📌JS의 실행 환경 구조
- JS는 싱글 스레드 언어, 하나에 한번의 작업만 실행가능
- JS가 동작하는 브라우저 또는 Node.js에 멀티 스레드 활용 가능한 이벤트 루프가 있음
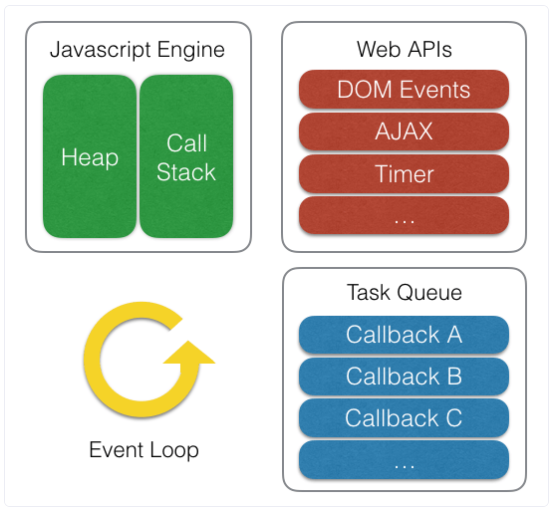
- JS 엔진에는
memory heap과 call stack이 있다.memory heap: 변수 선언 및 할당 저장되는 공간call stack: 함수를 실행시 쌓이는 스택, 함수 실행 순서를 제어
📖call stack
- LIFO(Last In First Out)
✒️예시
const foo = () => console.log('First');
const bar = () => setTimeout(() => console.log('Second'), 500);
const baz = () => console.log('Third');
bar();
foo();
baz();- 위 코드의 동작과정을 설명 하면
bar()을 만나서 콜스택에 넣는다setTimeout을 만나 Web API에서 실행하도록 Web API에 넘겨준다(0.5초 시작)bar()가 pop 되고,foo()를 만나 콜스택에 넣는다- foo의
console.log('First')가 실행되고foo()가 pop 된다
5-1. (0.5초 끝)setTimeout의 콜백 함수인console.log('Second')가 task Queue로 가서 콜 스택이 빌때 까지 대기중
5-2.baz()를 만나 콜스택에 넣고 그대로 실행, pop까지 - 콜스택 비어서
console.log('Second')가 콜스택에 들어가서 실행 됨
- 이벤트 루프는 call stack과 Queue를 계속 확인하면서 넣어줄 준비 중
✒️예시2
function delay() {
for (var i = 0; i < 100000; i++);
}
function baz() {
console.log('baz!'); // (4)
}
setTimeout(baz, 10); // 10ms sec 뒤에 baz 함수 실행
delay();- 위 코드에서
delay()가 콜스택을 매우 오래 차지하고 있는다 setTimeout은 Web API에서 10ms를 기다리고 Queu에서delay()에서 계속 대기중 즉, 10ms를 보장해주지 않음
✒️예시3
const button = document.querySelector('button');
button.addEventListener(() => { // addEventListener는 Web API, 비동기
showWaitingMessage(); // 기다리라는 메세지 띄워주고 싶음, DOM 조작
longTakingProcess(); // 매우 긴 작업
hideWaitingMessage();
showResult();
});- 위 코드에서 기다리라는 메세지는 나타나지 않음
- 콜 스택에서
showWaitingMessage()은 Web API에서 수행 되므로 Web API로 넘김 - 콜 스택에서는
longTakingProcess();라는 매우 긴 작업 진행중 showWaitingMessage()은 Web API에서 수행 되고 해당 렌더링 요청이 콜 스택에 진입하지 못하고(매우 긴 작업 때문에) Task Queue에서 계속 대기중
const button = document.querySelector('button');
button.addEventListener(function() {
showWaitingMessage();
setTimeout(() => {
longTakingProcess();
hideWaitingMessage();
showResult();
}, 0);
});- 이렇게 쓰면
showWaitingMessage();가 호출 스택에서 렌더링 까지 완료되고longTakingProcess();가 수행 되게 할 수 있음 setTimeout()을 쓰면 코드를 어디에 써도 마지막에 실행 시킬 수 있다.
출처 및 참고 : https://pozafly.github.io/javascript/event-loop-and-async/
