1. 델리게이트와 이벤트
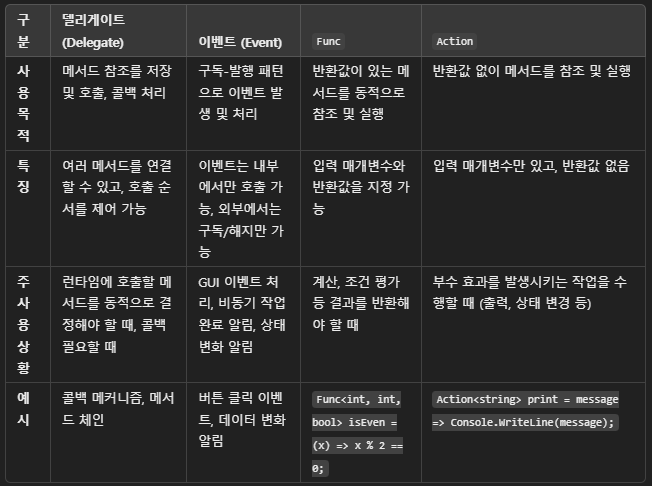
○ 델리게이트(Delegate) 란?
public delegate 반환형 델리게이트이름(매개변수);
- 델리게이트(delegate)는 메서드를 참조하는 할 수 있는 형식(type)
(메서드의 포인터라고 할 수 있음) - 다른 프로그래밍 언어에서는 함수 포인터라는 용어를 사용하기도 함. 동일한 기능은 아니고 비슷한 기능
- 델리게이트를 이용하면 메서드를 매개변수로 전달하거나 변수에 할당할 수 있음
- 델리게이트는 여러 메서드를 연결할 수 있으며, 필요에 따라 다른 메서드를 호출할 수 있음
- 마치 사용자 자료형 선언 같네?
- 델리게이트 선언은 새로운 자료형을 정의하는 것과 매우 유사함
- 델리게이트는 특정한 형식의 메서드를 참조할 수 있는 타입을 정의하는 것이기 때문
- 델리게이트 자체가 사용자 정의 자료형과 비슷하게 작동함
- 즉, 델리게이트 타입은 특정한 서명을 가진 메서드들을 가리킬 수 있는 타입이라고 할 수 있음
○ 델리게이트 특징
- 델리게이트는 일반적으로 메서드를 참조하는 데 사용됨
- 메서드 체인을 만들어 여러 메서드를 한꺼번에 호출할 수 있음
- 사용자(개발자)가 델리게이트에 직접 메서드를 추가하거나 제거할 수 있음
- 직접적으로 실행될 수 있으며, 실행 순서도 관리 가능함
public delegate void MyDelegate(string message);
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
MyDelegate del = PrintMessage;
del += PrintAnotherMessage; // 메서드 체인 추가
del("Hello, World!"); // 두 개의 메서드가 호출됨
}
static void PrintMessage(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
static void PrintAnotherMessage(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine("Another: " + message);
}
}○ 델리게이트 사용예제
- 메서드 등록해서 사용하기
delegate int Calculate(int x, int y);
static int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// 메서드 등록
Calculate calc = Add;
// 델리게이트 사용
int result = calc(3, 5);
Console.WriteLine("결과: " + result);
}
}- 하나 이상의 메서드 등록하기
- 메소드(기능)을 추가할 수 있음
delegate void MyDelegate(string message);
static void Method1(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method1: " + message);
}
static void Method2(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine("Method2: " + message);
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// 델리게이트 인스턴스 생성 및 메서드 등록
MyDelegate myDelegate = Method1;
myDelegate += Method2;
// 델리게이트 호출
myDelegate("Hello!");
Console.ReadKey();
}
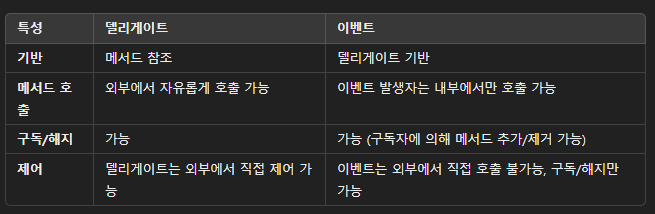
}○ 이벤트(event) 란?
