📌동기와 비동기
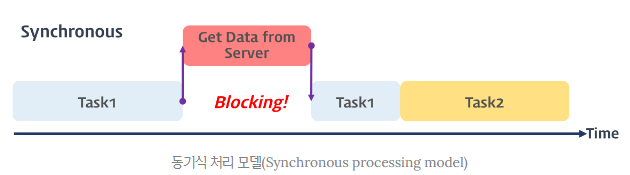
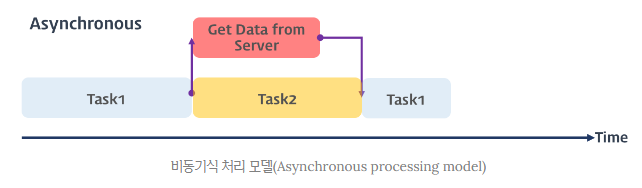
- 만약 동기식으로 다른 곳으로부터 데이터를 받아온다면? 받아오는 동안 페이지가 아무동작을 안하며 UX 관점에서 매우 안좋다. 즉, 비동기가 필요하다
- 하지만 비동기를 사용하면 서버로 데이터를 받아오고 그걸 가공해야할 텐데, 어느 시점에 서버로부터 응답이 올지 모르니 이러한 실행 순서를 보장하기 위해 가장 먼저 쓰는 것이 콜백함수
📌콜백으로 비동기 처리
- 모든 콜백이 Web API에서 수행되는 것은 아니고 호출 스택에서 바로 수행될 수도 있음
- 아래는 로직이 Web API에서 수행된다는 가정하에 작성
step1(function(value1) {
step2(value1, function(value2) {
step3(value2, function(value3) {
step4(value3, function(value4) {
step5(value4, function(value5) {
// value5를 사용하는 처리
});
});
});
});
});
step1();- 위의 코드를 이벤트루프와 연관지어 순서를 설명하면
step1()이 콜스택에 쌓임- Web API를 사용해야하므로 Web API로 넘김
step1()이 콜스택에서 pop(콜스택에서는 다음 코드 실행)- 실행 완료한 결과 및 다음 콜백함수
step2()가 Task Queue에서 대기중 - 콜스택 비면
step2()를 넣고 실행, 이렇게 반복
📖문제
- 가독성 문제
- 에러 처리의 한계
try {
setTimeout(() => { throw new Error('Error!'); }, 1000);
} catch (e) {
console.log('에러를 캐치하지 못한다..');
console.log(e);
}- 위 예에서
setTimeout()은 호출 스택에서 사라진 상태로 콜백함수인throw new Error가 호출 스택에서 수행 되어서setTimeout()이throw new Error를 호출안한걸로 처리됨, 즉 try문안에서 에러를 내도 캐치 못함
📌Promise
- 비동기 처리에 사용 되는 객체
function getImage(file) {
// Promise 객체를 리턴
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
const data = readFile(file); // 파일 읽어오기 시도
resolve(data); // 성공하면 resolve 함수 호출(보통 결과 값 인자로)
// resolve 함수 호출되면 fulfilled 상태로
} catch {
reject(new Error(err)); // 에러나면 reject 함수 호출(보통 에러 객체 인자로)
// reject 함수 호출되면 rejected 상태로
}
});
}
// 실행 부
getImage(file)
.then(data => console.log("성공함", data)) // then계속 이어쓰면서 콜백헬 대신 사용
.catch(error => console.log(error)) // 이전 then에서 난 에러 받음
.finally(() => console.log('Done!'));PromiseState: 프로미스 객체의 상태(비동기 처리 상태)- pending : 비동기 처리 아직 수행 되지 않음
- fulfilled : 비동기 처리 성공, resolve 함수가 호출되면 되는 프로미스 상태
- rejected : 비동기 처리 실패, reject 함수가 호출되면 되는 프로미스 상태
- 즉 비동기처리를 위해
Promise객체를 반환하도록 만들고, 이때Promise생성시 비동기 처리를 수행할 콜백함수를 인자로 준다. - 반환된
Promise객체에then, catch, finally를 사용해 콜백 함수를 대신 사용
📖Promise statice method
✒️Promise.resolve
const resolvedPromise = Promise.resolve([1, 2, 3]);
// 이 코드와 동일
// const resolvedPromise = new Promise(resolve => resolve([1, 2, 3]));
resolvedPromise.then(console.log); // [ 1, 2, 3 ]✒️Promise.reject
const rejectedPromise = Promise.reject(new Error('Error!'));
// 이 코드와 동일
const rejectedPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => reject(new Error('Error!')));
rejectedPromise.catch(console.log); // Error: Error!✒️Promise.all
-
프로미스가 담긴 이터러블을 인자로 받고 모든 프로미스를 병렬로 처리, 모든 프로미스가 처리완료 까지 기다린 후 결과 반환, 모두 성공 OR 하나 이상 실패
-
모든 프로미스 성공시 각각의 프로미스가
resolve한 결과를 배열에 담고 이 배열을resolve하는 새로운Promise반환, 이때 처리 완료 순서와 상관없이 처음 코드의 배열 순서를 유지
Promise.all([
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 3000)), // 1
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(2), 2000)), // 2
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(3), 1000)) // 3
]).then(console.log) // [ 1, 2, 3 ]
.catch(console.log);- 프로미스가 하나라도 실패시 가장 먼저 실패한 프로미스의 reject한 결과를 reject하는 새로운
Promise반환
Promise.all([
new Promise((resolve, reject) => setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('Error 1!')), 3000)),
new Promise((resolve, reject) => setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('Error 2!')), 2000)),
new Promise((resolve, reject) => setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('Error 3!')), 1000))
]).then(console.log)
.catch(console.log); // Error: Error 3!- 프로미스가 아닌 이터러블을 인자로 넘기면 자동으로
Promise.resolve로 래핑
Promise.all([
1, // => Promise.resolve(1)
2, // => Promise.resolve(2)
3 // => Promise.resolve(3)
]).then(console.log) // [1, 2, 3]
.catch(console.log);✒️Promise.race
Promise.all과 유사, 모두 성공한 경우에는 가장 먼저 처리된 프로미스의resolve한 처리 결과를resolve하는 새로운Promise반환
Promise.race([
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 3000)), // 1
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(2), 2000)), // 2
new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve(3), 1000)) // 3
]).then(console.log) // 3
.catch(console.log);- 프로미스 처리가 하나라도 실패하면 all과 동일
✒️Promise.allSettled
- 모든 프로미스가 처리되기를 기다렸다가 배열을 반환, 이 배열에는 모든
Promise들의 결과가 담김 - 실패한
Promise가 포함되어도 에러로 빠지지 않고fulfilled상태가 되면서 실패한Promise는 실패정보를 담고 있음
📖Promise with Event Loop
- Event Loop의 Queue에도 종류가 있고 Queue마다 우선순위가 있다
- MicroTask Queue : 우선 순위 1등, Promise callback, async callback 등
- Animation Frames : 우선 순위 2등, requestAnimationFrame 등
- Task Queue(MacroTask Queue) : 우선 순위 3등, setTimeout, setInterval 등
- Promise의 콜백함수는 MicroTask Queue로 가며 이는 Task Queue(MacroTask Queue)보다 우선순위가 높아 먼저 콜스택으로 간다
✒️예시
console.log('Start!');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Timeout!');
}, 0);
Promise.resolve('Promise!')
