)액션 처리 과정이 좀 복잡하기에 다시 간추려 설명하면
- 액션 클라이언트 선언
- 액션 목푯값 전달 함수 선언
- 액션 피드백값 콜백 함수 선언
- 액션 상태 콜백 함수 선언
- 액션 결괏값 콜백 함수 선언
액션 피드백값 콜백 함수는 액션 피드백을 액션 서버로부터 전달받으면 호출되는데, 피드백인 feedback_msg.feedback.formula 값을 저장하고, 이를 get_logger().info 함수를 이용해 터미널 창에 출력한다.
def get_arithmetic_action_feedback(self, feedback_msg):
action_feedback = feedback_msg.feedback.formula
self.get_logger().info('Action feedback: {0}'.format(action_feedback))다음은 액션 상태 콜백 함수이다. 이 함수는 비동기 future task 로 선언된 send_goal_future 의 add_done_callback 함수를 통해 콜백 함수로 선언된 함수이다. 액션 서버가 액션 목푯값을 전달받고 액션개념에서 설명했던 Goal State Machine이 accepted 상태일 때를 확인하여 처리하는 구문이다. 액션 목푯값이 문제없이 전달되었다면 액션 결괏값 콜백 함수를 선언하게 된다. 여기서 콜백 함수는 후술한 get_arithmetic_action_result 함수이다.
def get_arithmetic_action_goal(self, future):
goal_handle = future.result()
if not goal_handle.accepted:
self.get_logger().warning('Action goal rejected.')
return
self.get_logger().info('Action goal accepted.')
self.action_result_future = goal_handle.get_result_async()
self.action_result_future.add_done_callback(self.get_arithmetic_action_result)앞서 지정한 액션 결괏값 콜백 함수는 다음과 같다. 비동기 future task를 통해 현재의 상태값(status)과 결괏값(result)을 받고 상탯값이 STATUS_SUCCEEDED면 액션 서버로부터 전달받은 액션 결괏값인 계산식(action_result.all_formula)과 연산 합계(action_result.total_sum)를 터미널 창에 출력하게 된다.
def get_arithmetic_action_result(self, future):
action_status = future.result().status
action_result = future.result().result
if action_status == GoalStatus.STATUS_SUCCEEDED:
self.get_logger().info('Action succeeded!')
self.get_logger().info(
'Action result(all formula): {0}'.format(action_result.all_formula))
self.get_logger().info(
'Action result(total sum): {0}'.format(action_result.total_sum))
else:
self.get_logger().warning(
'Action failed with status: {0}'.format(action_status))4. 노드 실행 코드
액션 클라이언트 노드인 checker 노드는 topic_service_action_rclpy_example 패키지의 일부로 패키지 설정 파일에 entry_points로 실행 가능한 콘솔 스크립트의 이름과 호출 함수를 기입하도록 되어 있는데 우리는 하기와 같이 4개의 노드를 작성하고 ros2 run 과 같은 노드 실행 명령어를 통하여 각각의 노드를 실행시키고 있다. checker 노드는 topic_service_action_rclpy_example 패키지의 checker 폴더에 main.py의 main문에 실행 코드가 담겨져 있다.
entry_points={
'console_scripts': [
'argument = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.arithmetic.argument:main',
'operator = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.arithmetic.operator:main',
'calculator = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.calculator.main:main',
'checker = topic_service_action_rclpy_example.checker.main:main',
],
},즉, 하기와 같은 main함수가 실행 코드인데 rclpy.init를 이용하여 초기화하고 위에서 작성한 Checker 클래스를 checker라는 이름으로 생성한 다음 액션 목표값을 전달하는 send_goal_total_sum 함수를 실행시키고 있다. 여기서 args.goal_total_sum와 같이 프로그램의 실행 인자를 사용하는 부분이 있는데 이는 추후 강좌에서 자세히 다루도록 하겠다. 우선 실행 인자로 사용자가 노드를 실행시킬 때 액션 목표값을 설정할 수 있고 지정하지 않았을 때에는 50이라는 초깃값이 입력된다는 것만 알아두자. 목표값 전달 이후에는 rclpy.spin 함수를 이용하여 rclpy의 콜백함수가 실행될 수 있도록 하고 있다. 그 이외에는 지금까지 다른 강좌에서 설명한 바와 같이 종료 Ctrl + c와 같은 인터럽트 시그널 예외 상황에서는 checker를 소멸시키고 rclpy.shutdown 함수로 노드를 종료하게 된다. 약간의 차이점이 있다면 다른 토픽과 서비스와는 달리 액션은 별도로 checker.arithmetic_action_client.destroy() 와 같이 소멸시켜야 한다는 것이다.
import argparse
import sys
import rclpy
from topic_service_action_rclpy_example.checker.checker import Checker
def main(argv=sys.argv[1:]):
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter)
parser.add_argument(
'-g',
'--goal_total_sum',
type=int,
default=50,
help='Target goal value of total sum')
parser.add_argument(
'argv', nargs=argparse.REMAINDER,
help='Pass arbitrary arguments to the executable')
args = parser.parse_args()
rclpy.init(args=args.argv)
try:
checker = Checker()
checker.send_goal_total_sum(args.goal_total_sum)
try:
rclpy.spin(checker)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
checker.get_logger().info('Keyboard Interrupt (SIGINT)')
finally:
checker.arithmetic_action_client.destroy()
checker.destroy_node()
finally:
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()액선 서버인 calculator 노드는 토픽 서브스크라이버, 서비스 서버, 액션 서버를 포함한다. 실행 코드에 대한 설명은 이전에도 게속 설명했으니 생략하겠다.
import rclpy
from rclpy.executors import MultiThreadedExecutor
from topic_service_action_rclpy_example.calculator.calculator import Calculator
def main(args=None):
rclpy.init(args=args)
try:
calculator = Calculator()
executor = MultiThreadedExecutor(num_threads=4)
executor.add_node(calculator)
try:
executor.spin()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
calculator.get_logger().info('Keyboard Interrupt (SIGINT)')
finally:
executor.shutdown()
calculator.arithmetic_action_server.destroy()
calculator.destroy_node()
finally:
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()ROS2 액션 프로그래밍에 대해 알아보았다. 다음장에서는 파라미터 프로그래밍 코드에 대해 알아보겠다.
