■ 학습 개요
○ 오늘 계획
- 09:00~10:00 : 발제 문서 분석
- 10:00~11:00 : 발제
- 11:00~12:00 : 팀 회의
- 12:00~13:00 : 꾸준실습
- 13:00~14:00 : 점심😁
- 14:00~16:00 : 객체지향 특강2
- 16:00~17:00 : 첼린지 특강
- 17:00~18:00 : 저녁😁
- 19:00~19:30 : 팀회의(팀 이름, 팀 규칙)
- 19:00~21:00 : 숙련 팀프로젝트 복기
- 21:00~23:00 : 숙련 팀프로젝트 동료분들과 코드리뷰
○ 학습 회고
- 오늘은 객체지향 특강2를 들었다. 주말에 복기후 내용 정리를 해보고 싶다
■ 객체지향 프로그래밍 특강 2
■ 숙련 팀프로젝트 복기
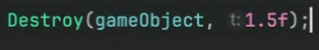
○ 일정 시간 뒤 게임 오브젝트 파괴
- 1.5초 뒤 파괴
○ Ray 인식
- ray는 어디에 접근해서 인식하는 걸까? 리지드바디? 콜라이더?
- Ray(레이)는 물리적 객체를 인식할 때 Collider(콜라이더)에 접근함. Ray는 특정 방향으로 투사되며, Raycast를 통해 레이가 닿는 물체의 콜라이더와의 충돌을 감지하게 됨
- 물체가 Raycast에 인식되기 위해서는 Collider 컴포넌트가 반드시 활성화되어 있어야 함. Rigidbody는 Raycast 충돌 인식과는 직접적인 연관이 없지만, 일반적으로 물리 연산이나 이동을 위해 추가됨. 요약하자면, Ray는 Collider에 닿았을 때 인식하며, 리지드바디는 선택 사항
- 추가적으로 Raycast는 RaycastHit 구조체를 통해 충돌 지점 정보나 물체의 태그 등을 확인할 수 있음
○ Mesh collider 인식 문제
- 왜 메쉬콜라이더만 넣었을때는 인식안되고 리지드바디를 함께 넣었을때는 인식이 되나?
- Mesh Collider만 추가하고 Rigidbody를 넣지 않았을 때 Ray가 인식하지 않는 것은 Unity의 물리 시스템에서 비-키네마틱 리지드바디가 없는 정적인 Collider는 Raycast에서 충돌 감지를 하지 않도록 되어 있기 때문
- 간단히 말해, Unity는 성능 최적화를 위해 Rigidbody가 없는 Collider는 움직이지 않는 정적 물체로 간주함. 이 경우 Raycast는 성능상의 이유로 정적 Collider와의 충돌을 무시하는 경우가 많음
- 이를 해결하기 위해 Rigidbody를 추가하면, Unity는 해당 물체가 물리 연산에 포함되어야 한다고 인식하고 Raycast에 의한 충돌 감지 대상에 포함시킴. 다만, 이 경우 Rigidbody를 isKinematic 모드로 설정해두면 물리 연산에는 참여하지 않으면서도 Raycast에서 감지할 수 있음
○ 건축 프리뷰
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class PreviewObject : MonoBehaviour
{
private List<Collider> colliderList = new List<Collider>(); // 충돌 물체들 저장
[SerializeField]
private int layerGround; // 땅으로 인식할 레이어 지정(레이어 번호)
private const int ignoreRaycastLayer = 2; // ignore_raycast (레이어 번호)
// 메테리얼 저장
[SerializeField]
private Material green;
[SerializeField]
private Material red;
void Update()
{
ChangeColor();
}
private void ChangeColor()
{
// 충돌 리스트에 하나라도 있으면 설치 불가 -> 빨강색
if (colliderList.Count > 0)
SetColor(red);
else
SetColor(green);
}
private void SetColor(Material mat) // 특정 재질을 지정
{
foreach (Transform tf_Child in this.transform)
{
Material[] newMaterials = new Material[tf_Child.GetComponent<Renderer>().materials.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < newMaterials.Length; i++)
{
newMaterials[i] = mat;
}
tf_Child.GetComponent<Renderer>().materials = newMaterials;
}
}
private void OnTriggerEnter(Collider other)
{
// 무시가능한 레이어 및 그라운드가 아니면 충돌리스트에 추가
if (other.gameObject.layer != layerGround && other.gameObject.layer != ignoreRaycastLayer)
colliderList.Add(other);
}
private void OnTriggerExit(Collider other)
{
// 벗어나면 리스트에서 제거
if (other.gameObject.layer != layerGround && other.gameObject.layer != ignoreRaycastLayer)
colliderList.Remove(other);
}
public bool isBuildable()
{
// 충돌리스트가 0일때만 빌드 가능
return colliderList.Count == 0;
}
}
- private void SetColor(Material mat) 함수
- Unity 엔진에서 특정 Material(재질)을 오브젝트와 그 자식 오브젝트들에 적용하는 역할을 합니다.
