Kotlin
JetBrains에서 개발한 JVM 언어
- 간결하고, 안전하며, 상호 운용 가능함
Types
Basic types
Kotlin의 원시 타입은 래퍼 타입으로 다룸
- 단, 바이트 코드로 컴파일될 때, 원시 타입으로 다룰 수 있는 상황에는 원시 타입으로 변환함
- e.g.
Byte,Short,Int,Long,Float,Double
Smart casts
is 연산자로 타입을 확인하면 이후 자동으로 형변환해줌
- 대부분의
val변수와 일부 상황의var변수에서 사용 가능
Exceptions
Kotlin에는 checked exception이 없음
- 프로젝트 규모가 커질 수록,
checked exception이 생산성과 코드 품질을 떨어트리기 때문 - Java를 위해 선언하고 싶다면
@Throws사용
Inheritance
Any
모든 클래스가 상속하는 클래스 (Java의 Object에 대응)
Nothing
'값이 존재할 수 없음'을 표현하며, 모든 클래스의 자식인 클래스
- 예외를 던지거나 무한 루프로 인해, 반환이 존재할 수 없는 함수의 반환 형식으로 쓰임
- 인스턴스를 만들 수 없음
open classes
Kotlin의 클래스는 기본적으로 final이며 상속이 불가능함
- 상속을 허용하기 위해 클래스에
open키워드를 적용해야 함
open methods and properties
Kotlin의 멤버 프로퍼티와 함수는 기본적으로 final이며 오버라이딩이 불가능함
- 재정의를 허용하기 위해 프로퍼티 혹은 함수에
open키워드를 적용해야 함 - 재정의 시
override키워드로 명시해야 함
sealed classes
sealed 클래스를 적용하면, 컴파일 이후 더 이상 상속이 불가능함
- 서드파티 모듈에서 해당 클래스를 확장할 수 없도록 만듬
enum처럼 활용할 수 있음
lateinit
프로퍼티 혹은 변수가 null을 허용하지 않고 늦게 초기화되고 싶을 때 사용
레퍼런스.isInitialized로 초기화 여부 확인
Visibility modifiers
외부 접근을 제한하는 키워드
privateprotectedinternal: 동일 모듈 내에서만 접근 가능- 모듈: Maven의 project, Gradle의 source set 등
public
Extensions
Decorator 패턴을 구현할 필요 없이, 기존 클래스에 프로퍼티나 함수를 추가함
- 내부적으로는 클래스에 멤버를 추가하는게 아닌, 정적(statically)으로 멤버를 실행함
Data classes
데이터 보관을 목적으로 기본적인 기능과 유용한 함수를 갖는 클래스
- 만족해야 하는 규칙:
- 생성자가 최소 하나의 인자를 가져야 함
- 모든 생성자 인자가
val혹은var이어야 함 abstract나open,sealed,inner불가능
- 여러 함수들을 가짐:
equals()/hashCode()toString()componentN()copy()
Generics
Java의 Generics와 닮아있지만, 더 엄격하고 안전함
- 공변성을 위해 Java의 wildcards 대신
Declaration-site variance와Type projections기능이 존재함
Declaration-site variance
interface Source<out T> {
fun nextT(): T
}클래스 정의 시 타입 인자의 공변성을 미리 정의할 수 있음
- 타입 인자의 공변성을 미리 정의함 (사용 시 정의할 필요가 없어짐)
out: 공변 (only produced), Java의<? extends T>in: 반공변 (only consumed), Java의<? super S>
- Java의 wildcards보다 직관적이고 안전함
Type projections
Use-site variance
fun copy(src: Array<out Any>, dest: Array<Any>) { ... }공변성을 미리 정의할 수 없는 경우(e.g. Array), 사용 시에 투영할 수 있음
out: 값을 얻기 위해 투영함 (only produced)in: 값을 넣기 위해 투영함 (only consumed)
Star-projections
타입 인자에 대해 모를 때, 모든 타입을 안전하게 수용하기 위해 사용함
- 미리 정의된 공변성에 따라 다르게 해석함
Foo<out T : TUpper>:Foo<*>가Foo<out TUpper>와 같음Foo<in T>:Foo<*>가Foo<in Nothing>과 같음Foo<T : TUpper>:Foo<*>가 읽을 땐Foo<out TUpper>, 쓸 땐Foo<in Nothing>과 같음
Generic constraints
fun <T : Comparable<T>> sort(list: List<T>) { ... }Java의 <T extends S>에 대응하는 Upper bounds 기능
Type erasure
Generic은 compile-time 검증을 위한 기능이며, 컴파일 시 Generic 정의가 지워짐
- 따라서 런타임 환경에서는 타입 인자에 대한 정보를 얻을 수 없음 (non reified)
inline reified functions는 타입 인자 정보를 기억함
Delegation
class Derived(b: Base) : Base by bDelegation 패턴을 쉽게 작성할 수 있도록 하는 기능
Delegated properties
class Example {
var p: String by Delegate()
}by 키워드로, getter와 setter의 기능을 위임하는 프로퍼티 기능
Lazy properties: 최초 호출 시 연산하고, 결과를 캐싱함 (lazy())Observable properties: 프로퍼티의 수정을 감지하고 동작을 수행함 (Delegates.observable())Vetoable properties: 프로퍼티의 수정 전 동작을 수행함 (Delegates.vetoable())- 다른 프로퍼티(
by this::delegate)나 Map(by map)에 위임할 수도 있음
Functions
infix
infix fun Int.shl(x: Int): Int { ... }
// calling the function using the infix notation
1 shl 2
// is the same as
1.shl(2).과 괄호 없이 호출할 수 있는 함수
Tail recursive