.then(res => console.log(res));
console.log('End!');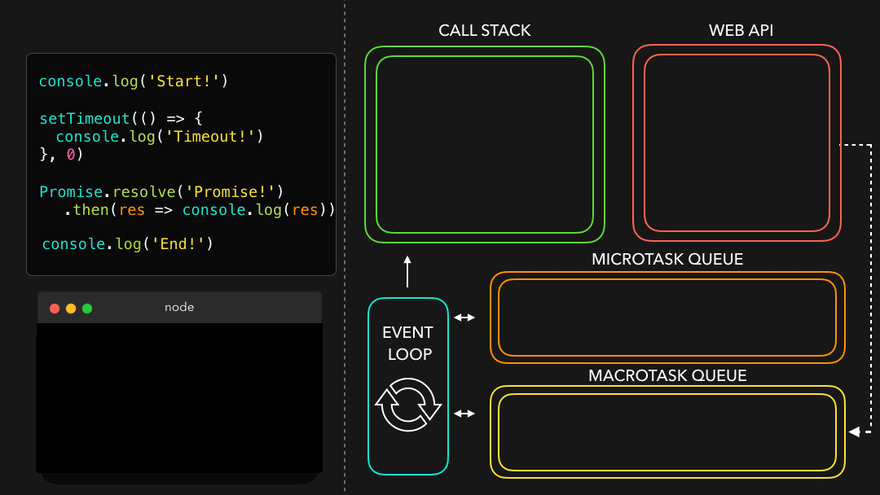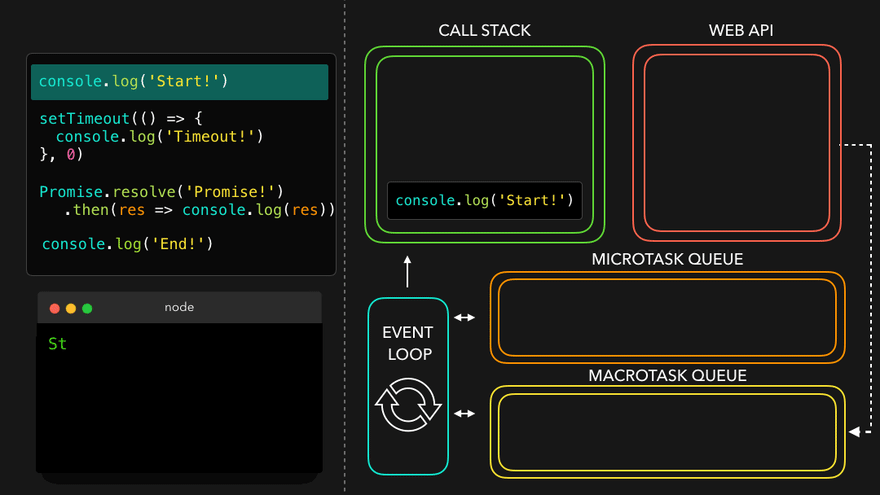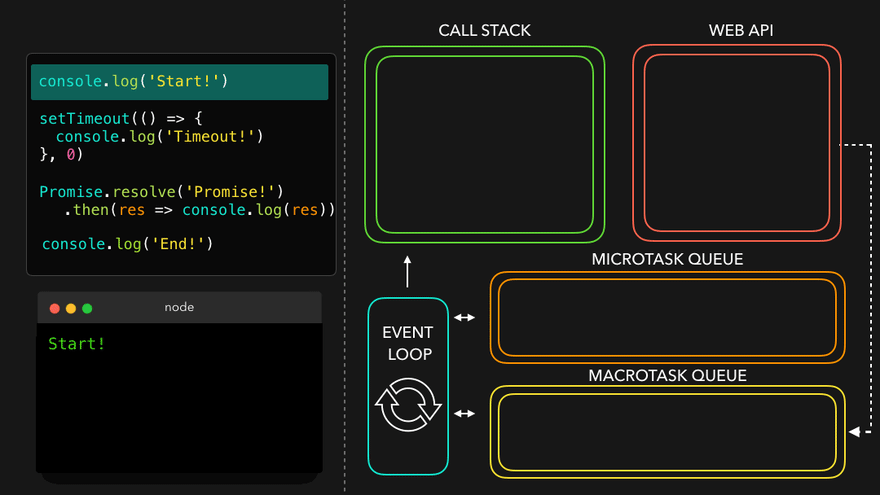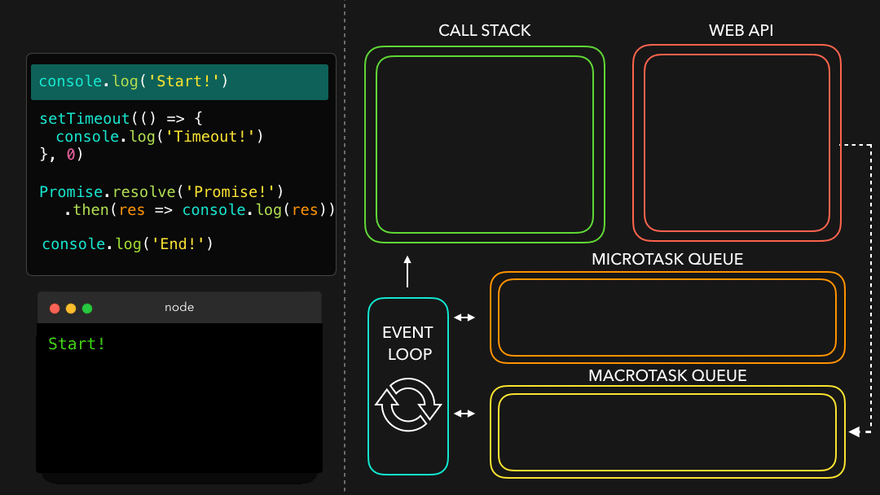
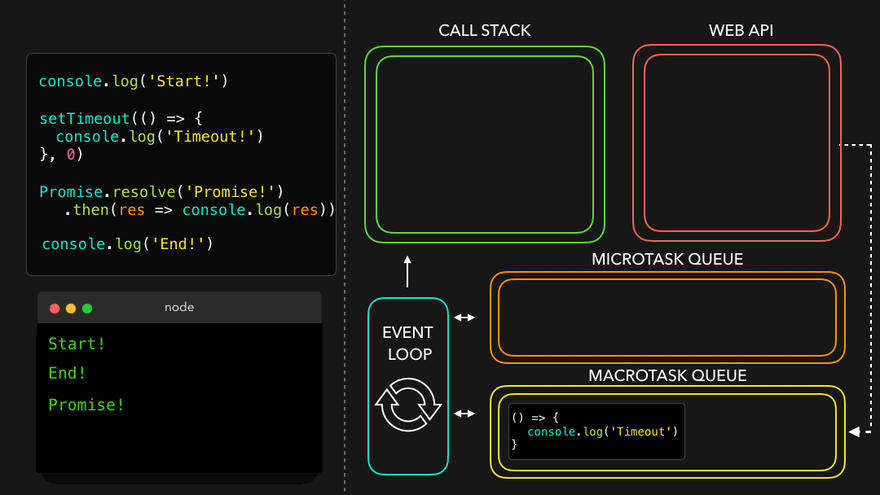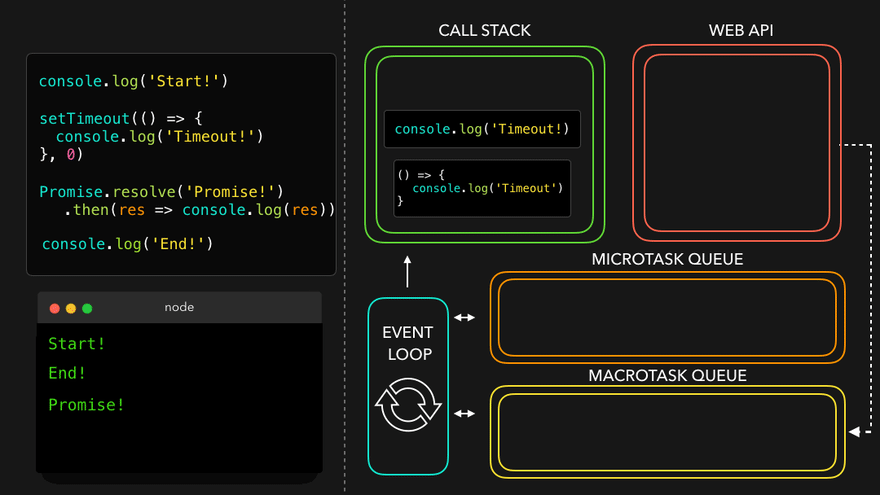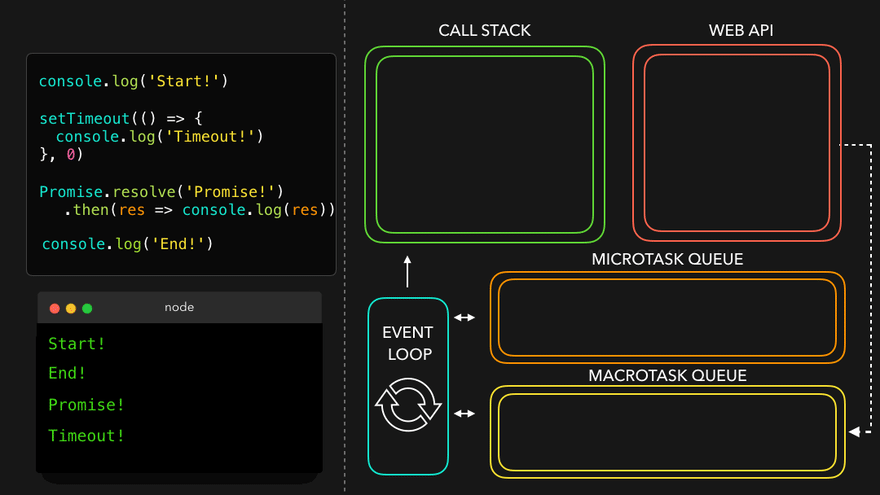