1. 제너릭
- 제너릭은 클래스나 메서드를 일반화시켜 다양한 자료형에 대응할 수 있는 기능
- 제너릭을 사용하면 코드의 재사용성을 높일 수 있음
- C#에서는
<T>형태의 키워드를 이용하여 제너릭을 선언 함 - 제너릭 클래스나 메서드에서 사용할 자료형은 선언 시점이 아닌 사용 시점에 결정
- 제너릭 클래스나 메서드를 사용할 때는
<T>대신 구체적인 자료형을 넣어 줌 class 클래스명<T> { 접근지정자 T 변수명; }클래스명<자료형> 인스턴스명 = new 클래스명<자료형>();
// 제너릭 클래스 선언 예시
class Stack<T>
{
private T[] elements;
private int top;
public Stack()
{
elements = new T[100];
top = 0;
}
public void Push(T item)
{
elements[top++] = item;
}
public T Pop()
{
return elements[--top];
}
}
// 제너릭 클래스 사용 예시
Stack<int> intStack = new Stack<int>();
intStack.Push(1);
intStack.Push(2);
intStack.Push(3);
Console.WriteLine(intStack.Pop()); // 출력 결과: 3- 제너릭을 두개 이상 사용하는 예시
class Pair<T1, T2>
{
public T1 First { get; set; }
public T2 Second { get; set; }
public Pair(T1 first, T2 second)
{
First = first;
Second = second;
}
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine($"First: {First}, Second: {Second}");
}
}Pair<int, string> pair1 = new Pair<int, string>(1, "One");
pair1.Display();
Pair<double, bool> pair2 = new Pair<double, bool>(3.14, true);
pair2.Display();// 출력
First: 1, Second: One
First: 3.14, Second: True2. out, ref 키워드
- out, ref 키워드는 메서드에서 매개변수를 전달할 때 사용
- out 키워드는 메서드에서 반환 값을 매개변수로 전달하는 경우에 사용
- ref 키워드는 메서드에서 매개변수를 수정하여 원래 값에 영향을 주는 경우에 사용
- out, ref 키워드를 사용하면 메서드에서 값을 반환하는 것이 아니라, 매개변수를 이용하여 값을 전달할 수 있음
- out 키워드를 사용할때 메서드 내에서 꼭 대입을 해야 함
- ref 키워드는 메서드 내에서 대입을 안해도 오류는 안 남
// out 키워드 사용 예시
void Divide(int a, int b, out int quotient, out int remainder)
{
quotient = a / b;
remainder = a % b;
}
int quotient, remainder;
Divide(7, 3, out quotient, out remainder);
Console.WriteLine($"{quotient}, {remainder}"); // 출력 결과: 2, 1// ref 키워드 사용 예시
void Swap(ref int a, ref int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int x = 1, y = 2;
Swap(ref x, ref y);
Console.WriteLine($"{x}, {y}"); // 출력 결과: 2, 1- 주의 사항
- 값의 변경 가능성 :
outref매개변수를 사용하면 메서드 내에서 해당 변수의 값을 직접 변경할 수 있음. 이는 예기치 않은 동작을 초래할 수 있으므로 주의가 필요 - 성능 이슈 :
ref매개변수는 값에 대한 복사 없이 메서드 내에서 직접 접근할 수 있기 때문에 성능상 이점이 있음. 그러나 너무 많은 매개변수를ref로 전달하면 코드의 가독성이 떨어지고 유지보수가 어려워질 수 있음 - 변수 변경 여부 주의 :
out매개변수는 메서드 내에서 반드시 값을 할당해야 함. 따라서out매개변수를 전달할 때 해당 변수의 이전 값이 유지되지 않으므로 주의해야 함
- 차이점
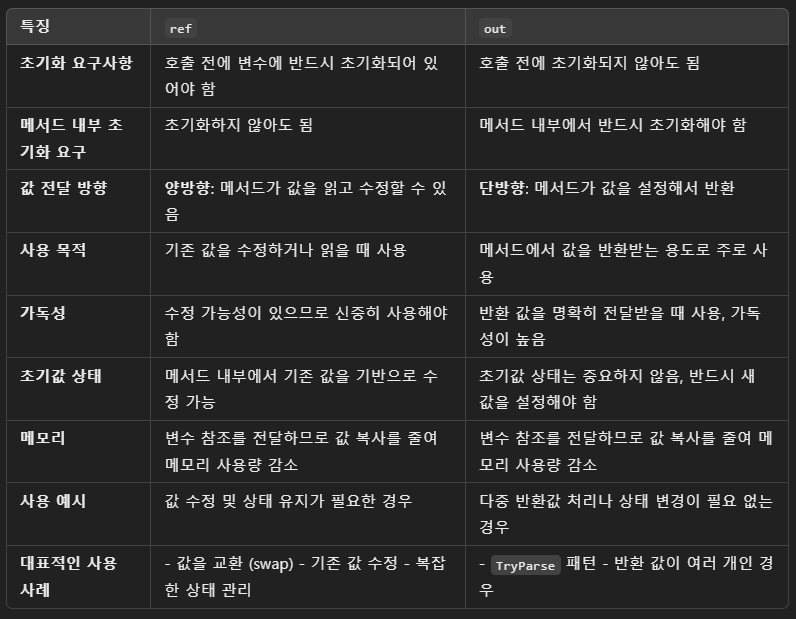
3. out
○ 개념
- 메서드의 매개변수로 사용되며, 해당 매개변수를 메서드 내부에서 반드시 초기화하여 반환하도록 강제하는 역할을 함
- 주로 여러 값을 반환하거나 반환 값 외의 추가 데이터를 전달할 때 사용
- out은 여러 값 반환이 필요한 오래된 코드베이스에서 많이 사용되었지만, 최신 코드에서는 주로 튜플이나 객체를 통해 대체되고 있음
○ 특징
- 초기화 필요 없음: 메서드를 호출하기 전에 out 매개변수는 초기화되지 않아도 됨
- 메서드 내부에서 초기화 필수: out으로 전달된 매개변수는 메서드 내부에서 반드시 값을 설정해야 함
- 메서드 호출 후 값 사용 가능: 메서드 호출이 끝난 후, out 매개변수에 설정된 값을 사용할 수 있습니다.
