트라이 (Trie)
: 문자열을 저장하고 효율적으로 탐색하기 위한 트리 형태의 자료 구조
트라이의 특징
- 검색어 자동완성, 사전 찾기 등에 이용된다.
- 문자열을 탐색할 때 단순하게 비교하는 것보다 효율적으로 찾을 수 있다.
L이 문자열의 길이일 때 탐색, 삽입은O(L)만큼 걸린다.
보통 문자열을 탐색할 때문자열의 개수 * 문자열의 길이만큼 시간복잡도를 가지지만, 트라이를 이용하면 찾는 문자열의 길이만큼만 시간복잡도가 걸린다.- 대신 각 정점이 자식에 대한 링크를 전부 가지고 있기에 저장 공간을 더 많이 사용한다는 단점이 있다.
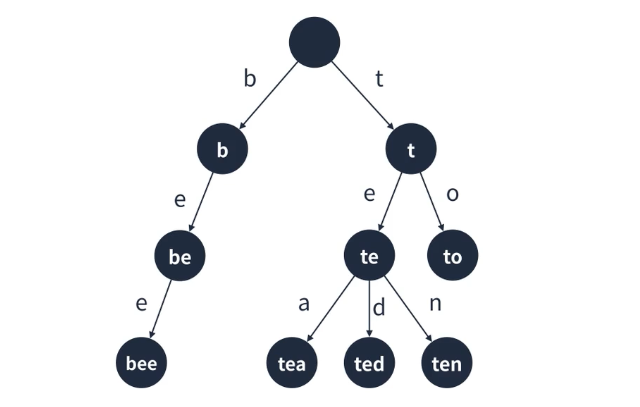
트라이 구조
- 루트는 비어있는 공백이다.
- 각 간선(링크)는 추가될 문자를 키로 가진다.
- 각 정점은 이전 정점의 값 + 간선의 키를 값으로 가진다.
- 해시 테이블과 연결 리스트를 이용하여 구현할 수 있다.
JavaScript로 구현하기
class Node {
constructor(value ='') {
this.value = value;
this.children = new Map();
}
}
// Node {value: '', children: Map(0)}
class Trie {
constructor() {
this.root = new Node();
}
insert(string) { // string = 'cat'
let currentNode = this.root; // root부터 탐색을 시작한다.
for (const char of string) { // 문자열을 맨 앞부터 문자 하나씩 순회한다. char = 'c'
if (!currentNode.children.has(char)) { // 현재 노드가 'c'를 간선으로 가지고 있지 않다면,
currentNode.children.set(char, new Node(currentNode.value + char)); // 새롭게 노드를 추가한다.
// Node {value:'', children: Map(1) {'c' => Node}}
}
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char); // 그러고나서 char 노드로 이동한다.
// 'c' 간선이 이어진 노드로 이동
// Node {value: 'c', children: Map(0)}
}
}
has(string) {
let currentNode = this.root;
for (const char of string) {
if (!currentNode.children.has(char)) {
return false;
}
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
return true;
}
}
const trie = new Trie();
trie.insert('cat');
trie.insert('can');
console.log(trie.has('cat')); // true
console.log(trie.has('can')); // true
console.log(trie.has('cap')); // false이렇게 구현한 위의 트라이 자료구조는 아래처럼 생겼을 것이다.







자료구조는 매번 볼때마다 어렵네요. class 문법도 잘쓰시니 대단합니다!