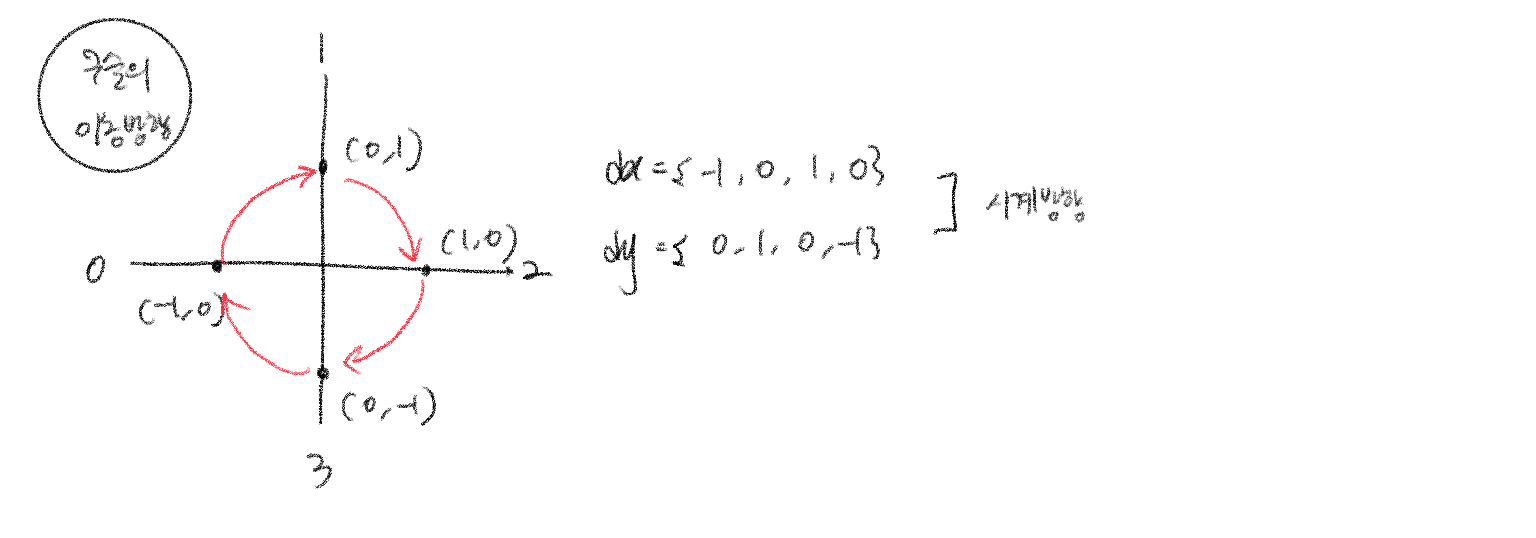설명
- 빨간 구슬과 파란 구슬이 동시에 움직인다.
- 구슬의 위치를 담는 클래스도 빨간, 파란 구슬의 위치를 둘 다 갖는다.
- 최단 거리 탈출을 위한 BFS에서 사용하는 방문 확인을 위한 visited 배열은 빨강, 파랑 두 위치를 기반으로 검증한다.
- 구슬의 이동은 #을 만날 때까지 한다.
- 이동은 상하좌우 4방향을 모두 거친다.(for문 사용)
- 두 구슬이 구멍에 빠지는 경우
파랑이 빠지는 경우)- 무조건 실패
- 큐에 남아있는 다른 경오로 성공 케이스가 있을 수 있으니 일단 continue로 넘긴다.
빨강만 구멍에 빠지는 경우 - 성공!
- 구멍에 빠지지 않고 이동만 한 경우
- 이동한 위치가 빨강, 파랑 둘 다 같다면 어떤 구슬을 더 뒤에 위치시킬지 판단해서 한칸 뒤로 이동시킨다.
- 상하좌우 방향에 따른 x,y값을 비교한다.
- 이동한 위치가 빨강, 파랑 둘 다 같다면 어떤 구슬을 더 뒤에 위치시킬지 판단해서 한칸 뒤로 이동시킨다.
- 최대 이동 횟수 10을 넘지 않을 때까지 반복하여 해결한다.