○ 사용예시
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// 변수 선언만 하고 초기화하지 않음
int result;
// out 매개변수로 메서드 호출
Calculate(5, 3, out result);
Console.WriteLine($"결과: {result}"); // 출력: 결과: 8
}
static void Calculate(int a, int b, out int sum)
{
// 반드시 값을 설정해야 함
sum = a + b;
}
}○ 주의 사항
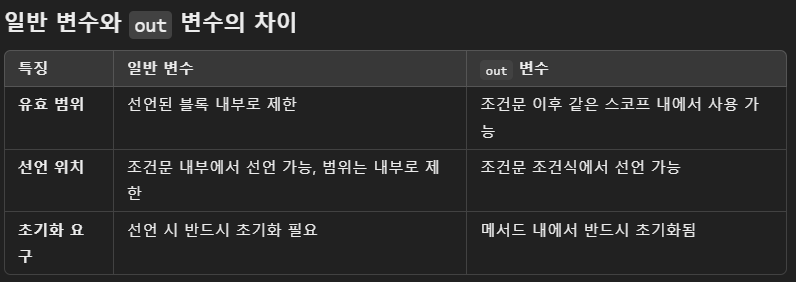
- 조건문 내부에서 선언된 변수는 조건문 외부에서도 유효
- out 변수는 조건문에서 선언되었을 때 스코프가 조건문 이후로 확장됨
- 단, 동일한 이름의 변수를 같은 스코프에서 다시 선언할 수 없음
- 값 초기화 주의
- TryParse 실패 시에도 result는 기본값(숫자의 경우 0)으로 초기화됨. 이 점은 out 변수의 특징
- 초기화 여부 확인 필요 없음
- out 매개변수는 메서드 내부에서 무조건 초기화되므로, 메서드 호출 이후에는 안전하게 값을 사용할 수 있음
- 다른 반환 메커니즘과 비교
- ref: 메서드 호출 전에 초기화된 값을 전달하며, 메서드 내에서 수정 가능.
- out: 초기화 여부와 상관없이 값을 전달하며, 메서드 내에서 반드시 초기화해야 함.
static void Example(out int value, ref int refValue)
{
value = 10; // out 매개변수는 초기화 필수
refValue += 10; // ref 매개변수는 초기화되어 있음
}
- 값 반환 방식의 대안
C# 7.0 이후부터는 튜플(Tuple)이나 ValueTuple을 사용하여 메서드에서 여러 값을 반환하는 것이 일반적
static (int sum, int product) CalculateValues(int a, int b)
{
return (a + b, a * b);
}
var (sum, product) = CalculateValues(5, 3);
Console.WriteLine($"합: {sum}, 곱: {product}");○ 유니티에서의 out
-
Unity에서는 여전히 out 키워드가 특정 상황에서 유용하게 사용됨
-
특히 Unity는 C# 7.0 이후의 최신 기능을 점진적으로 받아들이고 있지만, Unity API 자체가 out을 사용하는 경우가 많아서 이 키워드를 접할 일이 있음
-
Unity에서는 여전히 많이 쓰이는 이유
-
호환성과 성능
Unity는 최신 C# 기능을 점진적으로 도입하지만, 여전히 기존 API와의 호환성을 유지하기 위해 out을 사용하는 경우가 많음. 특히 Unity의 네이티브 엔진 코드와의 상호작용에서 out은 효율적인 데이터 반환 방법 -
간결함
out을 사용하면 필요하지 않은 객체나 데이터 구조를 추가로 생성하지 않고도 값을 반환할 수 있음. 이는 메모리 할당을 줄이는 데 도움이 됨 -
직관적 API 설계
Unity API는 사용하기 쉽도록 설계되어 있습니다. out은 초보자도 간단히 이해할 수 있으며, 명확하게 값이 반환됨을 나타내므로 직관적임
-
○ 사용예시
- Physics 관련 메서드
- 물리 엔진에서 Rycast와 같은 메서드는 out매개변수를 사용하여 충돌 정보나 결과를 반환함
out RaycastHit hit: 충돌된 객체와 관련된 정보를 반환하기 위해 사용됨hit객체를 통해 충돌 위치, 충돌된 객체, 노멀 벡터 등의 정보를 얻을 수 있음
using UnityEngine;
public class RaycastExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0)) // 마우스 클릭 시
{
Ray ray = Camera.main.ScreenPointToRay(Input.mousePosition);
if (Physics.Raycast(ray, out RaycastHit hit, 100f))
{
Debug.Log($"Hit Object: {hit.collider.gameObject.name}");
}
}
}
}- Try-Parse 패턴
- Unity 스크립트에서 문자열을 숫자로 변환해야 할 때 int.TryParse나 float.TryParse를 사용하는 경우가 많음. 이 메서드들 역시 out 매개변수를 활용함