1. SetColor 함수는 Material mat 파라미터를 받아 특정 재질을 지정합니다.
2. foreach 루프를 통해 현재 오브젝트(this.transform)의 모든 자식(tf_Child)을 순회합니다.
3. 각 자식의 Renderer 컴포넌트에서 현재 할당된 materials 배열 길이와 동일한 길이의 newMaterials 배열을 생성합니다.
4. 내부 for 루프를 통해 newMaterials 배열의 각 요소를 입력받은 mat으로 설정합니다.
5. 완성된 newMaterials 배열을 자식 오브젝트의 Renderer 컴포넌트의 materials 속성에 할당하여 해당 재질이 적용되도록 합니다.
- this.transform 의 자식들은 뭐가있어?
- this.transform의 자식들은 this 오브젝트 아래에 속한 하위 오브젝트들입니다. Unity에서 오브젝트는 계층 구조를 가질 수 있는데, this.transform은 현재 스크립트가 붙어 있는 오브젝트의 Transform 컴포넌트를 나타내며, 그 안에 포함된 자식 오브젝트들을 transform.GetChild(index) 또는 foreach를 통해 접근할 수 있습니다.
- 왜 굳이 transform 으로 하위 자식에 접근해?
- Unity의 모든 오브젝트는 Transform 컴포넌트를 기본적으로 가지며, 이 Transform은 오브젝트의 위치, 회전, 크기와 함께 계층 구조 상에서의 부모-자식 관계를 관리합니다.
- 이 코드에서 transform을 사용하는 이유도 현재 오브젝트(this)의 모든 자식들을 순회하여 같은 작업을 반복 적용하기 위한 효율적인 방법이기 때문
- transform을 사용하여 자식 오브젝트에 접근하는 이유
1. 자식 오브젝트 순회 : Transform은 부모와 자식 관계를 명확히 관리하고 있어, 특정 오브젝트의 자식들을 효율적으로 순회할 수 있습니다.
2. 위치 및 회전 : 오브젝트의 위치, 회전, 크기를 조정할 때 Transform을 통해 접근하는 것이 자연스럽습니다.
3. 계층 구조 관리 : Transform을 사용하면 하위 계층의 모든 자식들을 쉽게 탐색하고 수정할 수 있습니다.
○ 건축 건설
using System;
using System.Collections;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UI;
using Random = UnityEngine.Random;
public class Construct : MonoBehaviour
{
bool isConstructMode; //건축중인지 체크
ItemData data; // 스크립터블 오브젝트 데이터
public PlayerController controller;
public Transform dropPosition;
public GameObject inventoryWindow;
public GameObject craftPanalCanvas; // 기본 베이스 UI
public GameObject cancelInfoTxt;
public GameObject buildUI;
public Image buildUIImage;
public UICraft craftInventory;
public UIInventory inventory;
private bool isActivated = false; // CraftManual UI 활성 상태
private GameObject previewStructure; // 미리 보기 프리팹을 담을 변수
private GameObject structurePrefab; // 실제 생성될 프리팹을 담을 변수
[SerializeField]
private Transform playerTransform; // 플레이어 위치
private RaycastHit hitInfo;
[SerializeField]
private LayerMask layerMask; // 그라운드 레이어 마스크 저장
[SerializeField]
private float range;
private float needItemIndex;
private float needDuration = 5f;
private float curDuration = 0f;
private ItemData selectedItem;
private void Start()
{
controller = CharacterManager.Instance.Player.controller;
dropPosition = CharacterManager.Instance.Player.dropPosition;
CharacterManager.Instance.Player.controller.onCancelStruct += CancelStruct; // 취소 이벤트 등록
}
void Update()
{
if (previewStructure != null)
{
// 미리보기구조가 있다면 프리뷰 위치 업데이트
PreviewPositionUpdate();
}
if (Input.GetButtonDown("Fire2"))
{
cancelInfoTxt.SetActive(false);
buildUI.SetActive(true);
BuildUISet();
StartCoroutine("Build"); // 건설 시작
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Inventory내에 제작버튼
/// </summary>
public void OnCraftButton()
{
craftPanalCanvas.SetActive(true);
inventoryWindow.SetActive(false);
}
/// <summary>
/// 크래프트캔버스 취소하기버튼
/// </summary>
public void OnCancleButton()
{
craftPanalCanvas.SetActive(false);
inventoryWindow.SetActive(true);
}
/// <summary>
/// 인벤토리 건설하기버튼
/// </summary>
public void OnBuildButton()
{
CharacterManager.Instance.Player.controller.ToggleCursor(); // 마우스 커서 관리
SelectStructure(inventory.selectedItem); //선택건축물세팅
inventoryWindow.SetActive(false);
cancelInfoTxt.SetActive(true);
}
/// <summary>
/// 선택건축물 데이터를 담고있는 프리뷰,건축물 세팅 메소드
/// </summary>
void SelectStructure(ItemData data)
{
// 미리보기구조물 (스크립터블 오브젝트 데이터에서 프리펩 가져오기)