코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class P13460 {
static int N, M;
static char[][] board;
static boolean [][][][] visited; // 빨강, 파랑 두 위치 기반으로 검증한다.
static int holeX, holeY; // 구멍의 위치를 저장한다.
static Marble blue, red;
// 시계방향으로 이동한다.
static int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
static int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.setIn(new FileInputStream("src/Algorithm/P13460/input.txt"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
board = new char[N][M];
visited = new boolean[N][M][N][M];
// board 만들기
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String str = br.readLine();
for(int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
board[i][j] = str.charAt(j);
// hole을 만나는 경우
if (board[i][j] == 'O') {
holeX = i;
holeY = j;
} else if (board[i][j] == 'B') {
blue = new Marble(0, 0, i, j, 0);
} else if (board[i][j] == 'R') {
red = new Marble(i, j, 0, 0, 0);
}
}
}
System.out.println(bfs());
br.close();
}
public static int bfs() {
// 방문할 노드 저장
Queue<Marble> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 방문할 첫번째 노드를 저장(한번 이동한 것이니 count 1)
queue.add(new Marble(red.rx, red.ry, blud.bx, blue.by, 1));
// 방문했으므로 상태는 true
visited[red.rx][red.ry][blue.rx][blue.ry] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 방문할 queue에서 노드를 꺼낸다.
Marble marble = queue.poll()
int curRx = marble.rx;
int curRy = marble.ry;
int curBx = marble.bx;
int curBy = marble.by;
int curCnt = marble.count;
// 먼저, 이동 횟수가 10초과이면 실패이다. -> 처음에 이동 횟수를 확인해야함
if (curCnt > 10) {
return -1;
}
// 동서남북 # 만나기까지 이동한다. (위에서 정한 dx, dy 이동 방향을 생각한다.)
for (int i =0; i < 4; i++) {
int newRx = curRx;
int newRy = curRy;
int newBx = curBx;
int newBy = curBy;
boolean isRedHole = false;
boolean isBlueHole = false;
// 빨간 구슬 이동: # 벽을 만날 때까지
while (board[newRx + dx[i]][newRy + dy[i]] != '#') {
newRx += dx[i];
newRy += dy[i];
// 이동 중 hole을 만날 때
if (newRx == holeX && newRy == holeY) {
isRedHole = true;
break; // 빨간 구슬 이동 while문 탈출
}
}
// 파란 구슬 이동: # 벽을 만날 때까지
while (board[newBx + dx[i]][newBy + dy[i]] != '#') {
newBx += dx[i];
newBy += dy[i];
// 이동 중 hole을 만날 때
if (newBx == holeX && newBy == holeY) {
isBlueHole = true;
break;
}
}
// 파란 구슬이 빠진 경우
if(isBlueHole) {
// 남은 다른 좌표도 보기 위해 일단 넘긴다.
cotinue;
}
// 빨간 구슬만 구멍에 빠진 경우
if(isRedHole && !isBlueHole) {
return curCnt;
}
// 둘 다 구멍에 빠지지 않았고 이동할 위치가 같은 경우 -> 위치를 조정할 필요있다.
if(newRx == newBx && newRy == newBy){
// (-1, 0)으로 기울이기 -> 더 큰 x를 갖는 쪽이 앞쪽에 있는다.(벽을 만날 때, 판단하니까 벽에서 더 이동할 곳은 없다.)
if (i == 0){
if(curRx > curBx) newRx -= dx[i];
else newBx -= dx[i];
}
// (0,1)로 기울이기 -> 더 작은 y를 갖는 쪽이 뒤로 간다.
else if (i == 1){
if(curRy < curBy) newRy -= dy[i];
else newBy -= dy[i];
}
// (1,0)으로 기울이기 -> 더 큰 x를 갖는 쪽이 뒤로 간다.
else if(i == 2){
if(curRx < curBx) newRx -= dx[i];
else newBx -= dx[i];
}
// (0,1)로 기울이기 -> 더 큰 y를 갖는 쪽이 아래로 간다.
else{
if(curRy > curBy) newRy -= dy[i];
else newBy -= dy[i];
}
}
// 두 구슬이 이동할 위치가 처음 방문한 곳이라면 방문 표시하고, 큐에 넣고, 이동 횟수도 1증가시킨다.
if(!visited[newRx][newRy][newBx][newBy]) {
visited[newRx][newRy][newBx][newBy] = true;
queue.add(new Marble(newRx, newRy, newBx, newBy, curCnt + 1));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
// 구슬 클래스
class Marble {
int rx;
int ry;
int bx;
int by;
int count;
Marble(int rx, int ry, int bx, int by, int count) {
this.rx = rx;
this.ry = ry;
this.bx = bx;
this.by = by;
this.count = count;
}
} 좌표의 x,y를 통상적인 x축, y축으로 생각해서 접근하여 헷갈렸다.
구슬이 벽을 만나면 벽쪽으로는 더 이상 이동할 수 없음을 기억하자!