- 이벤트는 델리게이트에 기반한 메커니즘
- 객체가 특정 상황에서 다른 객체에게 알림을 보낼 수 있는 기능을 제공함
- 주로 발생자(event publisher)가 구독자(event subscriber)에게 특정 동작이나 상태 변경을 알릴 때 사용됨
○ 이벤트 특징
- 이벤트는 델리게이트와 비슷하지만, 더 제한적인 방식으로 동작함
- 이벤트 구독자는 이벤트 핸들러 메서드를 추가하거나 제거할 수 있지만, 이벤트 자체를 외부에서 직접 호출할 수 없음.
호출은 이벤트를 선언한 클래스 내에서만 가능함 - 보통 클래스 외부에서는 이벤트에 메서드를 구독(subscribe)하거나 해지(unsubscribe)만 할 수 있음
public delegate void MyDelegate(string message);
class Publisher
{
public event MyDelegate MyEvent;
public void RaiseEvent(string message)
{
if (MyEvent != null)
MyEvent(message); // 이벤트를 발생시킴
}
}
class Subscriber
{
public void OnMyEvent(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine("Event received: " + message);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Publisher pub = new Publisher();
Subscriber sub = new Subscriber();
pub.MyEvent += sub.OnMyEvent; // 구독
pub.RaiseEvent("Hello, Event!"); // 이벤트 발생
}
}
○ 이벤트 사용예제
- 공격 콜백 받기😥
- 다음 예제에서는 event 를 붙여서 사용함
- event는 할당연산자( = )를 사용할 수 없으며( += )와 ( -= )만 사용할 수 있음, 클래스 외부에서는 직접 이벤트를 호출할 수 없음
- 조금 더 보안성을 높이고 캡슐화 한 것
// 델리게이트 선언
public delegate void EnemyAttackHandler(float damage);
// 적 클래스
public class Enemy
{
// 공격 이벤트
public event EnemyAttackHandler OnAttack;
// 적의 공격 메서드
public void Attack(float damage)
{
// 이벤트 호출
// Invoke() 함수 실행 콜
// ? 는 null 조건부 연산자, 자세한 설명은 바로 밑에
OnAttack?.Invoke(damage);
// null 조건부 연산자, null이면 실행안함. null아니면 실행
// null 참조가 아닌 경우에만 멤버에 접근하거나 메서드를 호출
}
}
// 플레이어 클래스
public class Player
{
// 플레이어가 받은 데미지 처리 메서드
public void HandleDamage(float damage)
{
// 플레이어의 체력 감소 등의 처리 로직
Console.WriteLine("플레이어가 {0}의 데미지를 입었습니다.", damage);
}
}
// 게임 실행
static void Main()
{
// 적 객체 생성
Enemy enemy = new Enemy();
// 플레이어 객체 생성
Player player = new Player();
// 플레이어의 데미지 처리 메서드를 적의 공격 이벤트에 추가
enemy.OnAttack += player.HandleDamage;
// 적의 공격
enemy.Attack(10.0f);
}○ 델리게이트와 이벤트 차이점
- 델리게이트는 좀 더 유연하고 자유롭게 메서드를 다룰 수 있음
- 이벤트는 [구독-발행] 패턴에서 좀 더 안전하고 제한된 방법으로 동작하게 설계된 것
2. Func과 Action
○ Func, Action 란?
