lazy란?
로딩 중인 컴포넌트 코드가 처음으로 렌더링 될 때 까지 연기할 수 있다.
// lazy(load 함수)
const Example = lazy(() => import("./example.jsx"))load 함수
- Promise또는 thenable를 반환하는 함수이다.
- React는 반환된 컴포넌트를 처음 렌더링할 때까지
load함수를 호출하지 않는다. load함수가 호출되면 이행될 때까지 기다렸다가 이행된 값의default속성을 React 컴포넌트로 렌더링한다.
💡 반환된 Promise와 이행된 값이 모두 캐시되기 때문에
load함수를 두 번 이상 호출하지 않는다.
🚨 이행된 값의
default속성이 함수,React.memo,forwardRef컴포넌트와 같이 유효한 React 컴포넌트 유형이여야 한다.
주의사항
lazy 컴포넌트를 다른 컴포넌트 내부에서 선언하면 리렌더링마다 새로 생성된다.
- ⛔️ 이렇게 하면 리렌더링할 때마다 새로 생성된다.
function Component() {
const Example = lazy(() => import('./Example.jsx'));
// code...
}- ✅ lazy 컴포넌트를 컴포넌트 외부에 선언한다.
const Example = lazy(() => import('./Example.jsx'));
function Component() {
// ...
}정적 import와 동적 import
기존에는 import 문은 항상 파일 최상위 레벨에서만 써야 하는줄 알았는데 import에서도 정적 import, 동적 import가 나뉘어져있는 것을 잘 모르고 사용했던 것 같다.
정적 import
ES6에서 도입된 기능으로 모듈을 가져오는 가장 일반적인 방법이다.
import React from 'react';- 파일의 최상위 레벨에서만 사용 가능하다.
- 코드가 실행되기 전, 파싱 단계에서 처리된다.
- 호이스팅되어 파일의 맨 위로 끌어올려진다.
- 모듈의 전체 내용을 항상 가져온다.(트리쉐이킹 전)
동적 import
ES2020에 도입된 기능으로 import() 함수를 사용한다.
import('./math').then((math) => {
console.log(math.add(1, 2));
});- 코드의 어느 위치에서나 사용 가능하다.(함수 내부, 조건문 내부 등)
- 런타임에 실행되며 필요할 때만 모듈을 로드한다.
- Promise를 반환하므로 비동기적으로 처리된다.
- 코드 스플리팅과 지연 로딩(Lazy Loading)에 유용하다.
내부 동작 원리
export function lazy<T>(
ctor: () => Thenable<{default: T, ...}> // 동적 import를 수행하는 함수
): LazyComponent<T, Payload<T>> {
// payload 객체는 로딩 상태와 동적 임포트 결과 저장
const payload: Payload<T> = {
_status: Uninitialized,
_result: ctor,
};
const lazyType: LazyComponent<T, Payload<T>> = {
$$typeof: REACT_LAZY_TYPE, // React의 lazy 컴포넌트임을 나타내는 심볼
_payload: payload, // 위에서 생성한 payload 객체
_init: lazyInitializer, // 컴포넌트를 초기화하는 함수
};
return lazyType; // LazyComponent 객체 반환
}lazy 함수는 LazyComponent 객체를 반환한다.
LazyComponent 객체에는 타입, payload 객체, 초기화 함수가 포함되어 있다.
- 타입:
REACT_LAZY_TYPE리액트 앨리먼트 타입을 나타낸다.(파이버 노드를 생성할 때 사용) - payload 객체: 상태와 import 함수가 포함되어 있다.
- 초기화 함수: import 과정을 관리하고 결과를 처리한다.
