연결 리스트 (singly Linked List)
연결 리스트 (단일 연결리스트)의 각 node는 두 부분으로 이루어져 있는데 data부분과 다음 node를 가리키는 pointer가 있습니다.
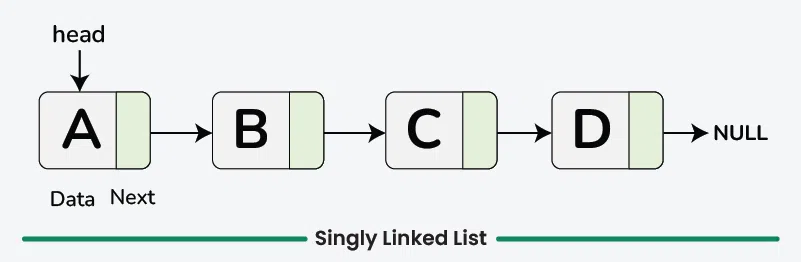
data파트는 말 그대로 저장할 data를 보관하는 곳이며,
pointer part는 next node의 주소값을 저장합니다.
만약 다음 노드가 존재하지 않다면 NULL을 저장합니다.
구현
// Definition of a Node in a singly linked list
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// Function to create a new Node
struct Node* newNode(int data) {
struct Node* temp =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = data;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}단일 연결 리스트의 선언과 새로운 node 생성은 위와 같습니다.
단일 연결리스트는 여러 operation도 가능한데
- Traversal (순회)
void traverseLinkedList(struct Node* head)
{
// Start from the head of the linked list
struct Node* current = head;
// Traverse the linked list until reaching the end (NULL)
while (current != NULL) {
// Print the data of the current node
printf("%d ", current->data);
// Move to the next node
current = current->next;
}
printf("\n");
}- Searching (탐색)
bool searchLinkedList(struct Node* head, int target)
{
// Traverse the Linked List
while (head != NULL) {
// Check if the current node's
// data matches the target value
if (head->data == target) {
return true; // Value found
}
// Move to the next node
head = head->next;
}
return false; // Value not found
}- Length (리스트의 길이)
int Length(struct Node* head)
{
// Initialize a counter for the length
int length = 0;
// Start from the head of the list
struct Node* curr = head;
// Traverse the list and increment
// the length for each node
while (curr != NULL) {
length++;
curr = curr->next;
}
// Return the final length of the linked list
return length;
}-
Insertion:
삽입의 경우 3가지 방법이 존재합니다.- Insert at the beginning
void InsertFront(struct node* head, int data) { node* newNode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); newNode->data = data; newNode->link = head; head = newNode; - Insert at the end
- Insert at a specific position
- Insert at the beginning
-
Deletion:
삭제도 3가지 방법이 존재합니다.- Delete from the beginning
- Delete from the end
- Delete a specific node
성능 평가
-
삽입 : (end 삽입 시 이지만 시작 위치에 삽입하는 경우 )
-
삭제 :
-
탐색 :
-
길이 확인 :
장점
-
동적 크기 : 배열과 달리 크기가 고정되지 않아 메모리의 효율적 활용이 가능합니다.
-
삽입/삭제 효율성 : 특히 리스트의 시작 위치에서 삽입 삭제가 로 매우 빠릅니다.
단점
-
메모리 오버헤드 : 각 node가 data와 pointer를 저장하므로 메모리 효율성이 떨어질 수 있습니다.
-
순차 접근만 가능하다 : 인덱스로 접근하는 배열과 달리, 특정 위치에 도달하려면 순차적으로 접근해야한다.
정리
배열과 비교하여 삽입 및 삭제에 유리하지만 순차 접근(next로만)만 가능하여 시간 복잡도 면에서는 다소 비효율적입니다.