Func과Action은 델리게이트를 대체하는 미리 정의된 제네릭 형식- C#에서 델리게이트(Delegate)를 간편하게 사용할 수 있도록 제공되는 제네릭 델리게이트 타입
Func및Action은 제네릭 형식으로 미리 정의되어 있어 매개변수와 반환 타입을 간결하게 표현할 수 있음- 이 둘은 함수나 메서드를 변수처럼 취급할 수 있게 해주며, 각각 리턴값이 있는 경우와 없는 경우에 주로 사용됨
- 미리 정의되어 있기 때문에 더 안전하고 간결함
○ Func
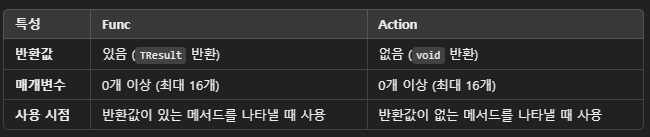
- Func는 반환값이 있는 메서드를 위한 델리게이트
- 입력 파라미터와 반환값의 형식을 지정할 수 있음
- 입력 매개변수는 0개 이상, 최대 16개까지 받을 수 있음
- 마지막 제네릭 형식 매개변수는 반환 타입을 나타냄
- 예를 들어,
Func<int, string>는int를 입력으로 받아string을 반환하는 메서드를 나타냄
- Func를 주로 이용하는 때
- 리턴값이 있는 메서드를 델리게이트로 사용하고 싶을 때
- 함수 포인터를 사용해야 할 때, 메서드나 기능을 인수로 넘겨주고 싶을 때
- LINQ 메서드와 함께 조건이나 변환을 표현할 때
○ Func 예시
- 두 숫자를 더하는 함수
Func<int, int, int> add = (x, y) => x + y;
Console.WriteLine(add(3, 4)); // 출력: 7- 입력 없이 현재 시간을 반환
Func<DateTime> getCurrentTime = () => DateTime.Now;
Console.WriteLine(getCurrentTime()); // 현재 시간 출력- 복잡한 작업을 람다로 표현
Func<int, int, bool> isGreater = (x, y) => x > y;
Console.WriteLine(isGreater(10, 5)); // 출력: True
○ Action
Action은 값을 반환하지 않는 메서드를 나타내는 델리게이트- void 리턴 타입을 가진 메서드에 해당하며, 입력 매개변수만 있음
- 최대 16개의 입력 파라미터를 받을 수 있음
- 예를 들어,
Action<int, string>은int와string을 입력으로 받고, 아무런 값을 반환하지 않는 메서드를 나타냄
- 예를 들어,
- Action을 주로 이용하는 때
- 리턴값이 필요 없는 작업을 수행할 때, 즉 부수 효과(Side Effect)만 있을 때
- 반환값이 없는 콜백이나 이벤트 핸들러를 사용할 때
- 메서드를 인수로 전달하면서 해당 메서드가 어떤 결과를 반환하지 않아도 될 때
// 이벤트 핸들러로서의 예시
Action onButtonClick = () => Console.WriteLine("Button clicked!");
onButtonClick();○ Action 예시
- 두 숫자를 더한 결과를 출력
Action<int, int> printSum = (x, y) => Console.WriteLine(x + y);
printSum(3, 4); // 출력: 7- 메시지를 출력하는 함수
Action<string> printMessage = message => Console.WriteLine(message);
printMessage("Hello, World!"); // 출력: Hello, World!- 매개변수가 없는 경우
Action sayHello = () => Console.WriteLine("Hello!");
sayHello(); // 출력: Hello!