초기화 함수(실제 컴포넌트 import)
function lazyInitializer<T>(payload: Payload<T>): T {
// 상태가 Uninitialized 일때 초기화 시작(처음 초기화하는 상태)
if (payload._status === Uninitialized) {
const ctor = payload._result;
const thenable = ctor(); // 동적 import 시작
thenable.then(
moduleObject => { // promise 성공 시 처리
if (
(payload: Payload<T>)._status === Pending ||
payload._status === Uninitialized
) {
const resolved: ResolvedPayload<T> = (payload: any);
resolved._status = Resolved; // 상태를 Resolved로 설정
resolved._result = moduleObject; // promise 결과 저장
}
},
error => { // promise 실패 시 처리
if (
(payload: Payload<T>)._status === Pending ||
payload._status === Uninitialized
) {
const rejected: RejectedPayload = (payload: any);
rejected._status = Rejected; // 상태를 Rejected로 설정
rejected._result = error; // promise 에러 저장
}
},
);
if (payload._status === Uninitialized) { // Promise가 아직 해결되지 않았다면
const pending: PendingPayload = (payload: any);
pending._status = Pending; // 상태를 Pending로 설정
pending._result = thenable; // Promise 저장
}
}
if (payload._status === Resolved) {
// 상태가 Resolved(성공)면 로드된 모듈의 default export를 반환
const moduleObject = payload._result;
return moduleObject.default;
} else {
// promise throw(로딩 중, 에러 상태)
throw payload._result;
}
}이 함수는 동적으로 import된 컴포넌트의 초기화와 로딩 상태를 관리한다.
컴포넌트가 처음 요청될 때 동적 import를 시작하고, 로딩 상태에 따라 적절히 처리하며 성공적으로 로드된 경우 해당 컴포넌트를 반환한다.
로딩이 실패하거나 아직 완료되지 않는 경우에는 Promise를 throw한다.
파이버 노드 생성
위에서 LazyComponent 객체의 타입(REACT_LAZY_TYPE)을 설정한 것을 여기서 확인하여 파이버 태그를 설정한 후 파이버 노드를 생성한다.
export function createFiberFromTypeAndProps(
type: any, // React$ElementType
key: null | string,
pendingProps: any,
owner: null | ReactComponentInfo | Fiber,
mode: TypeOfMode,
lanes: Lanes
): Fiber {
let fiberTag = FunctionComponent;
let resolvedType = type;
// code..
getTag: switch (type) {
case REACT_LAZY_TYPE:
fiberTag = LazyComponent; // 태그 설정
resolvedType = null;
break getTag;
// code..
}
// code..
const fiber = createFiber(fiberTag, pendingProps, key, mode); // 노드 생성
fiber.elementType = type;
fiber.type = resolvedType;
fiber.lanes = lanes;
return fiber;
}초기화 함수를 호출하는 단계
beginWork 함수는 현재 처리 중인 Fiber 노드의 유형에 따라 적절한 렌더링 작업을 수행한다.
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes
): Fiber | null {
// code..
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case LazyComponent: { // 파이버 태그가 LazyComponent인 경우
const elementType = workInProgress.elementType;
return mountLazyComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
elementType,
renderLanes
);
}
// code..
}
}beginWork 함수 내부에서 위에서 설정한 파이버 타입(LazyComponent)을 확인하여 mountLazyComponent 함수를 호출한다.
