Static, Extern
많은 프로그래밍 언어에는 static과 extern의 개념이 존재하고 각각 언어마다 의미하는 바가 같지는 않다.
C언어에서의 static과 extern을 알아보자.
1. static
변수를 static으로 선언을 하면, 해당 변수의 범위가 끝나더라도 프로그램의 생명주기 동안 변수를 계속 존재하도록 컴파일러에 지시한다. 함수의 경우, static은 선언된 파일 내부로 범위를 제안한다.
Static 변수
로컬 static변수
- 함수 내부의 static변수는 함수 호출 사이에 그 값을 유지한다.
#include <stdio.h>
void incrementCounter() {
static int counter = 0; // 한 번 초기화, 호출 사이에 유지됨
counter++;
printf("Counter: %d\n", counter);
}
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
incrementCounter(); // 각 호출마다 Counter가 증가함
}
return 0;
}
결과

함수가 끝났음에도 다음 함수가 실행 할 때, counter의 값이 유지되어 있는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
파일 범위 static 변수
- 파일 범위의 static 변수는 파일 내부에서는 접근 가능하지만 외부에서는 보이지 않아. 사실상 파일에 대해 private하다.
#include <stdio.h>
// 파일: main.c
static int fileScopedCounter = 0; // 오직 이 파일 안에서만 접근 가능
void incrementFileCounter() {
fileScopedCounter++;
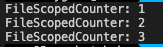
printf("FileScopedCounter: %d\n", fileScopedCounter);
}
int main() {
incrementFileCounter();
incrementFileCounter();
incrementFileCounter();
}결과
static 함수
마찬가지로, static 함수는 선언된 파일 내부에서만 접근할 수 있다.
// 파일: data.c
int globalVariable = 10;
// 파일: extern.c
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
// 파일: main.c
#include <stdio.h>
static int add(int a, int b); // 함수 프로토타입 선언
static int globalVariable; // 전역 변수에 대한 static 선언
int main() {
int result = add(3, 4);
printf("%d\n",result);
printf("%d\n", globalVariable);
}$ gcc main.c helper.c extern.c -o program && ./programgcc main.c helper.c extern.c -o program 로 실행하면 program 오브젝트 파일을 만들어준다.
./program으로 실행해주면 결과가 실행된다
결과
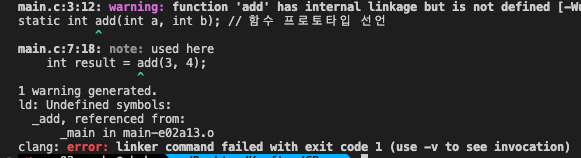
add 함수를 다른 파일에 정의 해놓았으나 static으로는 불러올 수 없다.
extern
static과 반대로, extern은 다른 파일이나 나중에 같은 파일에서 정의된 변수나 함수를 선언할 때 사용된다.
extern 변수
다른 파일에서 정의된 변수에 접근하려면 extern을 사용한다.
// 파일: main.c
#include <stdio.h>
extern int sharedCounter; // 다른 파일에서 정의됨
void printSharedCounter() {
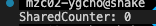
printf("SharedCounter: %d\n", sharedCounter);
}
int main(){
printSharedCounter();
}
// 파일: counter.c
int sharedCounter = 0; // 변수 정의
결과
extern 함수
함수는 기본적으로 extern이 default 값이다. 따라서 함수를 static 없이 선언한다면 전체 프로그램에서 접근할 수 있다.
// 파일: counter.c
int sharedCounter = 0; // 변수 정의
void incrementSharedCounter() {
sharedCounter++;
}
// 파일: main.c
#include <stdio.h>
extern int sharedCounter; // 다른 파일에서 정의됨
extern void incrementSharedCounter();
void printSharedCounter() {
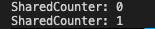
printf("SharedCounter: %d\n", sharedCounter);
}
int main(){
printSharedCounter();
incrementSharedCounter();
printSharedCounter();
}결과
정리:
static은 단일 파일 내에서 변수와 함수의 범위를 캡슐화하고 제어하여 함수 호출 사이의 상태를 유지하고 다른 파일에서의 접근을 방지하는데 도움을 준다. 반면, extern은 다른 파일 간에 변수와함수를 공유할 수 있는 문을 열어줌으로써 별도의 컴파일과 링킹을 가능하게 한다. 이 두 지정자를 올 바르게 활용하는 것은 잘 구조화되고 모듈식인 C 프로그래밍이 가능하게 한다.