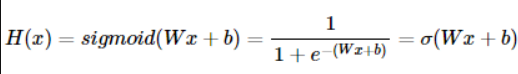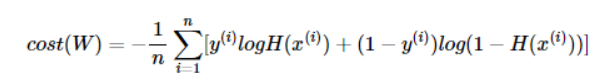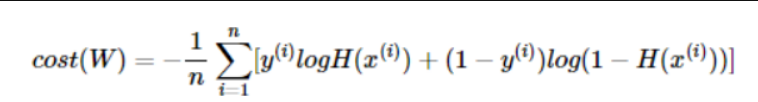로지스틱 회귀
1. 이진 분류 (Binary Classification)
- 두 개의 선택지 중 정답을 고르는 경우(정답, 오답 / 합격, 불합격)에 활용하는게 이진분류
- 이진 분류를 풀기 위한 대표적인 알고리즘이 로지스틱 회귀(Logistic Regression)
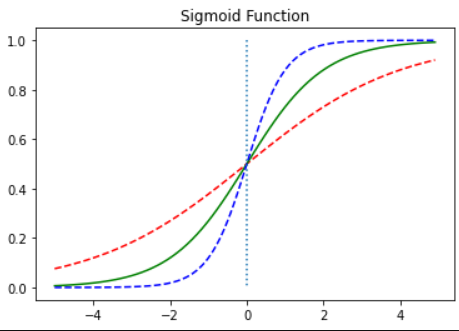
- 두 개의 선택지를 가진 데이터의 분포는 S 형태의 그래프를 가진다.
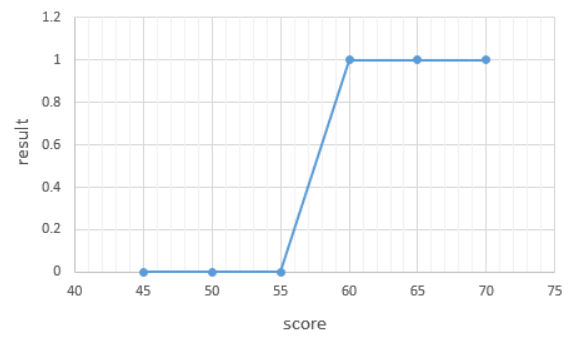
- S 그래프를 만들기 위해 선형회귀함수에 특정 함수 f 를 추가하는데 특정 함수 f 를 시그모이드 함수라고 함
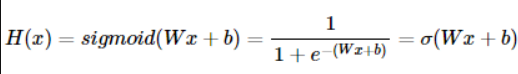
2. 시그모이드 함수
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def sigmoid(x):
return 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
x = np.arange(-5.0, 5.0, 0.1)
y1 = sigmoid(0.5*x)
y2 = sigmoid(x)
y3 = sigmoid(2*x)
plt.plot(x, y1, 'r', linestyle='--')
plt.plot(x, y2, 'g')
plt.plot(x, y3, 'b', linestyle='--')
plt.plot([0,0],[1.0,0.0], ':')
plt.title('Sigmoid Function')
plt.show()
3. 비용함수 (Cost Function)
- 최적의 W와 b를 찾을 수 있는 비용함수를 정의
- 시그모이드 함수가 적용된 비용함수를 미분하면 선형회귀 때와는 다르게 아래와 같은 그래프가 나온다
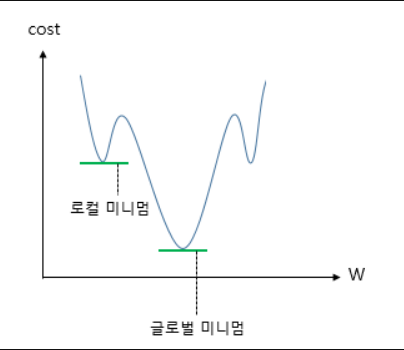
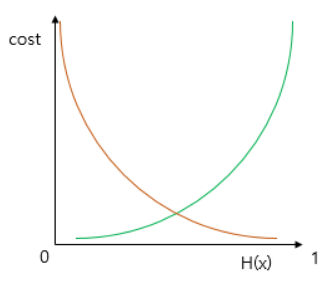
- 로컬 미니멈에 그치지 않고 글로벌 미니멈을 찾기 위해서 시그모이드 함수의 특징을 활용해야 한다.