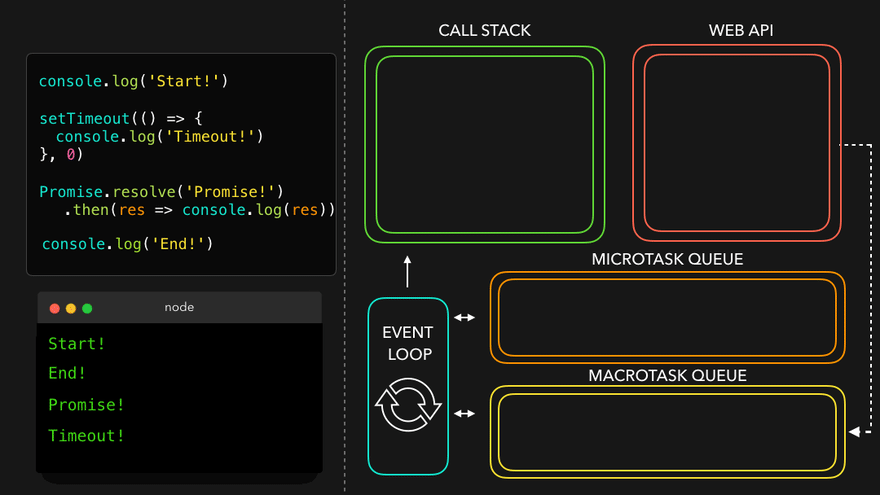
setTimeout만나서 WEB API로 넘김
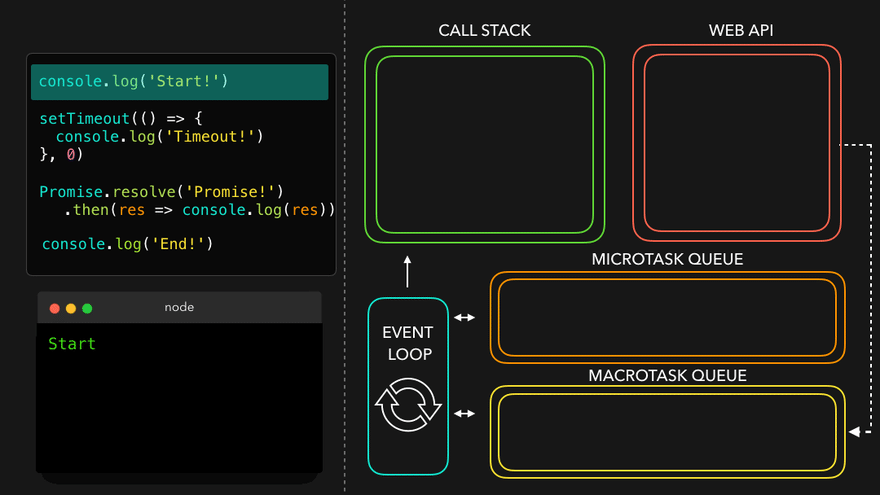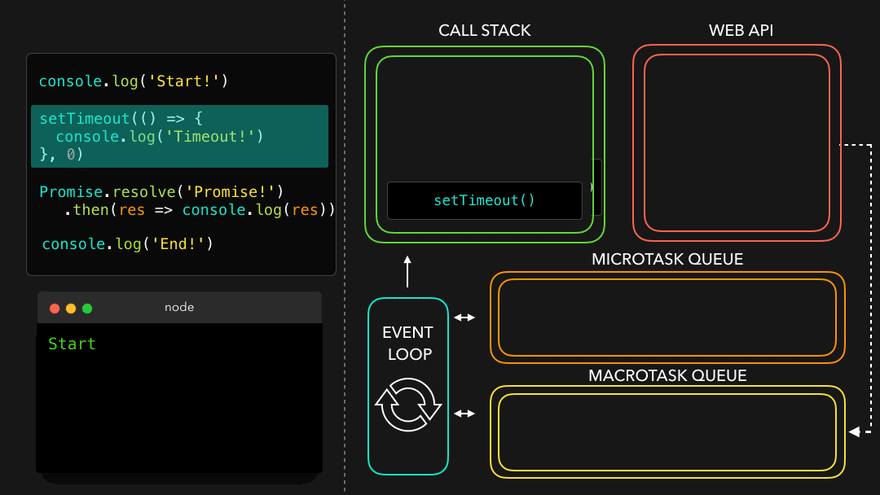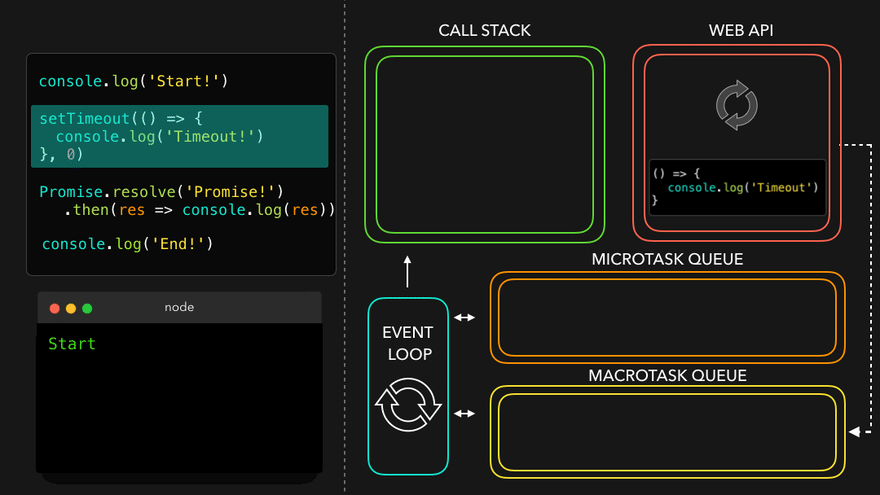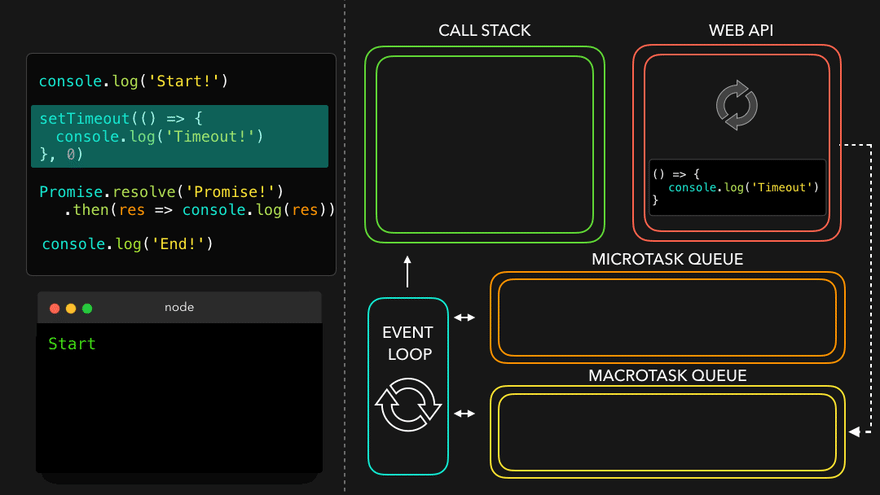
- WEB API의 콜백은 MacroTask Queue로, 프로미스의 콜백은 MicroTask Queue로
