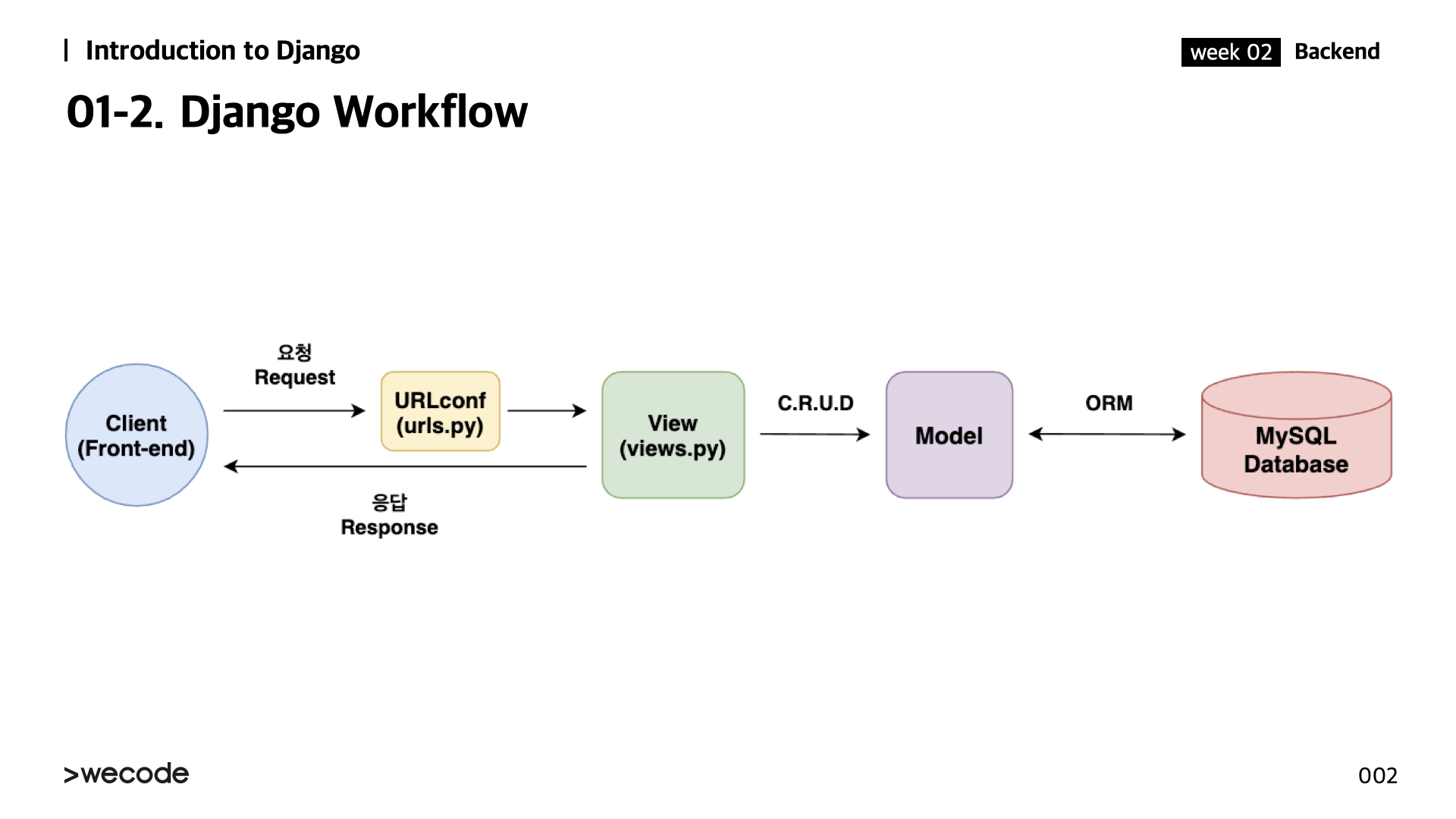
Django Workflow

Model & Data
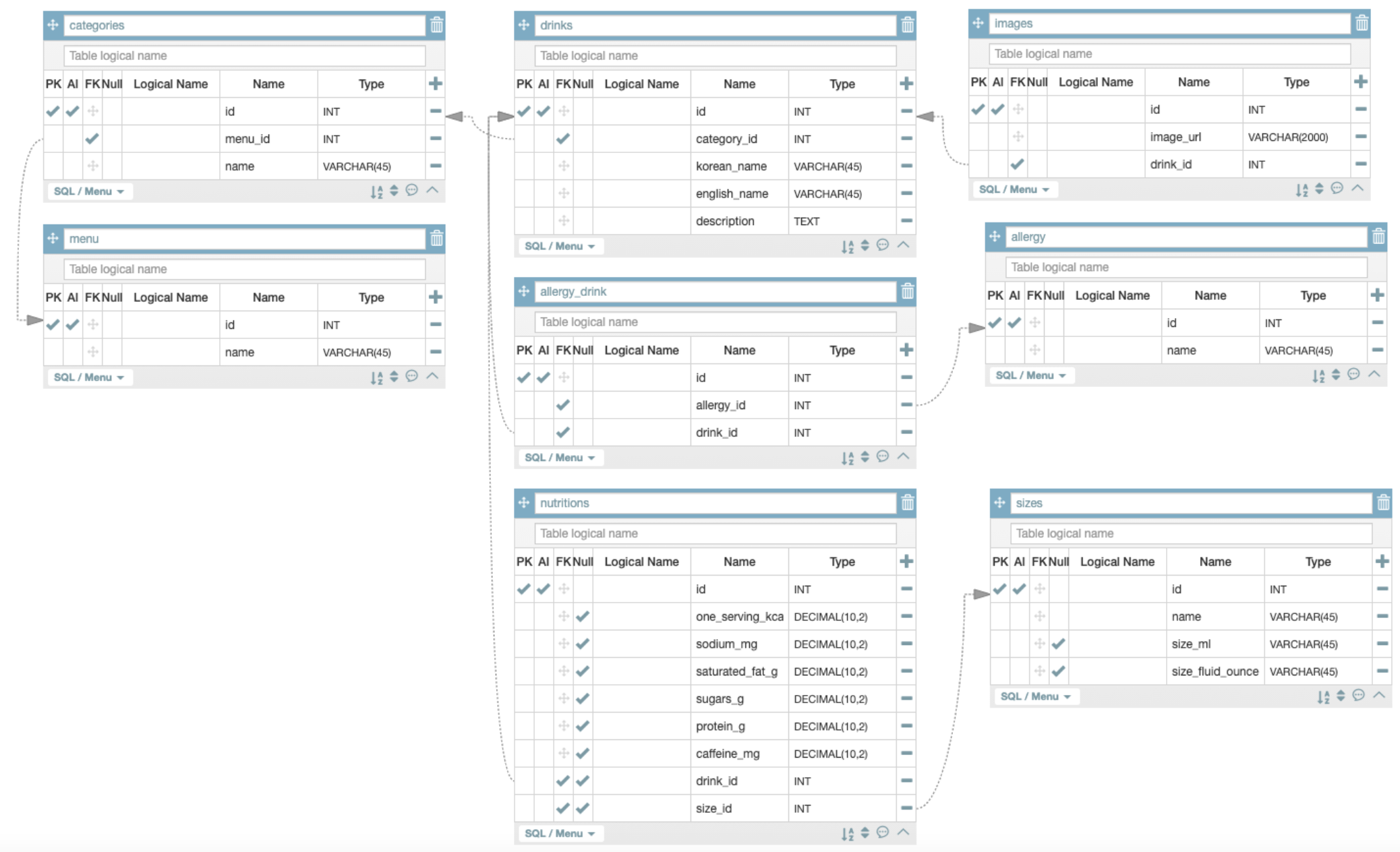
I made a data table in MySQL database by using migrate command after writing the classes on models.py, refering to the below ERD(Entity Relationship Diagram).