function mountLazyComponent(
_current: null | Fiber,
workInProgress: Fiber,
elementType: any,
renderLanes: Lanes
) {
// 레거시 모드에서의 마운트 처리
resetSuspendedCurrentOnMountInLegacyMode(_current, workInProgress);
const props = workInProgress.pendingProps;
const lazyComponent: LazyComponentType<any, any> = elementType;
let Component;
const payload = lazyComponent._payload; // payload 객체(상태, 동적 import 함수)
const init = lazyComponent._init; // 초기화 함수(실제 컴포넌트 import 수행)
Component = init(payload); // 초기화 함수 실행
workInProgress.type = Component; // 로드한 컴포넌트 타입을 설정
if (typeof Component === "function") {
if (isFunctionClassComponent(Component)) {
// 클래스 컴포넌트인 경우
const resolvedProps = resolveClassComponentProps(Component, props, false);
workInProgress.tag = ClassComponent;
return updateClassComponent(
null,
workInProgress,
Component,
resolvedProps,
renderLanes
);
} else {
// 함수형 컴포넌트인 경우
const resolvedProps = disableDefaultPropsExceptForClasses
? props
: resolveDefaultPropsOnNonClassComponent(Component, props);
workInProgress.tag = FunctionComponent;
return updateFunctionComponent(
null,
workInProgress,
Component,
resolvedProps,
renderLanes
);
}
} else if (Component !== undefined && Component !== null) {
// 특수한 타입인 경우(forwardRef, memo)
const $$typeof = Component.$$typeof;
if ($$typeof === REACT_FORWARD_REF_TYPE) {
// forwardRef인 경우
const resolvedProps = disableDefaultPropsExceptForClasses
? props
: resolveDefaultPropsOnNonClassComponent(Component, props);
workInProgress.tag = ForwardRef;
return updateForwardRef(
null,
workInProgress,
Component,
resolvedProps,
renderLanes
);
} else if ($$typeof === REACT_MEMO_TYPE) {
// memo 컴포넌트인 경우
const resolvedProps = disableDefaultPropsExceptForClasses
? props
: resolveDefaultPropsOnNonClassComponent(Component, props);
workInProgress.tag = MemoComponent;
return updateMemoComponent(
null,
workInProgress,
Component,
disableDefaultPropsExceptForClasses
? resolvedProps
: resolveDefaultPropsOnNonClassComponent(
Component.type,
resolvedProps
),
renderLanes
);
}
}
// 유효하지 않는 컴포넌트인 경우 에러 처리
const hint = "";
throw new Error(
`Element type is invalid. Received a promise that resolves to: ${Component}. ` +
`Lazy element type must resolve to a class or function.${hint}`
);
}초기화 함수(lazyInitializer)를 호출하여 실제 컴포넌트를 로드하고, 로드한 컴포넌트의 타입에 맞게 적절히 처리한다.
- 함수형 컴포넌트 처리
- 클래스형 컴포넌트 처리
- forwardRef 컴포넌트 처리
- React.memo 컴포넌트 처리
정리하기
-
lazy 함수가 호출되면 즉시 LazyComponent 객체를 생성하여 반환한다.
-
이 시점에서는 실제 컴포넌트가 로드되지 않는다.
-
React가 이 lazy 컴포넌트를 렌더링하려고 할 때
- 초기화 함수(
lazyInitializer)가 호출된다. - 실제 컴포넌트를 동적으로 로드한다.
- 로딩이 완료되면 상태와 결과(컴포넌트)가 업데이트 된다.
- 로드한 컴포넌트 타입에 맞게 적절히 처리한다.
- 초기화 함수(
-
이후 렌더링 시에는 이미 로드된 컴포넌트를 사용한다.
React lazy + Suspense + Error Boundary
React lazy의 컴포넌트 로드(동적 import)는 Promise를 반환하기 때문에 Suspense를 통해 로딩 인디케이터를 렌더링할 수 있고, 동적 import를 수행하는 중 네트워크가 끊기거나 하면 에러가 발생할 수 있어 Error Boundary를 활용해 에러를 적절히 처리하여 사용자 경험(UX)을 향상시킬 수 있다.
const LazyComponents = lazy(() => import("../components/LazyComponents"));
function App() {
const [shouldLoad, setShouldLoad] = useState(false);
return (
<>
<h1>React lazy</h1>
<button onClick={() => setShouldLoad((prev) => !prev)}>
{shouldLoad ? "지우기" : "로드 시작"}
</button>
{shouldLoad && (
<ErrorBoundary fallback={<div>에러 발생!</div>}>
<Suspense fallback={<div>로딩 중...</div>}>
<LazyComponents />
</Suspense>
</ErrorBoundary>
)}
</>
);
}
첫 로드에서는 컴포넌트가 로드될 때까지 Supense가 트리거되어 Fallback 컴포넌트를 렌더링하고 로드가 완료되면 로드한 컴포넌트를 렌더링한다.
그 후 다시 컴포넌트를 사용해도 캐시가 되어있어 로딩 컴포넌트가 렌더링되지 않는 것을 볼 수 있다.