- 시그모이드 함수의 출력값이 0과 1사이므로 y= 0.5인 로그함수를 충족한다.
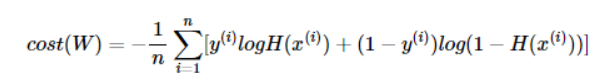
4. 파이토치로 로지스틱 회귀 구현하기
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
torch.manual_seed(1)
<torch._C.Generator at 0x20ae0f61190>
x_data = [[1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 1], [4, 3], [5, 3], [6, 2]]
y_data = [[0], [0], [0], [1], [1], [1]]
x_train = torch.FloatTensor(x_data)
y_train = torch.FloatTensor(y_data)
print(x_train.shape)
print(y_train.shape)
torch.Size([6, 2])
torch.Size([6, 1])
W = torch.zeros((2, 1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
hypothesis = 1 / (1 + torch.exp(-(x_train.matmul(W) + b)))
print(hypothesis)
tensor([[0.5000],
[0.5000],
[0.5000],
[0.5000],
[0.5000],
[0.5000]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
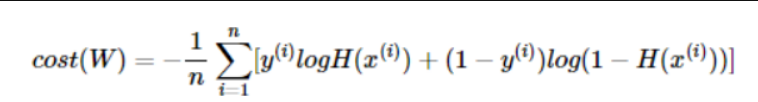
losses = -(y_train * torch.log(hypothesis) +
(1 - y_train) * torch.log(1 - hypothesis))
print(losses)
tensor([[0.6931],
[0.6931],
[0.6931],
[0.6931],
[0.6931],
[0.6931]], grad_fn=<NegBackward0>)
cost = losses.mean()
print(cost)
tensor(0.6931, grad_fn=<MeanBackward0>)
5. 내장된 로지스틱회귀 함수활용
F.binary_cross_entropy(hypothesis, y_train)
tensor(0.6931, grad_fn=<BinaryCrossEntropyBackward0>)
x_data = [[1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 1], [4, 3], [5, 3], [6, 2]]
y_data = [[0], [0], [0], [1], [1], [1]]
x_train = torch.FloatTensor(x_data)
y_train = torch.FloatTensor(y_data)
W = torch.zeros((2, 1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
optimizer = optim.SGD([W, b], lr=1)
nb_epochs = 1000
for epoch in range(nb_epochs + 1):
hypothesis = torch.sigmoid(x_train.matmul(W) + b)
cost = -(y_train * torch.log(hypothesis) +
(1 - y_train) * torch.log(1 - hypothesis)).mean()
optimizer.zero_grad()
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
if epoch % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch {:4d}/{} Cost: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, nb_epochs, cost.item()
))
Epoch 0/1000 Cost: 0.693147
Epoch 100/1000 Cost: 0.134722
Epoch 200/1000 Cost: 0.080643
Epoch 300/1000 Cost: 0.057900
Epoch 400/1000 Cost: 0.045300
Epoch 500/1000 Cost: 0.037261
Epoch 600/1000 Cost: 0.031673
Epoch 700/1000 Cost: 0.027556
Epoch 800/1000 Cost: 0.024394
Epoch 900/1000 Cost: 0.021888
Epoch 1000/1000 Cost: 0.019852
hypothesis = torch.sigmoid(x_train.matmul(W) + b)
print(hypothesis)
tensor([[2.7648e-04],
[3.1608e-02],
[3.8977e-02],
[9.5622e-01],
[9.9823e-01],
[9.9969e-01]], grad_fn=<SigmoidBackward0>)
prediction = hypothesis >= torch.FloatTensor([0.5])
print(prediction)
tensor([[False],
[False],
[False],
[ True],
[ True],
[ True]])
print(W)
print(b)
tensor([[3.2530],
[1.5179]], requires_grad=True)
tensor([-14.4819], requires_grad=True)