- TryParse는 변환이 성공하면 true를 반환하며, 변환된 값을 out 매개변수를 통해 제공함
using UnityEngine;
public class ParseExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
string input = "123";
if (int.TryParse(input, out int result))
{
Debug.Log($"Parsed number: {result}");
}
else
{
Debug.Log("Parsing failed.");
}
}
}4. ref
○ 개념
- C#의 ref 키워드는 메서드의 매개변수로 전달된 변수를 참조로 전달하기 위해 사용
- 이를 통해 메서드 내부에서 해당 변수의 값을 수정할 수 있으며, 수정된 값은 메서드 호출 이후에도 반영
- ref는 변수의 참조를 전달함으로써 값 수정 및 성능 최적화를 가능하게 함
- 다만, 불필요한 값 변경을 방지하기 위해 꼭 필요한 경우에만 사용하는 것이 좋음
○ 특징
- 참조로 전달
- 값 형식 변수도 참조로 전달되기 때문에 원본 변수가 수정됨
- 포인터와는 다르지만, 비슷한 참조 개념을 제공함
- 초기화 필요
- ref 키워드를 사용하는 변수는 메서드 호출 전에 반드시 초기화되어야 함
- 양방향 데이터 흐름
- 메서드가 변수의 값을 읽을 수도, 수정할 수도 있음
- out과 비교
- out: 메서드 내부에서 반드시 초기화되어야 하며, 호출 전에 초기화되지 않아도 됨
- ref: 호출 전에 초기화되어 있어야 하며, 메서드 내부에서 값을 읽고 수정할 수 있음
○ 사용예시
1. 기본예제
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int number = 10; // 초기화 필수
Console.WriteLine($"Before: {number}");
// ref를 사용하여 변수 전달
ModifyValue(ref number);
Console.WriteLine($"After: {number}");
}
static void ModifyValue(ref int value)
{
value *= 2; // 원본 변수 수정
}
}- 출력
Before: 10
After: 20
2. 여러 값 수정
- ref를 사용하면 여러 개의 변수를 수정할 수 있음
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int a = 5, b = 3;
Swap(ref a, ref b);
Console.WriteLine($"After Swap: a = {a}, b = {b}");
}
static void Swap(ref int x, ref int y)
{
int temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
}- 출력
After Swap: a = 3, b = 5
3. 배열과 ref
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3 };
Console.WriteLine($"Before: {string.Join(", ", numbers)}");
ModifyArray(ref numbers);
Console.WriteLine($"After: {string.Join(", ", numbers)}");
}
static void ModifyArray(ref int[] arr)
{
arr = new int[] { 10, 20, 30 }; // 배열 자체를 새로운 것으로 변경
}
}
- 출력
Before: 1, 2, 3
After: 10, 20, 30○ 주의 사항
- 초기화 필요
- ref로 전달하려는 변수는 반드시 메서드 호출 이전에 초기화되어 있어야 함
- 값 수정 여부에 주의
- ref 매개변수는 원본 값을 수정하므로, 불필요한 값 변경을 방지하기 위해 신중히 사용해야 함
- out과의 혼동 방지
- ref: 메서드 호출 전에 값이 있어야 하며, 읽고 쓸 수 있음.
- out: 메서드 호출 전에 초기화 필요 없음, 메서드 내부에서 값을 반드시 설정해야 함.
○ ref를 사용하는 상황
- 성능 최적화: 값 형식의 큰 데이터(예: 구조체)를 복사하지 않고 참조로 전달하여 메모리 비용을 절약.
- 상태 변경: 메서드 호출 후 변수를 직접 수정해야 하는 경우.
- 배열 요소 수정: 배열이나 컬렉션의 특정 요소를 참조로 전달해 수정해야 할 때.