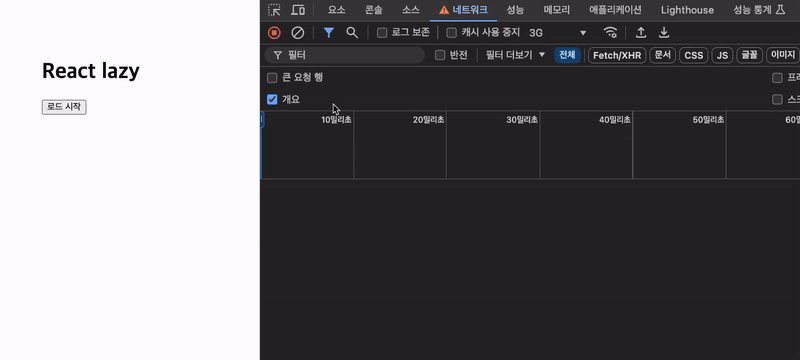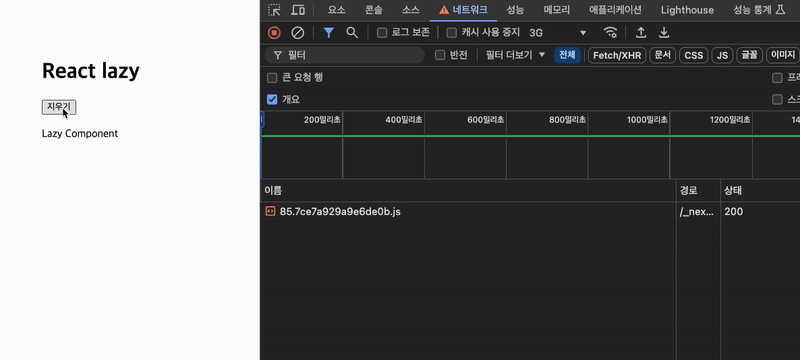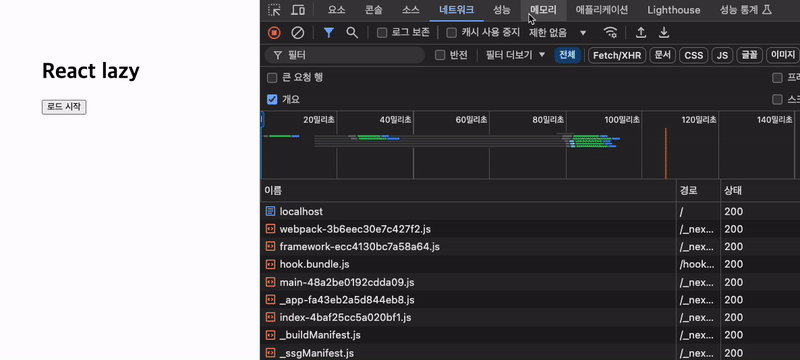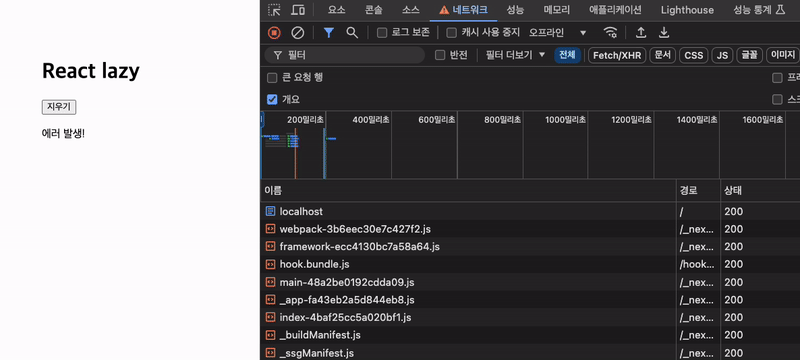
이번에는 기존 캐시를 비우고 네트워크를 오프라인으로 변경한 후 컴포넌트를 로드하면 에러 바운더리에 트리거되어 Error Fallback 컴포넌트가 렌더링되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
🙃 도움이 되었던 자료들
lazy - React 공식문서(v18.3.1)
ES2020: import() – dynamically importing ES modules
How lazy() works internally in React?
Implementing Code Splitting and Lazy Loading in React

멋있으십니다.