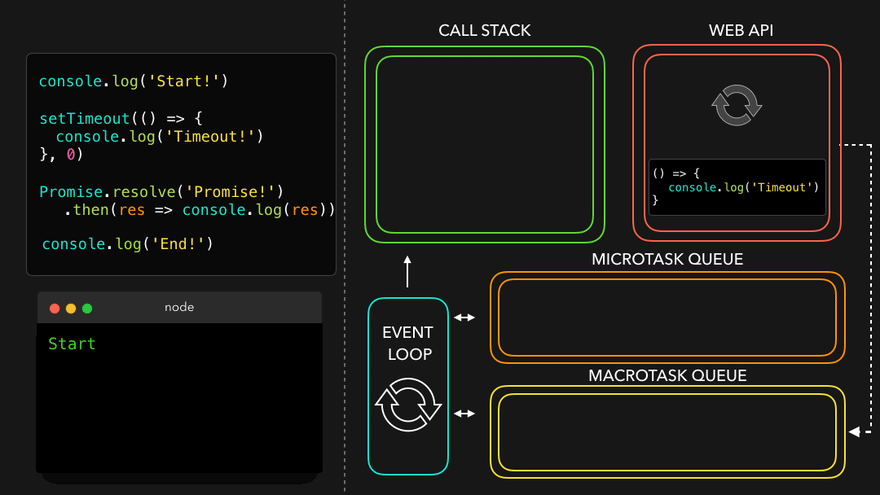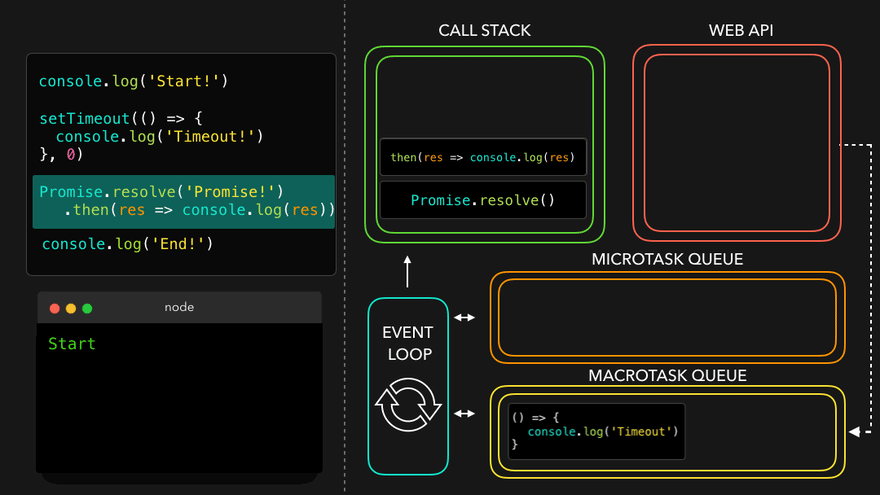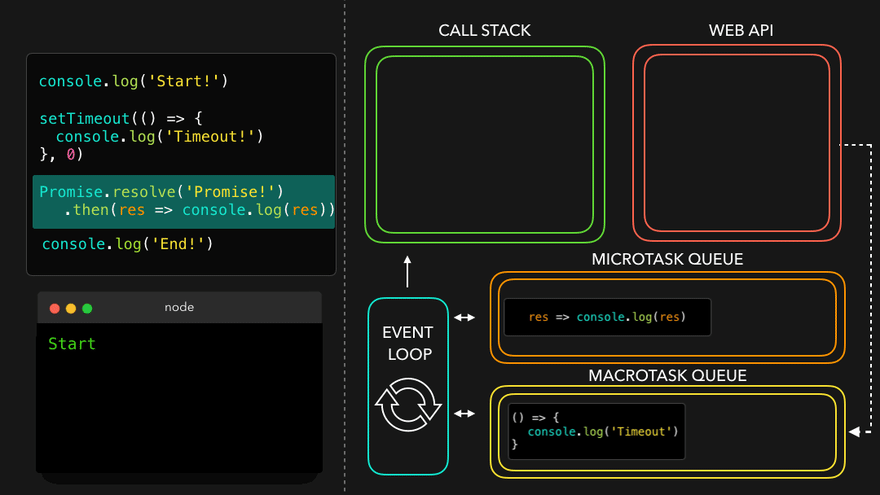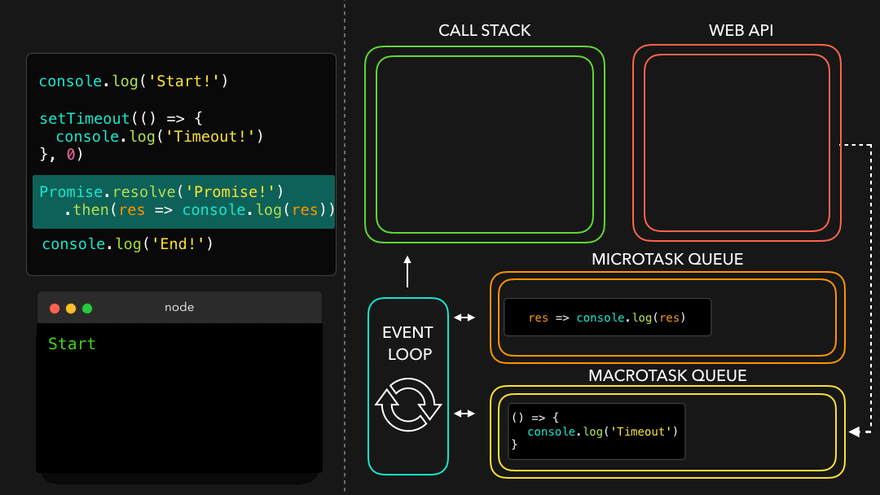
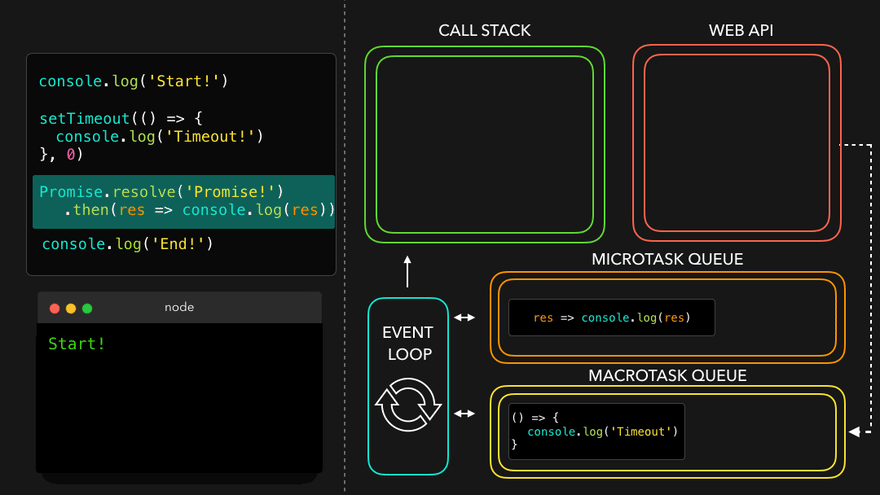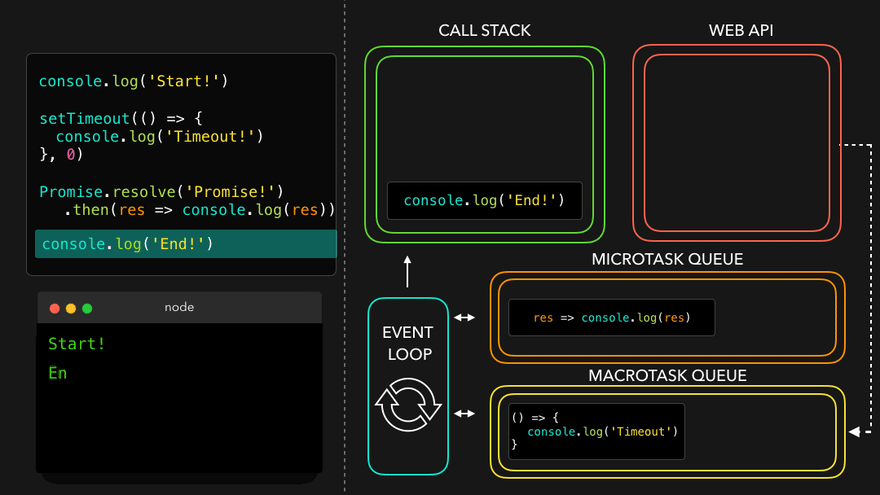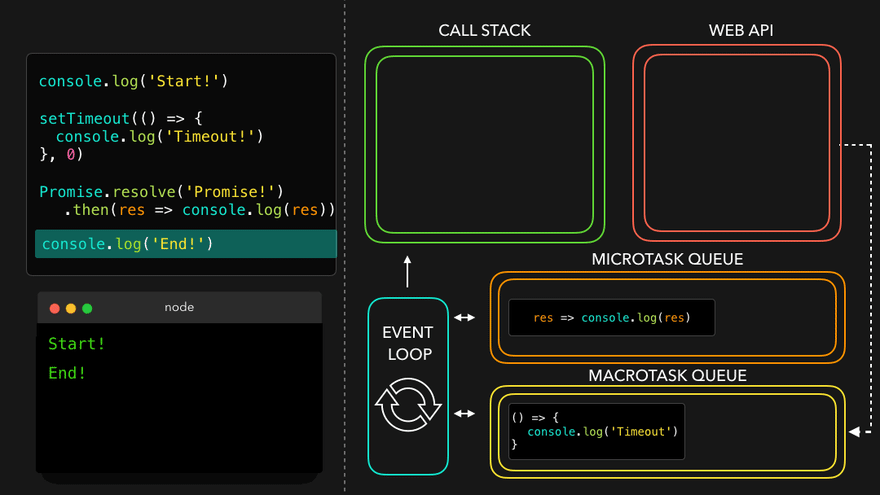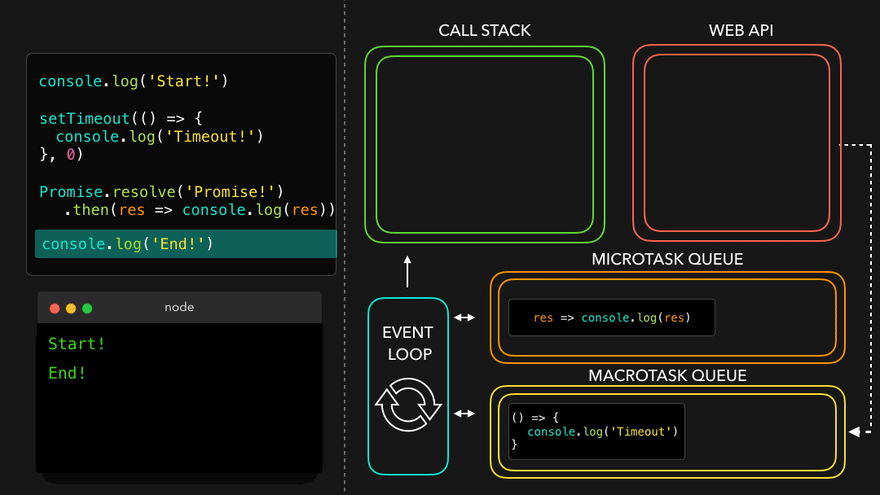
- MicroTask Queue가 먼저 콜스택으로