1. Creating data from Django Shell
We should import data of model class.
from products.models import Menu, Categoty1) Creating 음료 menu using create() method
>>> Menu.objects.create(name="음료")2) Creating 상품 menu using save() method
>>> a3 = Menu(name="상품")
>>> a3.save()3) Creating 음료 and 푸드 menu using bulk_create() method
>>> a1 = Menu(name="음료")
>>> a2 = Menu(name="푸드")
>>> Menu.objects.bulk_create([a1, a2])- Check
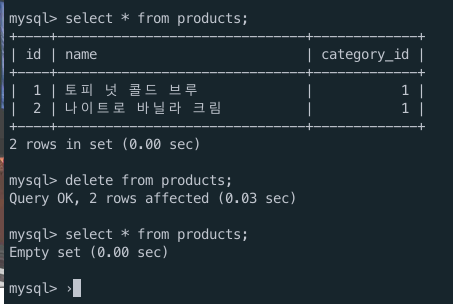
Menutable from MySQL database usingSELECTcommand
>>> SELECT * FROM menus;4) Creating category data when Category table refers to Menu id
>>> a1 = Menu.objects.get(name="음료")
>>> Category.objects.create(name="콜드 브루 커피", menu=a1)
5)Checking id of 콜드브루커피 in Menu
>>> b1 = Category.objects.get(name="콜드 브루 커피")
>>> b1.menu.id6) Creating 브레드 and 케이크 category under 푸드 Menu using bulk_create()
>>> a2 = Menu.objects.get(name="푸드")
>>> Category.objects.bulk_create([
Category(name="브레드", menu=a2),
Category(name="케이크", menu=a2)
])2. Reading data
1) Selecting 음료 menu using get() method and name field
>>> Menu.objects.get(name="음료")2) Selecting 음료 menu using get() method and id field
>>> Menu.objects.get(id=1)3) Getting all data from Category table using all() method
>>> Category.objects.all()4) Getting only the data referring to the 음료 menu among the Category data using filter() method
>>> Category.objects.filter(menu_id=1)
OR
>>> Category.objects.filter(menu__name="음료")5) Getting name data of all data refering to 푸드 menu using for loop
>>> for category in Category.objects.filter(menu__name="푸드"):
print(category.name)6) Getting all categories refering to 음료 menu in the form of QuerySet
>>> a1 = Menu.objects.get(name="음료")
>>> a1.category_set.all()7) Getting the number of categories refering to 음료 menu using count() method
>>> a1 = Menu.objects.get(name="음료")
>>> a1.category_set.count()8) Getting Menu's name data to which 블렌디드 category refers
>>> c2 = Category.objects.get(name="블렌디드")
>>> c2.menu.name3. Deleting data
-
DELETE FROM 테이블명 [WHERE 조건]; -
To delete the entire data from the table :
DELETE FROM <table name>; -
To delete partial data:
DELETE FROM <table name> WHERE id = 1; -
To delete entire data from the table using
truncate:TRUNCATE TABLE <테이블명>; -
delete & truncate:
deleteandtruncateboth delete data, leaving the table info as is.
The difference betweendeleteandtruncateis thatdeletehave the space in the disc after deleting the data, whiletruncatemakes it go back to the status that the table is just created. So after thetruncatecommand, there's only column left. Buttruncatecommand executes a commit
automatically, so we can't recover the data.
4. null=True in CharField
I faced the below error message when migrating.

So I added null=True on the CharField as below and then the error was fixed.


*But what makes me confused is, according to the Django documentation, we should avoid using Null on string-based fields.
5. To insert all the multiple data in a table at once
INSERT INTO 테이블명 (컬럼1, 컬럼2,,,,)
VALUES
('값1','값2'),
('값1','값2'),
('값1','값2');출처: https://private.tistory.com/63 [공부해서 남 주자]
6. To apply the content on models.py to DB
-
makemigrations: the process that creates the migration file(schematics) to apply the python code we wrote onmodels.pyto the database. -
migrate: To apply the migration file(schematics), created with makemigrations command, to the database.
Should read
QuerySet API reference
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.0/ref/models/querysets/
Model field reference
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.2/ref/models/fields/
Django 모델 ForeignKeyField on_delete 종류
https://vallhalla-edition.tistory.com/60
Many-to-one relationships
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.1/topics/db/examples/many_to_one/
Django 개발 : URLconf - URL 정의
클래스, 객체, 인스턴스
https://gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/09/17/class-object-instance.html
