데이터 타입(Data Type)
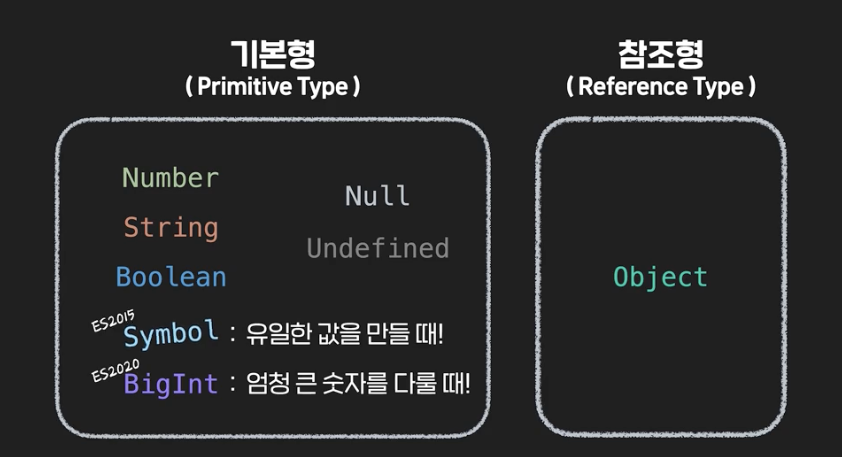
심볼(Symbol)
코드 내에서 유일한 값을 가진 변수 이름을 만들 때 사용
심볼 생성
괄호 안에 심볼에 대한 설명을 붙일 수도 있다.
// 심볼 생성
const user = Symbol("this is user");심볼 비교
심볼 값을 담게 된 user라는 변수는 다른 어떤 값과 비교해도 true가 될 수 없는 고유한 변수가 된다.
const symbolA = Symbol('this is Symbol');
const symbolB = Symbol('this is Symbol');
console.log(symbolA === symbolB); // false
console.log(symbolA === 'this is Symbol'); // falseBigInt
아주 큰 정수(Integer)를 표현하기 위해 등장한 데이터 타입이다.
- 안전한 최대 정수
2**53 -1, 약 9,000조- 안전한 최소 정수
-(2**53 - 1), 약 -9,000조
사용법
일반 정수 마지막에 알파벳n을 붙이거나 BigInt라는 함수를 사용한다.
console.log(9007199254740993n); // 9007199254740993n
console.log(BigInt('9007199254740993')); // 9007199254740993n🔥 주의사항 - BigInt 타입은 큰 정수를 표현하기 위한 데이터 타입으로 소수 표현에는 사용할 수 없다.
💡 참고사항 - BigInt 생정자에 문자열로 값을 넘겨주면 큰 정수를 그대로 사용하더라도 안전한 최대 정수로 처리한다.
Falsy 값
Falsy 값은 false로 암묵적 타입 변환이 된다. Falsy 값은 아래와 같다.
false,null,undefined,NaN,0,-0,""(빈 문자열)
null 병합 연산자(??)
물음표 두 개(??)를 사용해서 null 혹은 undefined 값을 가려내는 연산자이다.
사용법
연산자의 왼편의 값이 null 이나 undefined라면 연산자의 오른편의 값이 리턴된다.
const apple = null;
const banana = undefined;
const grape = "purple";
// "red", 연산자의 왼편이 null
const test1 = apple ?? "red";
// "yellow", 연산자의 왼편이 undefined
const test2 = banana ?? "yellow";
// "purple", 연산자의 왼편의 값이 null or undefined가 아니므로 기존 변수의 값 출력
const test3 = grape ?? "Codeit";null 병합 연산자와 OR 연산자 차이
- null 병합 연산자(??)는 왼편의 값이 null이나 undifined인지 확인
- OR 연산자(||)는 왼편의 값이 falsy인지 확인
함수
일련의 과정을 문으로 구현하고 코드 블록으로 감싸서 하나의 실행 단위로 정의 한 것이다.
함수 정의
1. 함수 선언문
- 함수 이름을 생략할 수 없다.
- 표현식이 아닌 문이다.
function add(x, y){
return x + y;
}2. 함수 표현식
- 함수 이름을 생략(익명 함수)할 수 있다.