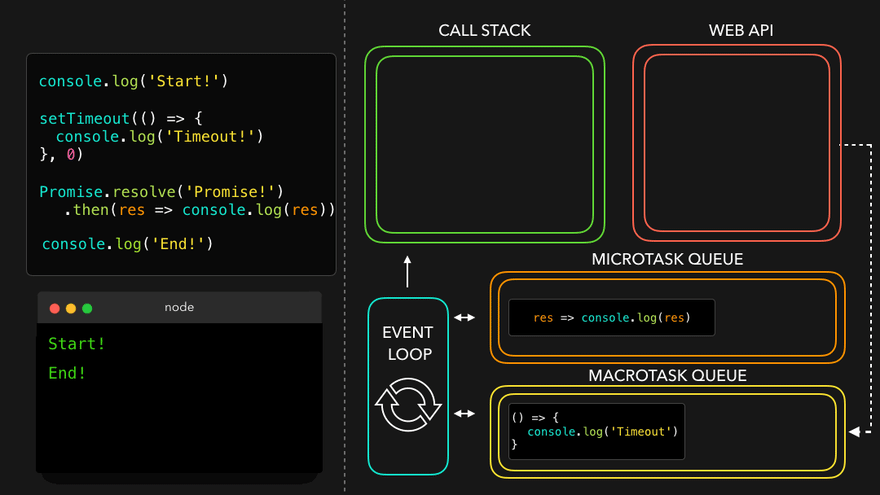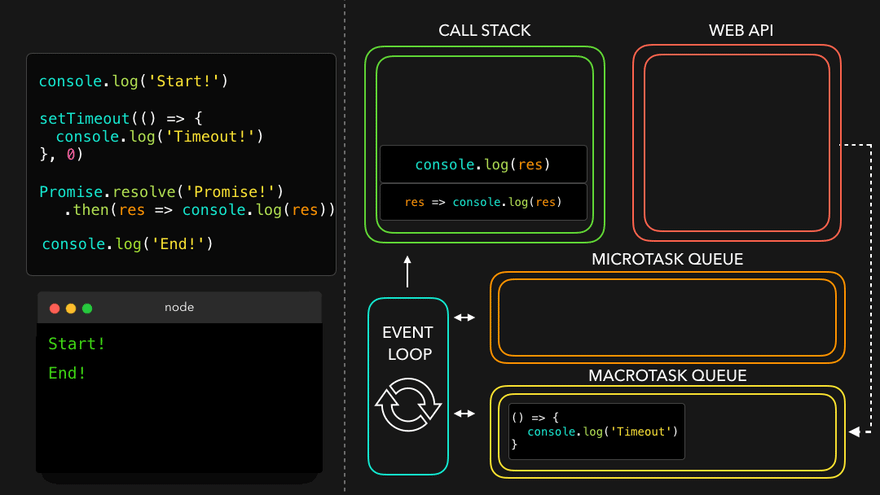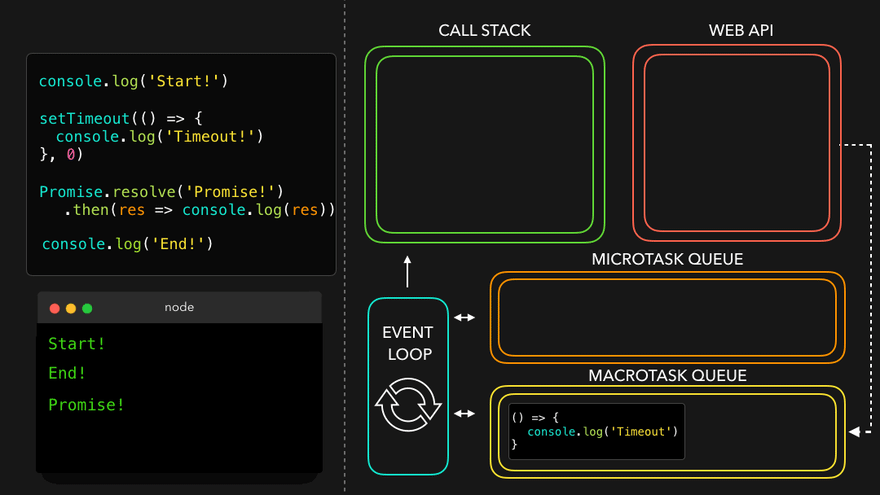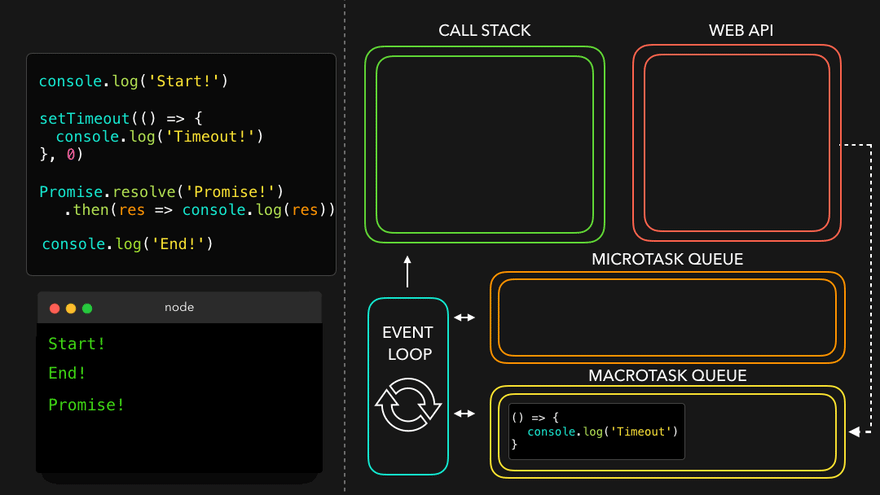
- 남은 MacroTask Queue의 콜백이 콜스택으로
📌Async/Await
- Promise를 더 쉽게 다룰 수 있게하는 문법
Promise.resolve('Hello!');
// 위 코드는 아래 코드와 같다.
async function greet() {
return 'Hello!'
