병합 정렬이란
분할 정복 알고리즘 기법을 사용하는 정렬 방법이다.
정렬할 데이터를 작은 단위로 분할 후, 다시 정렬하며 병합한다.
분할을 할 때는 정렬을 고려하지 않고 그저 분할만 진행하고
병합을 할 때 정렬순서를 고려하여 병합을 한다.
(이는 재귀적 알고리즘으로 이루어진다.)
병합 정렬 과정
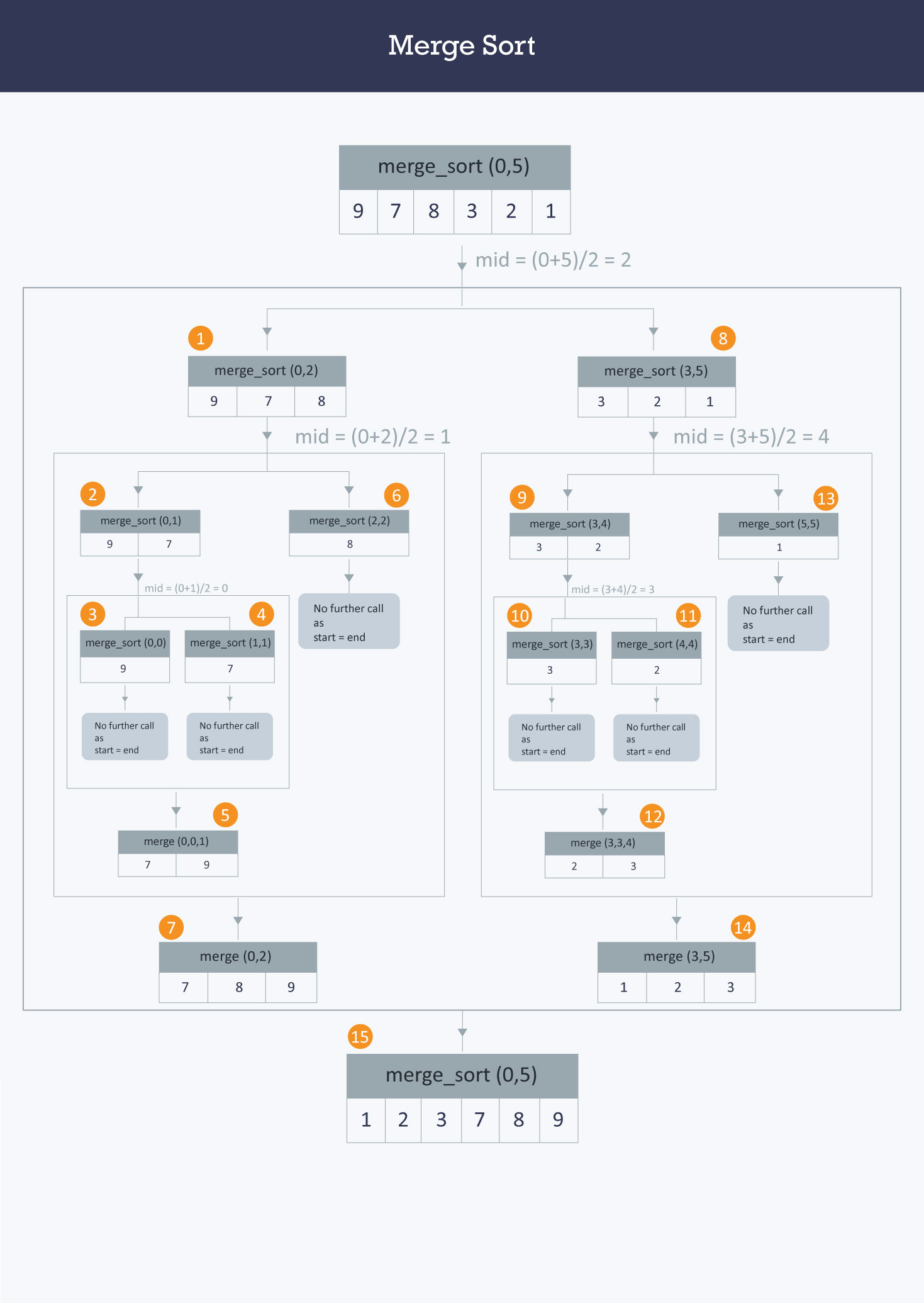
데이터를 반복적으로 더 이상 분할할 수 없는 단위가 될 때 까지 중간값(mid = first index + last index / 2)을 기준으로 분할한다.
분할이 완료되면 병합을 진행하는데 이때 우선 순위에 맞춰 합쳐진다.
모든 부분 배열이 병합되면 최종적으로 전체 배열이 정렬된다.
구현
아래는 c언어로 구현된 병합 정렬 입니다.
// C program for Merge Sort
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Merges two subarrays of arr[].
// First subarray is arr[l..m]
// Second subarray is arr[m+1..r]
void merge(int arr[], int l, int m, int r)
{
int i, j, k;
int n1 = m - l + 1;
int n2 = r - m;
// Create temp arrays
int L[n1], R[n2];
// Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[]
for (i = 0; i < n1; i++)
L[i] = arr[l + i];
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++)
R[j] = arr[m + 1 + j];
// Merge the temp arrays back into arr[l..r
i = 0;
j = 0;
k = l;
while (i < n1 && j < n2) {
if (L[i] <= R[j]) {
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else {
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of L[],
// if there are any
while (i < n1) {
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
k++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of R[],
// if there are any
while (j < n2) {
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
// l is for left index and r is right index of the
// sub-array of arr to be sorted
void mergeSort(int arr[], int l, int r)
{
if (l < r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
// Sort first and second halves
mergeSort(arr, l, m);
mergeSort(arr, m + 1, r);
merge(arr, l, m, r);
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int A[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("%d ", A[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 };
int arr_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Given array is \n");
printArray(arr, arr_size);
mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1);
printf("\nSorted array is \n");
printArray(arr, arr_size);
return 0;
}성능평가
정렬 해야할 Data가 개 일 때 배열을 반복적으로 절반씩 나누는 과정에서 의 시간이 소요되고, 각 병합단계에서 개의 요소를 비교해야 하기 때문에
시간복잡도는 입니다.
장점
-
Stability : 동일한 값을 가진 요소들의 순서가 유지된다.
-
Guaranteed worst-case performance : 시간 복잡도 을 항상 보장하므로, 최악의 경우에도 효율적이다.
-
Simple to implement
-
Naturally Parallel : 분할된 배열을 독립적으로 처리할 수 있어 병렬 처리가 가능하다.
단점
-
Space complexity: 추가적인 메모리가 필요하다. 각 단계에서 임시 배열을 사용하여 데이터를 저장해야 하기 때문에 메모리 사용이 크다.
-
Not in-place 정렬이다.
정리
이러한 병합 정렬은 대규모 데이터 정렬에 유용하며 Python, Java Android and Swift와 같은 언어의 library methods에서 변형된 상태로 사용됩니다.
특히 TimSort는 병합 정렬의 변형으로, 비원시 타입(Object, array 등)을 정렬할 때 자주 사용된다.