- 함수 이름이 아닌 식별자로 호출해야 한다.
const add = function(x, y){
return x + y;
};3. Function 생성자 함수
- 일반적인 방법은 아니다.
- 클로저를 생성하지 않는다.
const add = new function('x', 'y', 'return x + y');4. 화살표 함수
- 표현이 간결하고 가독성이 좋다
const add = (x, y) => x + y;5. 즉시 실행 함수(IIFE)
- 선언과 동시에 실행이 이뤄지기 때문에 일반적으로 프로그램 초기화 기능에 활용
(function init(){
// 프로그램이 실행 될 때 기본적으로 동작할 코드들..
})();⭐️ this ⭐️
자바스크립트에서 this는 함수를 호출한 객체를 가르킨다.
const user = {
firstName: 'woohyeok',
lastName: 'lee',
getFullName: function () {
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`;
},
};
console.log(user.getFullName()); // getFullName 안에서의 this는 getFullName을 호출한 user객체가 담긴다!옵셔널 체이닝(Optional Chaining)
왼편의 프로퍼티 값이
undefinedornull이 아니라면 그 다음 프로퍼티 값을 리턴하고 그렇지 않은 경우에는undefined를 리턴한다.
에러 발생 코드
function printCatName(user) {
console.log(user.cat.name);
}
const user = {
name: 'Young',
}
console.log(user.cat); // undefined
printCatName(user); // TypeError: Cannot read property 'name' of undefined옵셔널 체이닝 사용 코드
function printCatName(user) {
console.log(user.cat?.name);
// 위에 코드를 삼항연산자로 풀어 쓴 코드이다.
console.log((user.cat === null || user.cat === undefined) ? undefined : user.cat.name);
}
const user = {
name: 'Young',
}
console.log(user.cat); // undefined
printCatName(user); // undefined옵셔널 체이닝 + null 병합 연산자 코드
function printCatName(user) {
console.log(user.cat?.name ?? "함께 지내는 고양이가 없습니다.");
}
const user = {
name: 'Young',
}
printCatName(user); // 함께 지내는 고양이가 없습니다. => 왼쪽에서 undefined가 반환되어서 오른쪽 값이 리턴되었다.⭐️ 구조 분해(Destructuring) ⭐️
배열의 요소나 객체의 프로퍼티 값들을 개별적인 변수에 따로 따로 할당할 수 있다.
// 배열 디스트럭처링
const members = ['코딩하는효준', '글쓰는유나', undefined, '편집하는민환', '촬영하는재하'];
const [macbook, ipad, airpod = '녹음하는규식', ...coupon] = members;
console.log(macbook); // 코딩하는효준
console.log(ipad); // 글쓰는유나
console.log(airpod); // 녹음하는규식
// rest parameter 사용
console.log(coupon); // (2) ["편집하는민환", "촬영하는재하"]
// 객체 디스트럭처링
const macbookPro = {
title: '맥북 프로 16형',
price: 3690000,
memory: '16 GB 2667 MHz DDR4',
storage: '1TB SSD 저장 장치',
};
const { title:product, price, color = 'silver', ...rest } = macbookPro;
// 프로퍼티의 키 값 이름 변경
console.log(product); // 맥북 프로 16형
console.log(price); // 3690000
// default parameter
console.log(color); // silver
console.log(rest); // {memory: "16 GB 2667 MHz DDR4", storage: "1TB SSD 저장 장치"}에러와 에러 객체
에러가 발생하면 에러에 대한 정보를
name과message라는 프로퍼티가 담고 있는 에러 객체가 만들어진다.
대표적인 에러 객체는 아래와 같다.
- SyntaxError
- ReferenceError
- TypeError
에러 객체 생성
new키워드와 에러 객체 이름을 딴 함수를 통해 에러 객체를 만들 수 있고, throw키워드로 에러를 발생시킬 수 있다.
throw new TypeError("타입 에러가 발생했습니다.");try...catch문
try...catch문은 자바스크립트에서 대표적인 에러 처리 방법이다.
사용법
try...catch문에서 에러의 유무와 상관없이 항상 동작해야 할 코드가 필요하다면 finally문을 활용할 수 있다.
try {
// 실행할 코드
} catch (error) {
// 에러가 발상했을 때 실행할 코드
} finally {
// 항상 실행할 코드
}