○ 심화 사용예제
- Func 예제
// Func를 사용하여 두 개의 정수를 더하는 메서드
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
// Func를 이용한 메서드 호출
Func<int, int, int> addFunc = Add;
int result = addFunc(3, 5);
Console.WriteLine("결과: " + result);- Action 예제
// Action을 사용하여 문자열을 출력하는 메서드
void PrintMessage(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
// Action을 이용한 메서드 호출
Action<string> printAction = PrintMessage;
printAction("Hello, World!");- 활용 예제
class GameCharacter
{
private Action<float> healthChangedCallback;
private float health;
public float Health
{
get { return health; }
set
{
health = value;
healthChangedCallback?.Invoke(health); // HP가 변할때마다 알아서 호출이 됨
}
}
public void SetHealthChangedCallback(Action<float> callback)
{
healthChangedCallback = callback;
}
}
// 게임 캐릭터 생성 및 상태 변경 감지
GameCharacter character = new GameCharacter();
character.SetHealthChangedCallback(health =>
{
if (health <= 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("캐릭터 사망!");
}
});
// 캐릭터의 체력 변경
character.Health = 0;- 종합예시
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// Func: 두 수를 더하고 결과를 반환
Func<int, int, int> add = (a, b) => a + b;
int result = add(10, 20);
Console.WriteLine(result); // 출력: 30
// Action: 두 수를 더한 결과를 출력 (반환값 없음)
Action<int, int> printSum = (a, b) => Console.WriteLine(a + b);
printSum(10, 20); // 출력: 30
}
}○ Func와 Action 차이점
- Func은 반환값이 있는 경우에 사용되며, 입력 매개변수와 반환값을 모두 정의할 수 있음
- Action은 반환값이 없는 경우에 사용되며, 주로 입력 매개변수를 받고 부수적인 작업(출력, 상태 변경 등)을 수행함
- 둘 다 델리게이트의 역할을 간편하게 처리할 수 있도록 도와주며, 람다 표현식이나 LINQ에서 매우 유용하게 사용됨
3. 델리게이트, 이벤트, 펑크, 액션은 각각 언제 쓰이는걸까
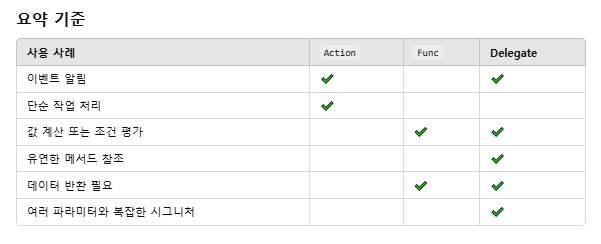
○ 델리게이트
- 런타임에 호출할 메서드를 동적으로 결정해야 할 때
- 콜백 패턴을 구현할 때
- 여러 메서드를 체인으로 연결해 한꺼번에 호출해야 할 때
- 메서드 호출을 다형성 있게 처리하고자 할 때
○ 이벤트
- 구독-발행(Publisher-Subscriber) 패턴을 구현할 때
- 객체가 상태 변화나 특정 동작을 알릴 때
- 이벤트 발생자는 외부에서 메서드를 호출하지 못하게 하고, 내부에서만 호출을 허용해야 할 때
- GUI 프로그램에서 버튼 클릭, 데이터 변경 등 특정 동작을 구독하고 반응해야 할 때
- 주로 GUI 이벤트 처리, 비동기 작업 완료 시 알림 등에 사용
○ Func
- 메서드가 반환값을 가지는 경우에 메서드를 인수로 전달할 때
- 주로 LINQ, 람다 표현식 등과 함께 사용
- 계산, 처리, 조건 평가 등과 같이 결과값을 반환해야 하는 메서드를 동적으로 처리할 때
- Func는 여러 입력을 받아서 결과를 반환해야 하는 모든 상황에서 유용하게 사용
○ Action
- 반환값이 필요 없는 경우에 메서드를 인수로 전달할 때
- 부수 효과(Side Effect)를 일으키는 코드에서 주로 사용 (예: 출력, 로그 작성, 상태 변경 등)
- 이벤트 핸들러, 콜백에서 반환값이 필요하지 않을 때
- 비동기 작업의 완료 처리를 정의할 때
- Action은 주로 출력, 상태 변경 등의 부수적인 작업을 수행할 때 적합
○ 요약