}- async는 함수 앞에 사용한다, 해당 함수가 프로미스를 리턴하도록 강제한다
- await은 async 함수 내부에서만 쓸 수 있으며, 프로미스 객체 앞에 사용한다.
- await은 프로미스가 fulfilled 될때 까지 기다림(async 내부의 다음 코드를 기다려주는것) 프로미스가 아닌 결과 값을 리턴한다.
📖async await with Event Loop
const one = () => Promise.resolve('One!');
async function myFunc() {
console.log('In function!');
const res = await one();
console.log(res); // await은 이거를 기다려주는 거임
}
console.log('Before function!');
myFunc();
console.log('After function!'); // 이건 기다려주지 않음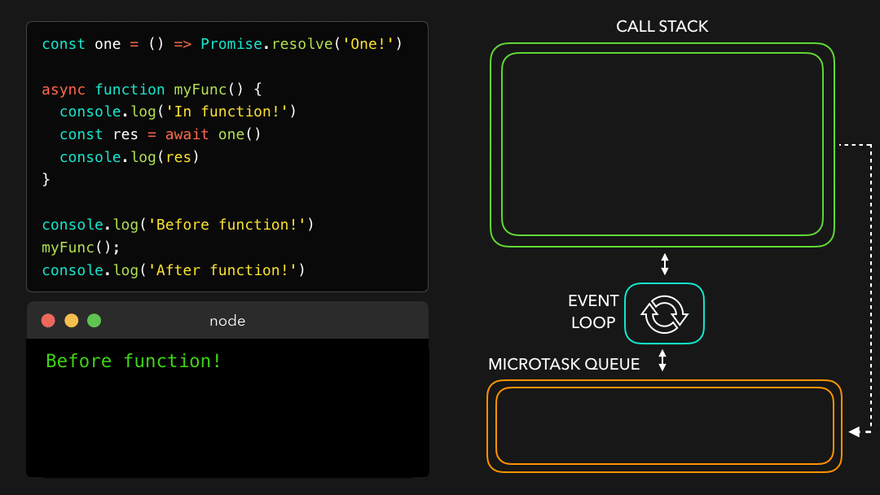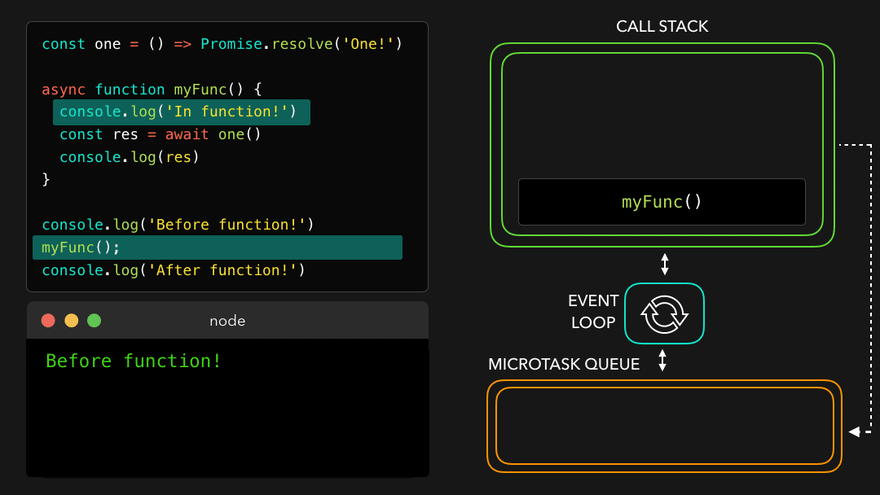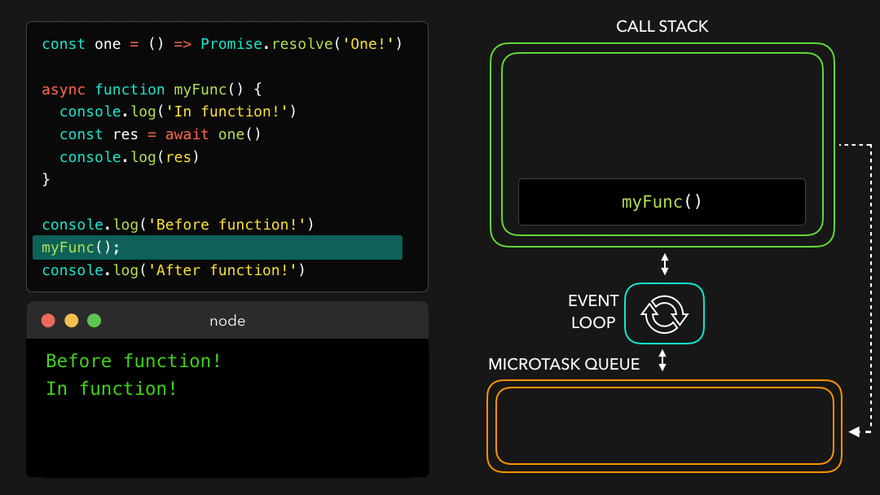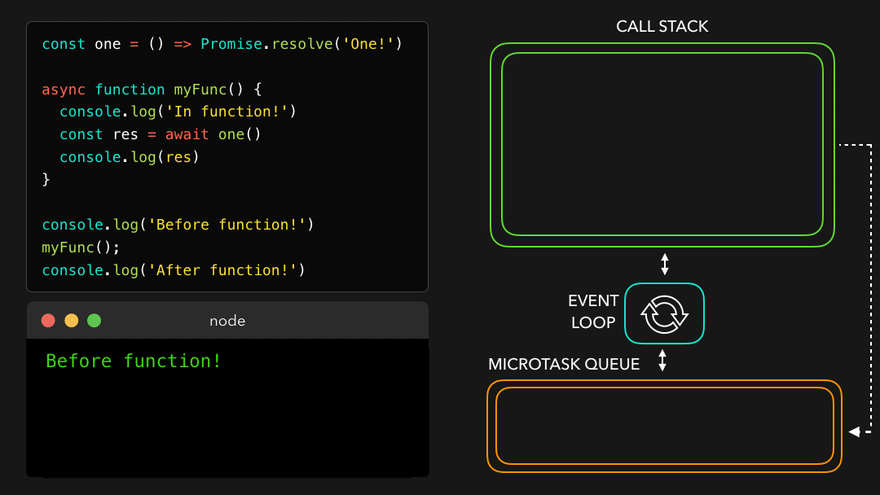
await만나서 해당async함수를 MicroTask Queue로
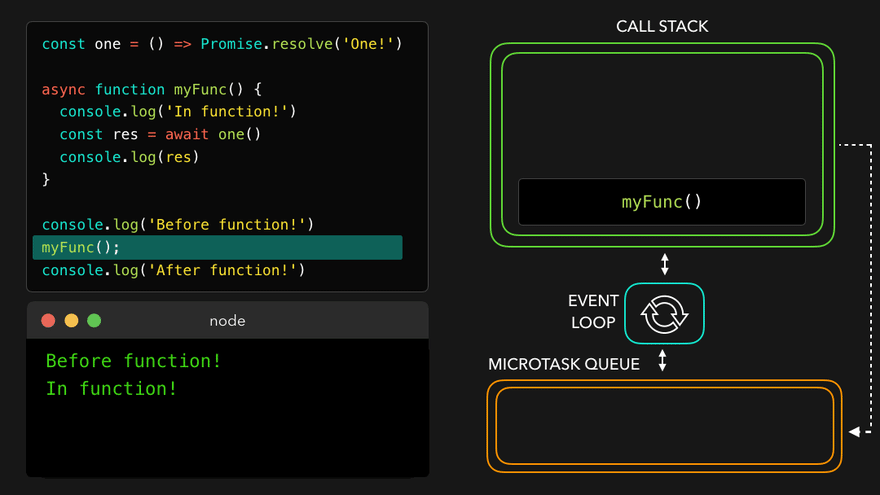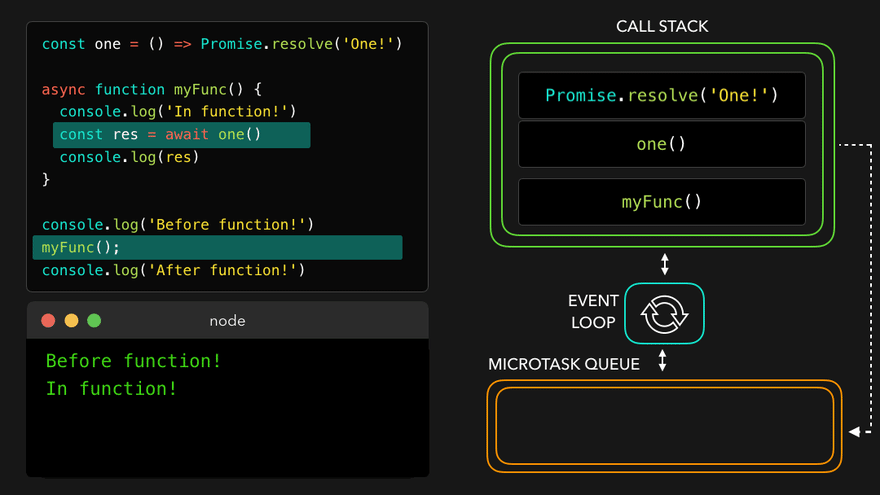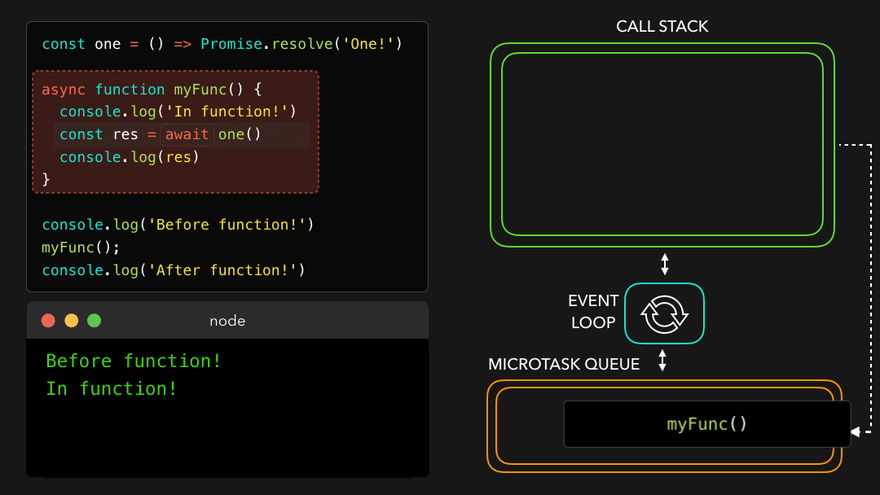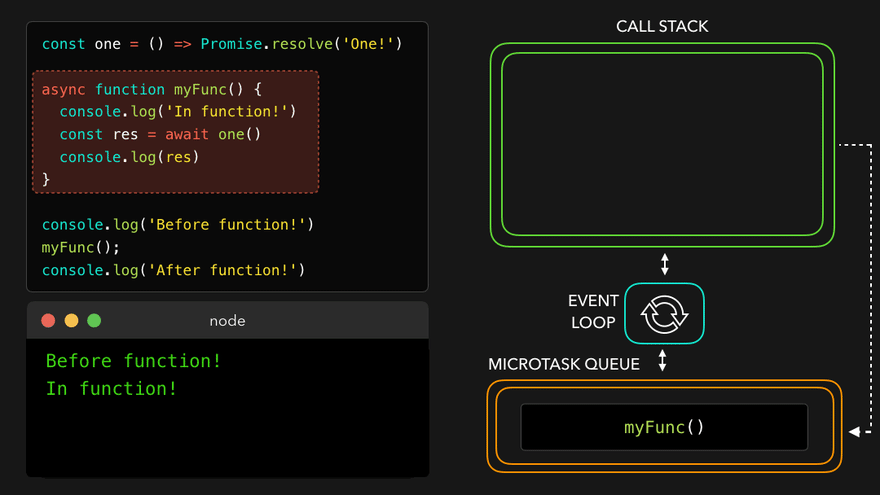