val eps = 1E-10 // "good enough", could be 10^-15
// tailrec expression
tailrec fun findFixPoint(x: Double = 1.0): Double =
if (Math.abs(x - Math.cos(x)) < eps) x else findFixPoint(Math.cos(x))
// is the same as
private fun findFixPoint(): Double {
var x = 1.0
while (true) {
val y = Math.cos(x)
if (Math.abs(x - y) < eps) return x
x = Math.cos(x)
}
}tailrec 키워드를 적용하면, 재귀 호출을 반복문으로 바꿔줌
StackOverflow에러를 예방할 수 있음
inline
inline fun <T> lock(lock: Lock, body: () -> T): T { ... }컴파일 시 함수 호출을 함수 내용으로 변환시켜줄 함수
- Closure는 외부 Scope의 변수를 참조할 수 있기 때문에 메모리 사용량이 크며, 이때
inline을 활용하기 좋음 - 인자로 받은 람다도 inline함 (인자에
noinline키워드를 적용하여 해제함) inline함수에서의 반환은 외부 함수의 반환으로 사용할 수 있음 (non-local returns)- 인자로 받은 람다에도
non-local return을 적용하려면crossinline키워드를 적용해야 함
- 인자로 받은 람다에도
Coroutines
fun postItem(item: Item) {
launch {
val token = preparePost()
val post = submitPost(token, item)
processPost(post)
}
}
suspend fun preparePost(): Token {
// makes a request and suspends the coroutine
return suspendCoroutine { /* ... */ }
}비동기 Non-blocking 프로그래밍을 위한 API
- Java의 Threading을 대체함
- 더 적은 스레드를 사용하여 문맥교환 비용을 줄임
- 다른 비동기 라이브러리의 Callbacks 방식과 Futures 방식을 대체함
- Scoping 코드로 콜백 체이닝 코드보다 이해하기 쉽게 만듬
- 전통적인 명령형 프로그래밍 모델을 그대로 적용할 수 있도록 함 (top-down imperative)
DSL
import com.example.html.*
fun result() =
html {
head {
title {+"XML encoding with Kotlin"}
}
body {
h1 {+"XML encoding with Kotlin"}
p {+"this format can be used as an alternative markup to XML"}
// an element with attributes and text content
a(href = "http://kotlinlang.org") {+"Kotlin"}
// mixed content
p {
+"This is some"
b {+"mixed"}
+"text. For more see the"
a(href = "http://kotlinlang.org") {+"Kotlin"}
+"project"
}
p {+"some text"}
// content generated by
p {
for (arg in args)
+arg
}
}
}Domain-specific language; 특정 도메인에 특화된 언어
- Kotlin의 함수를 통해 복잡한 계층 구조를 선언적으로 만들 수 있는 Type-safe 빌더를 설계할 수 있음
Collections
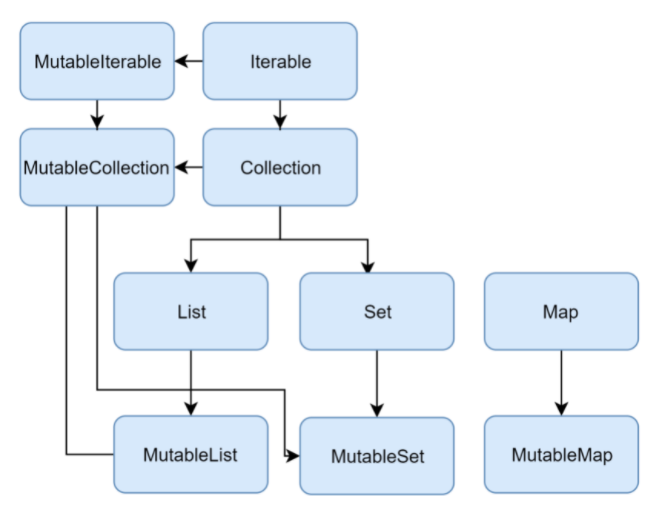
Kotlin에서 제공하는 기본 컬렉션 클래스들
- 기본적으로 Immutable이며, Mutable 컬렉션을 따로 지원함
Ranges
if (i in 1..4) { // equivalent of 1 <= i && i <= 4
print(i)
}수의 범위를 표현하는 클래스
- Progression:
first와last,step으로 Iteration을 정의 (Java의 for문처럼)
Sequences
val oddNumbers = generateSequence(1) { it + 2 } // `it` is the previous element
println(oddNumbers.take(5).toList())
//println(oddNumbers.count()) // error: the sequence is infinite수열을 표현하는 클래스
- 유한하거나 무한하게 만들 수 있음
Iterable과 달리 여러 연산을 한 번에 수행함 (executed lazily)- 단, 크기가 작은 컬렉션은 오버헤드로 인해 오히려 성능이 떨어질 수 있음
Scope functions
| 함수 | 객체 참조 | 반환 값 | Extension function 여부 |
|---|---|---|---|
let | it | Lambda result | Yes |
run | this | Lambda result | Yes |
run | - | Lambda result | No (Context object 없이 호출) |
with | this | Lambda result | No (Context object를 인자로 받음) |
apply | this | Context object | Yes |
also | it | Context object | Yes |
람다를 활용해 객체를 조작하는 let과 run, with, apply, also 함수
- nullable 객체를 non-null 인자 람다로 다루고 싶을 때:
let - 객체로 새로운 지역 변수(local variables) 값을 만들어낼 때:
let - 객체를 설정(configure)할 때:
apply - 객체를 설정(configure)하고 특정 값을 연산(compute)할 때:
run - 여러 구문을 통해 하나의 값(expression)을 만들 때: non-extension
run - 부가적인 행동(additional effects)이 필요할 때:
also - 객체의 함수 호출을 그룹화(grouping)할 때:
with