previewStructure = Instantiate(data.previewStructure, playerTransform.position + playerTransform.forward, Quaternion.identity);
// 실제설치구조물 (스크립터블 오브젝트 데이터에서 프리펩 데이터)
structurePrefab = data.RealStructurePrefab;
}
/// <summary>
/// 미리보기프리팹 위치값 매프레임 업데이트
/// </summary>
private void PreviewPositionUpdate()
{
Debug.DrawRay(playerTransform.position, transform.forward * range, Color.red);
// hitInfo : 부딪힌 오브젝트 저장
// 부딪힌 오브젝트 레이어 마스크가 그라운드면
if (Physics.Raycast(playerTransform.position, playerTransform.forward, out hitInfo, range, layerMask))
{
if (hitInfo.transform != null)
{
Vector3 location = hitInfo.point;
previewStructure.transform.position = location; // 미리보기구조물의 위치를 부딪힌 위치로 지정
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 왼쪽 마우스 클릭시 건설실행 (Duration값 만큼 딜레이)
/// </summary>
public IEnumerator Build()
{
yield return new WaitForSeconds(needDuration);
if (previewStructure && previewStructure.GetComponent<PreviewObject>().isBuildable()) //빌드가 가능 하다면
{
// 실제 구조물을 히트포인트에 복제
Instantiate(structurePrefab, hitInfo.point, Quaternion.identity);
// 기존 미리보기 구조물 삭제
Destroy(previewStructure);
ResetPreview();
}
buildUI.SetActive(false);
}
private void BuildUISet()
{
buildUIImage.fillAmount = curDuration / needDuration;
if(curDuration >= needDuration)
return;
if (curDuration < needDuration)
{
curDuration += Time.deltaTime;
if (curDuration >= needDuration)
{
curDuration = needDuration;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 아이템을 소비해 건물을 지을때 사용
/// </summary>
public void UseResource(float NeedValue)
{
needItemIndex = NeedValue;
}
/// <summary>
/// 건축취소 Fkey입력시 호출함수
/// </summary>
private void CancelStruct()
{
if (previewStructure != null)
Destroy(previewStructure);
ResetPreview();
craftPanalCanvas.SetActive(false);
cancelInfoTxt.SetActive(false);
buildUI.SetActive(false);
}
// 데이터 삭제
private void ResetPreview()
{
previewStructure = null;
structurePrefab = null;
}
}
■ 매일매일 알고리즘
○ 없는 숫자 더하기(하)
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int solution(vector<int> numbers)
{
int answer = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
// find : 벡터 내에 존재하는지 검사
// 벡터의 시작과 끝을 검색하여 target이 벡터에 있으면 해당 위치의 반복자를 반환하고, 없으면 vec.end()를 반환
if (find(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), i) == numbers.end())
{
answer += i;
}
}
return answer;
}
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int solution(vector<int> numbers) {
int answer = 45;
// 총합에서 벡터에 포함된 원소들만 빼면,
// 포함되지 않은 원소의 합만 남는다
for (int i = 0 ; i < numbers.size() ; i++)
answer -= numbers[i];
return answer;
}
○ 더 크게 합치기(중)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int solution(int a, int b)
{
int answer = 0;
// stoi : 문자열을 정수로
// to_string : 정수를 문자열로
int temp1 = stoi(to_string(a) + to_string(b));
int temp2 = stoi(to_string(b) + to_string(a));
// max : 큰값 찾기
answer = max(temp1, temp2);
return answer;
}
○ 없는 숫자 더하기(상)
- 문제 링크
- 내 풀이(못풀음!)
- 다른 사람 풀이
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
string solution(string p)
{
stringstream ss(p);
string temp;
int xsum = 0, nsum = 0;
while (getline(ss, temp, ' '))
{
if (temp.back() == 'x')
{
if (temp.size() == 1) xsum++;
else xsum += stoi(string(temp.begin(), temp.end() - 1));
}
else if(temp!="+") nsum += stoi(temp);
}
if (xsum == 0) return to_string(nsum);
else {
string xres;
if (xsum == 1) xres = "x";
else xres = to_string(xsum) + "x";
if (nsum == 0) return xres;
else return xres + " + " + to_string(nsum);
}
}