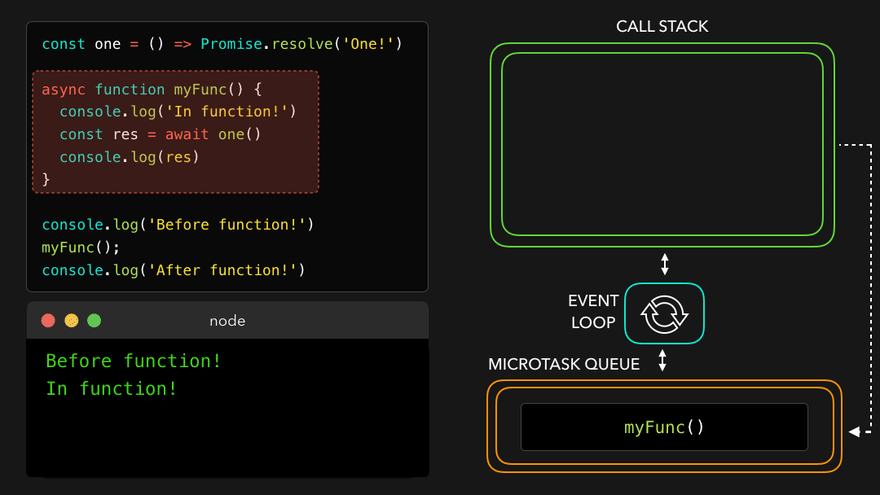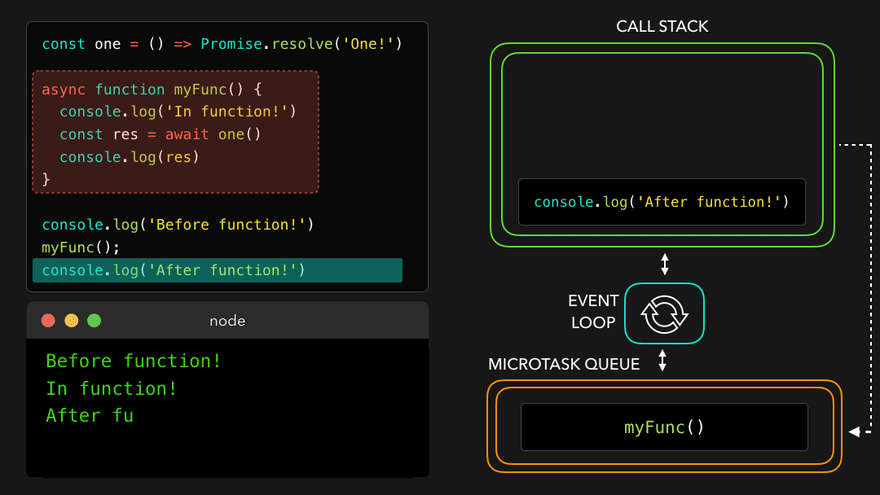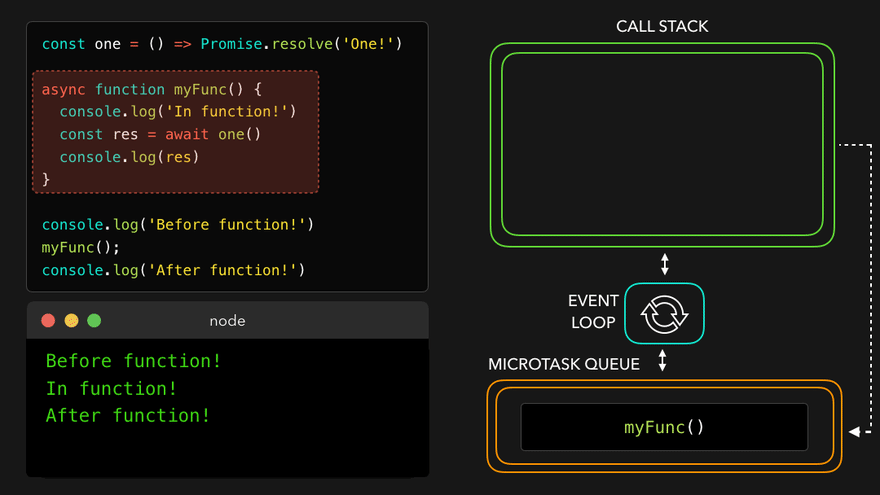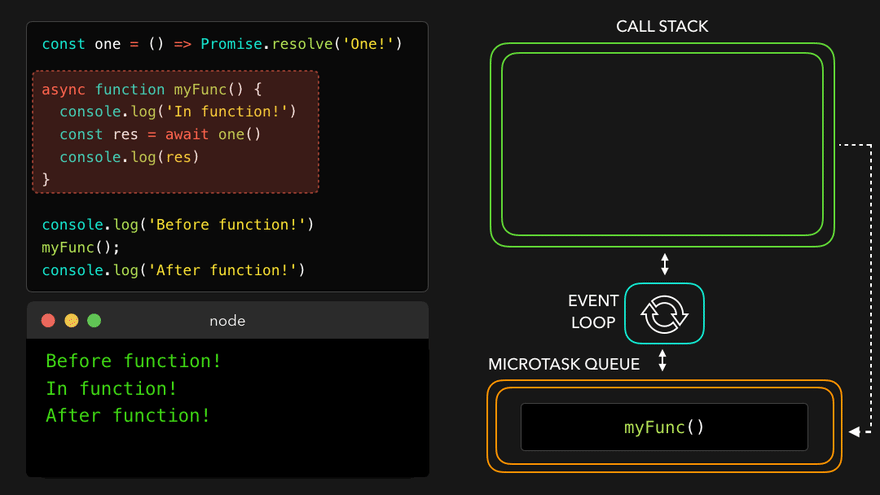
- 콜스택 비어서
async함수를 콜스택으로 보내고 남은 부분 실행
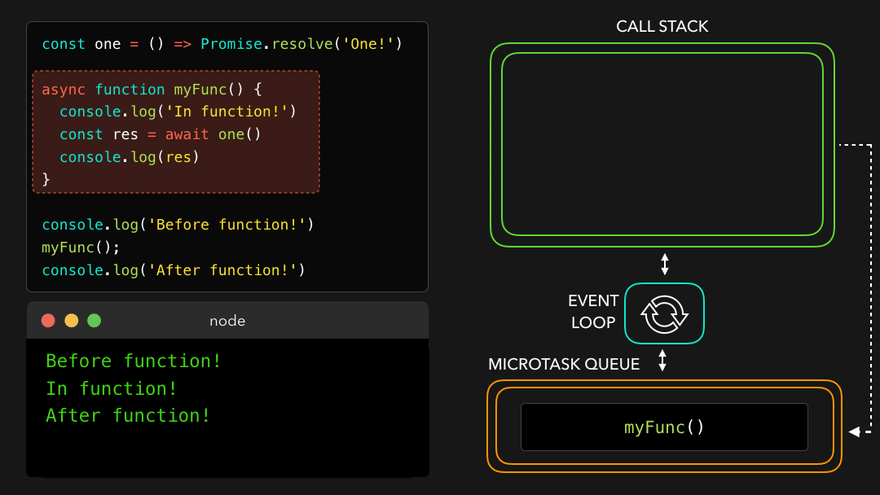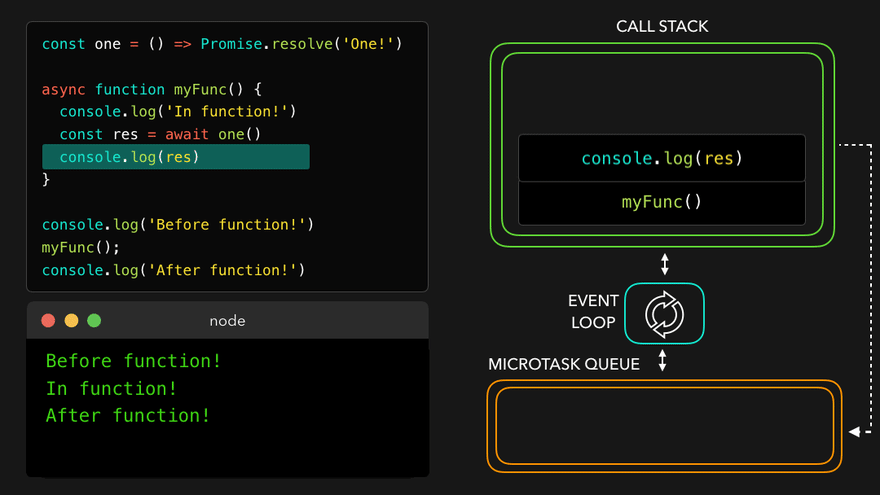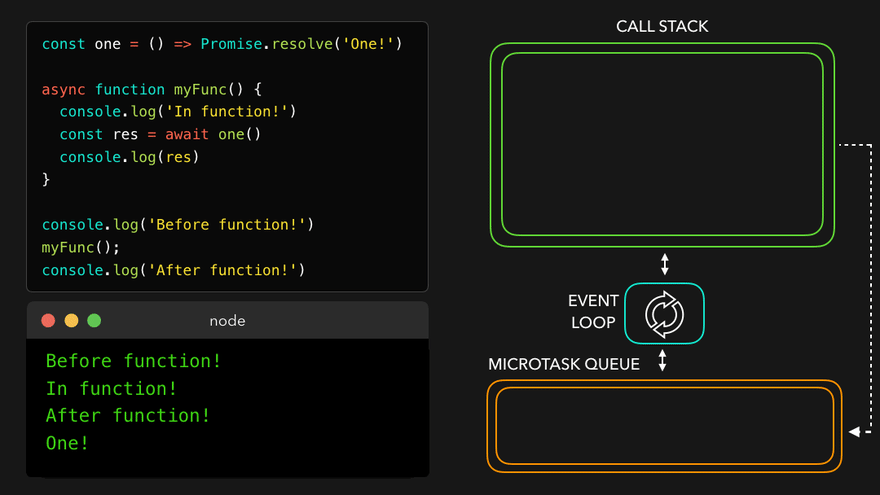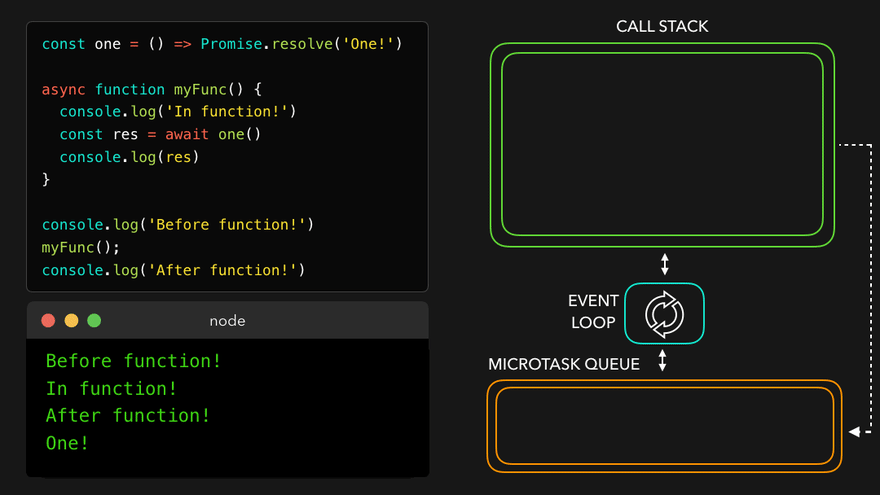
출처 : https://poiemaweb.com/es6-promise, https://pozafly.github.io/javascript/event-loop-and-async/
